Three resistors having resistances \(r_1, r_2~\text{and}~r_3\) are connected as shown in the given circuit. The ratio \(\frac{i_3}{i_1}\) of currents in terms of resistances used in the circuit is:

1. \(\frac{r_1}{r_1+r_2}\)
2. \(\frac{r_2}{r_1+r_3}\)
3. \(\frac{r_1}{r_2+r_3}\)
4. \(\frac{r_2}{r_2+r_3}\)

1. \(\frac{r_1}{r_1+r_2}\)
2. \(\frac{r_2}{r_1+r_3}\)
3. \(\frac{r_1}{r_2+r_3}\)
4. \(\frac{r_2}{r_2+r_3}\)
The effective resistance of a parallel connection that consists of four wires of equal length, equal area of cross-section, and same material is \(0.25~\Omega\). What will be the effective resistance if they are connected in series?
1. \(1~\Omega\)
2. \(4~\Omega\)
3. \(0.25~\Omega\)
4. \(0.5~\Omega\)
In a potentiometer circuit, a cell of emf \(1.5~\text{V}\) gives a balance point at 36 cm length of wire. If another cell of emf 2.5 V replaces the first cell, then at what length of the wire, the balance point occur?
1. 64 cm
2. 62 cm
3. 60 cm
4. 21.6 cm
Match Column I and Column II with appropriate relations.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (A) | Drift Velocity | (P) | \(\dfrac{ \mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{ne}^2 \rho}\) |
| (B) | Electrical Resistivity | (Q) | \(nev_d\) |
| (C) | Relaxation Period | (R) | \(\dfrac{ \mathrm{eE}}{\mathrm{m}} \tau\) |
| (D) | Current Density | (S) | \(\dfrac{E}{J}\) |
| (A) | (B) | (C) | (D) | |
| 1. | (R) | (P) | (S) | (Q) |
| 2. | (R) | (Q) | (S) | (P) |
| 3. | (R) | (S) | (P) | (Q) |
| 4. | (R) | (S) | (Q) | (P) |
Graph shows the variation of resistivity with temperature for a material. The material can be-
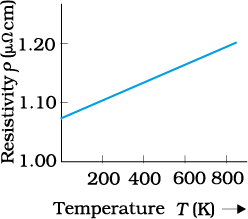
1. Copper
2. Aluminum
3. GaAs
4. Nichrome
The curve in the given graph shows the variation of potential difference 'V' across a conductor with current 'I' flowing through a conductor. The dashed line in the graph given below represents:
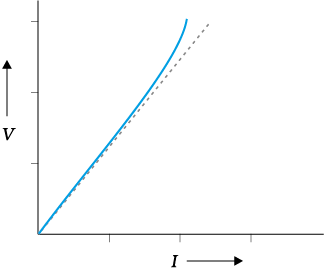
1. A non-ohmic conductor
2. An ohmic conductor
3. A semiconductor
4. An insulator
Which one of the following is correct?
| 1. | After acquiring drift speed by the electrons, there is no acceleration of the electrons. |
| 2. | To have a large amount of electric current, the drift speed of the electrons should be very large. |
| 3. | When electrons drift in metal from lower to higher potential, all the free electrons move in the same direction. |
| 4. | The paths of the electrons between two successive collisions are curved in the presence of electric field. |
A light bulb is rated at \(100~\text {W}\) for a \(220~\text {V}\) supply, the resistance of the bulb is:
1. \(423~\Omega\)
2. \(440~\Omega\)
3. \(444~\Omega\)
4. \(484~\Omega\)
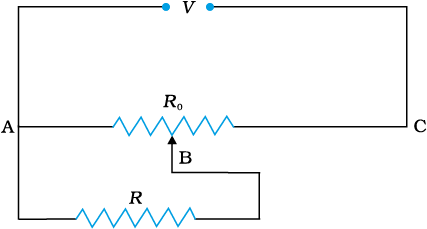
A resistance of draws current from a potentiometer. The potentiometer has a total resistance (as shown in the figure). A voltage V is supplied to the potentiometer. What is the voltage across R when the sliding contact is in the middle of the potentiometer?
In a meter bridge (shown in the figure), the null point is found at a distance of \(33.7\text{ cm}\) from \(A.\) If now a resistance of \(12~\Omega\) is connected in parallel with \(S,\) the null point occurs at \(51.9\text{ cm}.\) The values of \(R\) and \(S\) are respectively:
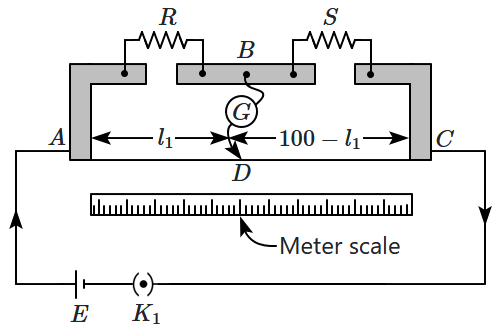
1. \(13.5~\Omega,~6.86~\Omega\)
2. \(13.5~\Omega,~13.5~\Omega\)
3. \(6.86~\Omega,~6.86~\Omega\)
4. \(6.86~\Omega,~13.5~\Omega\)






