Select Question Set:
Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): | The centre-of-mass of an isolated system of particles remains at rest if it is initially at rest. |
| Reason (R): | Internal forces acting within a system cannot change the velocity of the centre-of-mass which is proportional to the total momentum of the system. |
| 1. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 2. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
| 3. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
Subtopic: Center of Mass |
76%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
When a fat person tries to touch his toes (as shown in the figure), keeping the legs straight, he generally falls because of:
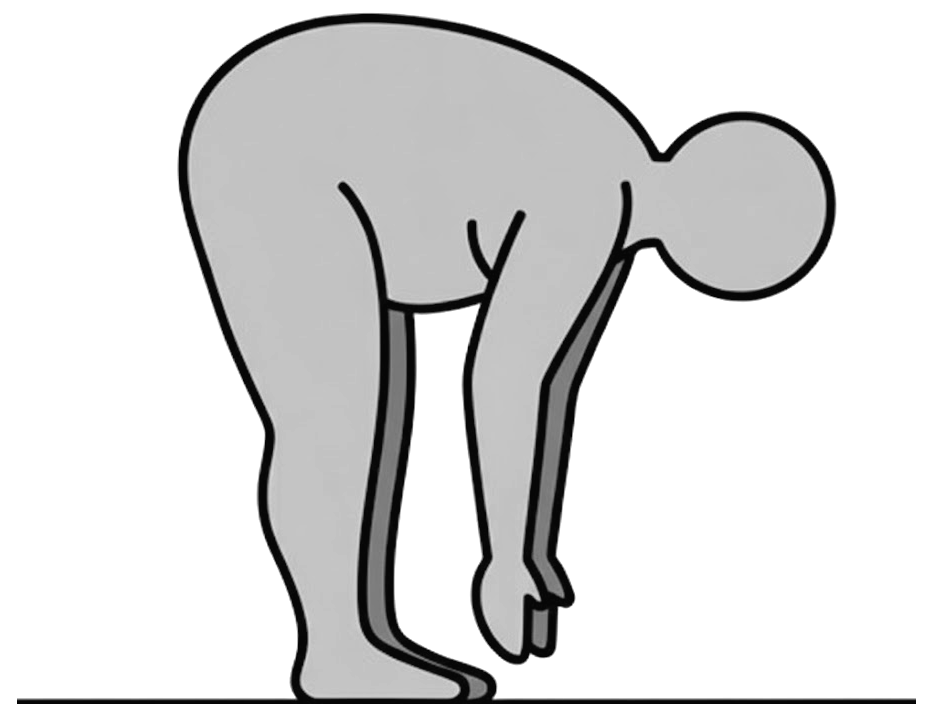
1. torque produced
2. weight
3. dizziness
4. none of these

1. torque produced
2. weight
3. dizziness
4. none of these
Subtopic: Center of Mass |
80%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
A body falling vertically downwards under gravity breaks into two parts of unequal masses. The centre of mass of the two parts taken together shifts horizontally towards:
| 1. | heavier piece |
| 2. | lighter piece |
| 3. | does not shift horizontally |
| 4. | depends on the vertical velocity at the time of breaking |
Subtopic: Center of Mass |
67%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Links
Two point masses, \(m_{A}=2\) g and \(m_{B}=3\) g, are connected by a massless rod of length \(1\) m (see figure). The centre-of-mass of the system will lie at a distance of:

1. \(0.4\) m from \(m_{A}\)
2. \(0.6\) m from \(m_{A}\)
3. \(0.5\) m from \(m_{A}\)
4. \(0.7\) m from \(m_{A}\)

1. \(0.4\) m from \(m_{A}\)
2. \(0.6\) m from \(m_{A}\)
3. \(0.5\) m from \(m_{A}\)
4. \(0.7\) m from \(m_{A}\)
Subtopic: Center of Mass |
83%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): | If polar ice melts, days will be longer. |
| Reason (R): | Moment of inertia increases and thus angular velocity decreases. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
Subtopic: Angular Momentum |
79%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Let \(\overrightarrow A\) be a unit vector along the axis of rotation of a purely rotating body and \(\overrightarrow B\) be a unit vector along the velocity of a particle P of the body away from the axis. The value of \(\overrightarrow A.\overrightarrow B\) is:
1. \(1\)
2. \(-1\)
3. \(0\)
4. None of these
Subtopic: Angular Momentum |
78%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Links
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
A pulley of radius \(1.5~\text m\) is rotated about its axis by a force, \(F=(12t-3t^{2})~\text N\) applied tangentially (while \(t\) is measured in seconds). If the moment of inertia of the pulley about its axis of rotation is \(4.5~\text{kg-m}^2,\) the number of rotations made by the pulley before its direction of motion is reversed, will be \(\dfrac K \pi\). The value of \(K\) is:
| 1. | \(12\) | 2. | \(14\) |
| 3. | \(16\) | 4. | \(18\) |
Subtopic: Rotational Motion: Dynamics |
56%
Level 3: 35%-60%
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
A force is applied to a hollow spherical shell so that it acts through its centre. It causes an acceleration of \(3\) m/s2. If the same force is applied to the spherical shell, acting tangent to its surface, the acceleration will be: (Assuming no friction is available.)
| 1. | \(3\) m/s2 | 2. | \(2\) m/s2 |
| 3. | zero | 4. | \(1\) m/s2 |
Subtopic: Rotational Motion: Dynamics |
57%
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Four \(2~\text{kg}\) masses are connected by \(\dfrac{1}{4}~\text{m}\) spokes to an axle as in figure given below. A force \(F\) of \(24~\text{N}\) acts on a lever \(\dfrac{1}{2}~\text{m}\) long to produce an angular acceleration \(\mathit{\alpha}\). The magnitude of \(\mathit{\alpha}\) (in rad/s2) is:


| 1. | \(2\) | 2. | \(12\) |
| 3. | \(6\) | 4. | \(3\) |
Subtopic: Torque |
76%
Level 2: 60%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
A \(\sqrt {34}\) m long ladder weighing \(10\) kg leans on a frictionless wall. Its feet rest on the floor \(3\) m away from the wall as shown in the figure. If \(\mathrm F_ \mathrm f\) and \(\mathrm F_ \mathrm w\) are the reaction forces of the floor and the wall, then ratio of \(\mathrm F_ \mathrm w / \mathrm F_ \mathrm f\) will be: (Take \(g=10\) m/s2)

1. \(\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{110}} \)
2. \(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{113}} \)
3. \(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{109}} \)
4. \( \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{109}}\)

1. \(\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{110}} \)
2. \(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{113}} \)
3. \(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{109}} \)
4. \( \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{109}}\)
Subtopic: Torque |
67%
Level 2: 60%+
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Select Question Set:






