A network of resistors is connected to a 16 V battery with an internal resistance of , as shown in the figure. The equivalent resistance of the network is:


A network of resistors is connected to a 16 V battery with an internal resistance of , as shown in the figure. The current in resistor between B and C will be:
A network of resistors is connected to a 16 V battery with an internal resistance of , as shown in the figure. The voltage drop across AB is:
1. 2 V
2. 25 V
3. 4 V
4. 6 V
A battery of 10 V and negligible internal resistance is connected across the diagonally opposite corners of a cubical network consisting of 12 resistors each of resistance (as shown in the figure). The total current in the network is:
The current in the branch AB in the given network is:
1. 5/8 A
2. 5/2 A
3. 15/8 A
4. 3/2 A
The four arms of a Wheatstone bridge have the following resistances as shown in the figure. A galvanometer of 15Ω resistance is connected across BD. What is the current through the galvanometer when a potential difference of 10 V is maintained across AC?
1. 4.87 mA
2. 3.72 mA
3. 5.01 mA
4. 2.65 mA
In a meter bridge (shown in the figure), the null point is found at a distance of \(33.7\text{ cm}\) from \(A.\) If now a resistance of \(12~\Omega\) is connected in parallel with \(S,\) the null point occurs at \(51.9\text{ cm}.\) The values of \(R\) and \(S\) are respectively:

1. \(13.5~\Omega,~6.86~\Omega\)
2. \(13.5~\Omega,~13.5~\Omega\)
3. \(6.86~\Omega,~6.86~\Omega\)
4. \(6.86~\Omega,~13.5~\Omega\)
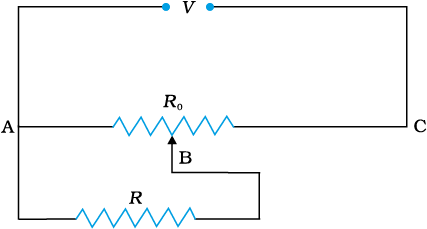
A resistance of draws current from a potentiometer. The potentiometer has a total resistance (as shown in the figure). A voltage V is supplied to the potentiometer. What is the voltage across R when the sliding contact is in the middle of the potentiometer?
A light bulb is rated at \(100~\text {W}\) for a \(220~\text {V}\) supply, the resistance of the bulb is:
1. \(423~\Omega\)
2. \(440~\Omega\)
3. \(444~\Omega\)
4. \(484~\Omega\)
Which one of the following is correct?
| 1. | After acquiring drift speed by the electrons, there is no acceleration of the electrons. |
| 2. | To have a large amount of electric current, the drift speed of the electrons should be very large. |
| 3. | When electrons drift in metal from lower to higher potential, all the free electrons move in the same direction. |
| 4. | The paths of the electrons between two successive collisions are curved in the presence of electric field. |










