For a given cell, a 0.1 molar solution has a resistance of \(20 \ \Omega\) and molar conductivity of \(0.154 \times 10^{-3} S~cm^2~mol^{-1} \).
The value of the cell constant is:
The value of the cell constant is:
| 1. | \(3.08 \times 10^{-7} cm^{-1}\) | 2. | \(30.8 \times 10^{-7} cm^{-1}\) |
| 3. | \(0.308 \times 10^{-9} cm^{-1}\) | 4. | \(4.08 \times 10^{-6} cm^{-1}\) |
Subtopic: Conductance & Conductivity |
77%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The decreasing order of electrical conductivity of the following aqueous solutions is :
0.1 M Formic acid (A),
0.1 M Acetic acid (B),
0.1 M Benzoic acid (C)
1. A > B > C
2. A > C > B
3. C > B > A
4. C > A > B
Subtopic: Conductance & Conductivity |
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Resistance of 0.2 M solution of an electrolyte is 50 . The specific conductance of the solution is 1.3 S m-1. If the resistance of the 0.4 M solution of the same electrolyte is 260 , its molar conductivity is:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Subtopic: Conductance & Conductivity |
58%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The resistivity of a 0.8 M solution of an electrolyte is 5×10−3 Ω cm. If λm is 2.5×10x,
the value of x is:
1. 4
2. 8
3. 5
4. 9
the value of x is:
1. 4
2. 8
3. 5
4. 9
Subtopic: Conductance & Conductivity |
78%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The limiting molar conductivities of a divalent cation \(\left(\mathrm{M}^{2+}\right)~\)and a monovalent anion \(\left(\mathrm{A}^{-}\right)~\)are \(57 \mathrm{~S} \mathrm{~cm}^2\) \( \mathrm{mol}^{-1}\) and \(73 \mathrm{~S} \mathrm{~cm}^2 \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\) respectively. What is the limiting molar conductivity of their compound in \(\mathrm{S}~ \mathrm{cm}^2 \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\)?
1. 203
2. 421
3. 143
4. 303
1. 203
2. 421
3. 143
4. 303
Subtopic: Conductance & Conductivity |
84%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The graph represents the variation of molar conductance (\(\Lambda_m\)) with the square root of concentration (\(\sqrt{C}\)) for two electrolytes, 'A' and 'B'. Based on the graph, the nature of both electrolytes is:
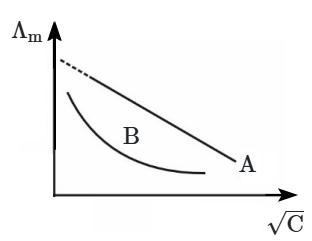
1. A → Strong Electrolyte, B→ Strong Electrolyte
2. A → Weak Electrolyte, B → Strong Electrolyte
3. A → Strong Electrolyte, B → Weak Electrolyte
4. A → Weak electrolyte, B → Weak Electrolyte

1. A → Strong Electrolyte, B→ Strong Electrolyte
2. A → Weak Electrolyte, B → Strong Electrolyte
3. A → Strong Electrolyte, B → Weak Electrolyte
4. A → Weak electrolyte, B → Weak Electrolyte
Subtopic: Conductance & Conductivity |
83%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Determine the cell constant of a conductivity cell containing a 0.01 M KCl solution at 298 K. The given data includes a resistance of 1750 Ω and a conductivity of 0.152×10−3 S cm−1.
| 1. | \(266 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}^{-1}\) | 2. | \(166 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~cm}^{-1}\) |
| 3. | \(266 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~cm}^{-1}\) | 4. | \(166 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}^{-1}\) |
Subtopic: Conductance & Conductivity | Kohlrausch Law & Cell Constant |
55%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Given below are two statements :
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
| Statement I | For \(\mathrm{Kl},\) molar conductivity increases steeply with dilution. |
| Statement II | For carbonic acid, molar conductivity increases slowly with dilution. |
| 1. | Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is correct. |
| 2. | Both Statement I and Statement II are correct. |
| 3. | Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect. |
| 4. | Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect. |
Subtopic: Conductance & Conductivity |
From NCERT
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.




