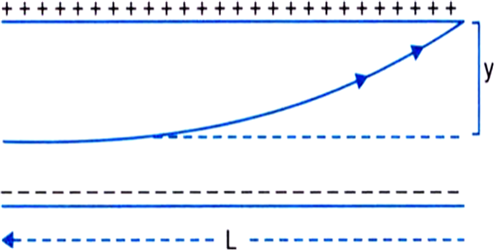
A particle of mass m and charge (–q) enters the region between the two charged plates initially moving along the x-axis with speed (as shown in the figure). The length of the plate is L and a uniform electric field E is maintained between the plates. The vertical deflection of the particle at the far edge of the plate is:
1. \(\frac{2 q E L^2}{3 m\left(v_x\right)^2}\)
2. \(\frac{2 q E L^2}{m\left(v_x\right)^2}\)
3. \(\frac{3 q E L^2}{2 m\left(v_x\right)^2}\)
4. \(\frac{q E L^2}{2 m\left(v_x\right)^2}\)

1. \(\frac{2 q E L^2}{3 m\left(v_x\right)^2}\)
2. \(\frac{2 q E L^2}{m\left(v_x\right)^2}\)
3. \(\frac{3 q E L^2}{2 m\left(v_x\right)^2}\)
4. \(\frac{q E L^2}{2 m\left(v_x\right)^2}\)
| 1. | \(\dfrac{Q+q}{4 \pi r_{2}^{2}}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{q}{4 \pi r_{1}^{2}}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{-Q+q}{4 \pi r_{2}^{2}}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{-q}{4 \pi r_{1}^{2}}\) |
A long charged cylinder of linear charged density is surrounded by a hollow co-axial conducting cylinder. What is the electric field in the space between the two cylinders at distance d from the common axis?
1. \(\frac{2 \lambda}{\pi \varepsilon_0 d}\)
2. \(\frac{\lambda}{2 \pi \varepsilon_0 d}\)
3. \(\frac{\lambda}{\pi \varepsilon_0 d}\)
4. \(\frac{\pi \lambda}{2 \varepsilon_0 d}\)
Sure check for the presence of electric charge is:
1. Process of induction
2. Repulsion between bodies
3. Attraction between bodies
4. Frictional force between bodies
If a solid and a hollow conducting sphere have the same radii then:
1. the hollow sphere will hold more maximum charge.
2. the solid sphere will hold more maximum charge.
3. both the spheres will hold the same maximum charge.
4. both the spheres can't hold a charge.
Five balls marked \(a\) to \(e\) are suspended using separate threads. Pairs \((b,c)\) and \((d,e)\) show electrostatic repulsion while pairs \((a,b), (c,e)\) and \((a,e)\) show electrostatic attraction. The ball marked \(a\) must be:
1. negatively charged.
2. positively charged.
3. uncharged.
4. Any of the above is possible
When a plastic rod rubbed with wool is brought near the knob of a negatively charged gold-leaf electroscope, the gold leaves:
1. Contract
2. Dilate
3. Start oscillating
4. Collapse completely
Which of the following is not true about the electric charge?
1. Charge on a body is always an integral multiple of a certain charge known as the charge of an electron.
2. Charge is a scalar quantity.
3. Net charge on an isolated system is always conserved.
4. Charge can be converted into energy and energy can be converted into charge.
Which of the following processes involves the principle of electrostatic induction?
1. Pollination
2. Chocolate making
3. Xerox copying
4. All of these
When a conducting soap bubble is negatively charged then:
1. Its size starts varying arbitrarily
2. It expands
3. It contracts
4. No change in its size takes place




