An engine pump is used to pump a liquid of density ρ continuously through a pipe of cross-sectional area A. If the speed of flow of the liquid in the pipe is v, then the rate at which kinetic energy is being imparted to the liquid is
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
The kinetic energy acquired by a mass m in travelling a certain distance d starting from rest under the action of a constant force is directly proportional to
(1)
(2) Independent of m
(3)
(4) m
An open knife edge of mass 'm' is dropped from a height 'h' on a wooden floor. If the blade penetrates upto the depth 'd' into the wood, the average resistance offered by the wood to the knife edge is
(1) mg
(2)
(3)
(4)
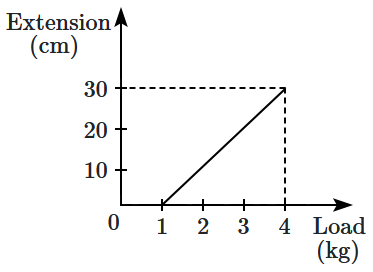
1. \(0.1\text{ N/cm}\)
2. \(5\text{ N/cm}\)
3. \(0.3\text{ N/cm}\)
4. \(1\text{ N/cm}\)
A particle which is constrained to move along the x-axis, is subjected to a force in the same direction which varies with the distance x of the particle from the origin as . Here k and a are positive constants. For , the functional form of the potential energy U(x) of the particle is-
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
The force acting on a body moving along x-axis varies with the position of the particle as shown in the fig.
The body is in stable equilibrium at
1. x = x1
2. x = x2
3. both x1 and x2
4. neither x1 nor x2
A particle is placed at the origin and a force F = kx is acting on it (where k is positive constant). If U(0) = 0, the graph of U(x) versus x will be (where U is the potential energy function)
1.
2.
3.
4.
A body of mass 1 kg begins to move under the action of a time dependent force \(F = 2 t\) \(\hat{i} + 3 t^{2}\ \hat{j}\) N, where \(\hat{i}\) and \(\hat{j}\) are unit vectors along X and Y axis, What power will be developed by the force at the time (t) ?
1. \(\left(2 t^{2} + 4 t^{4}\right) W\)
2. \(\left(2 t^{3} + 3 t^{4}\right) W\)
3. \(\left(2 t^{3} + 3 t^{5}\right) W\)
4. \(\left(2 t + 3 t^{3}\right) W\)
A particle of mass m is driven by a machine that delivers a constant power of k watts. If the particle starts from rest the force on the particle at time t is:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Two particles of masses m1,m2 move with initial velocities u1 and u2. On collision, one of the particles get excited to higher level, after absorbing energy . If final velocities of particles be v1 and v2, then we must have
1. m12u1+m22u2-=m12v1+m22v2
2. m1u12+m2u2=m1v12+m2v22-
3. m1u12+m2u22-=m1v12+m2v22
4. m12u12+m22u22+=m12v12+m22v22















