Time taken by the projectile to reach from A to B is t. Then the distance AB is equal to :

1.
2.
3.
4. 2ut
A से B तक पहुंचने में प्रक्षेप्य द्वारा लिया गया समय t है। तब दूरी AB किसके बराबर है?

1.
2.
3.
4. 2ut


A body is projected at such an angle that the horizontal range is three times the greatest height. The angle of projection is
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
एक पिंड को इस तरह के कोण पर प्रक्षेपित किया जाता है कि क्षैतिज परास महत्तम ऊँचाई से तीन गुना अधिक है। प्रक्षेप का कोण है-
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
A stone projected with a velocity u at an angle θ with the horizontal reaches maximum height H1. When it is projected with velocity u at an angle with the horizontal, it reaches maximum height H2. The relation between the horizontal range R of the projectile, H1 and H2 is
(1)
(2) R = 4(H1 – H2)
(3) R = 4(H1 + H2)
(4)
एक पत्थर जो u वेग के साथ क्षैतिज से θ कोण पर प्रक्षेपित होता है, यह अधिकतम ऊंचाई H1 तक पहुंचता है। जब इसे u वेग से क्षैतिज के साथ कोण पर प्रक्षेपित किया जाता है, यह अधिकतम ऊंचाई H2 तक पहुंचता है। प्रक्षेप की क्षैतिज परास R, H1 और H2 के बीच संबंध है-
(1)
(2) R = 4(H1 – H2)
(3) R = 4(H1 + H2)
(4)
A particle (A) is dropped from a height and another particle (B) is thrown in horizontal direction with speed of 5 m/sec from the same height. The correct statement is
| 1. | Both particles will reach at ground simultaneously |
| 2. | Both particles will reach at ground with same speed |
| 3. | Particle (A) will reach at ground first with respect to particle (B) |
| 4. | Particle (B) will reach at ground first with respect to particle (A) |
एक कण (A) एक ऊंचाई से छोड़ा जाता है और एक अन्य कण (B) को 5m/se की चाल के साथ क्षैतिज दिशा में उसी ऊंचाई से फेंक दिया जाता है। सही कथन है-
| 1. | दोनों कण एक साथ जमीन पर पहुंचेंगे |
| 2. | दोनों कण समान चाल से जमीन पर पहुंचेंगे |
| 3. | कण (A) कण (B) के सापेक्ष जमीन पर पहले पहुंच जाएगा |
| 4. | कण (B) कण (A) के सापेक्ष में जमीन पर पहले पहुंच जाएगा |
At the top of the trajectory of a projectile, the directions of its velocity and acceleration are
(1) Perpendicular to each other
(2) Parallel to each other
(3) Inclined to each other at an angle of 45°
(4) Antiparallel to each other
एक प्रक्षेप्य के प्रक्षेप पथ के शीर्ष पर, इसके वेग और त्वरण की दिशाएं हैं-
(1) एक-दूसरे के लंबवत
(2) एक दूसरे के समांतर
(3) 45° के कोण पर एक दूसरे से झुके हुए
(4) एक दूसरे के प्रति समांतर
Two bodies are projected with the same velocity. If one is projected at an angle of 30° and the other at an angle of 60° to the horizontal, the ratio of the maximum heights reached is
(1) 3 : 1
(2) 1 : 3
(3) 1 : 2
(4) 2 : 1
दो पिंड समान वेग से प्रक्षेपित किए जाते हैं। यदि एक को क्षैतिज से 30° के कोण पर और दूसरे को 60° के कोण पर प्रक्षेपित किया जाता है, तो अधिकतम ऊंचाइयों का अनुपात कितना होता है?
(1) 3 : 1
(2) 1 : 3
(3) 1 : 2
(4) 2 : 1
The horizontal range and the maximum height of a projectile are equal.The angle of projection of the projectile is
1. 2.
3. 4.
एक प्रक्षेप्य की क्षैतिज परास और अधिकतम ऊंचाई बराबर है। प्रक्षेप्य के प्रक्षेप का कोण है-
1. 2.
3. 4.
A particle moves in space such that
Where x, y, z are measured in metre and t in second. The acceleration of the particle at t=3s is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
एक कण अंतरिक्ष में इस प्रकार गति करता है कि
जहां x, y, z को मीटर में और t को सेकेण्ड में मापा जाता है। t = 3s पर कण का त्वरण है-
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
An electric fan has blades of length 30 cm as measured from the axis of rotation. If the fan is rotating at 1200 r.p.m, the acceleration of a point on the tip of the blade is about
| 1. | 1600 m/sec2 | 2. | 4740 m/sec2 |
| 3. | 2370 m/sec2 | 4. | 5055 m/sec2 |
एक बिजली के पंखे में ब्लेड की लंबाई 30cm है जिसे घूर्णन अक्ष से मापा जाता है। यदि पंखा 1200 घूर्णन प्रति मिनट से घूर्णन कर रहा है, ब्लेड की नोक का एक बिंदु का त्वरण लगभग है-
| 1. | 1600 m/sec2 | 2. | 4740 m/sec2 |
| 3. | 2370 m/sec2 | 4. | 5055 m/sec2 |
In 1.0 s, a particle goes from point A to point B, moving in a semicircle of radius 1.0 m (see figure). The magnitude of the average velocity is

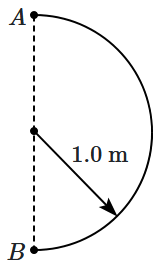
| 1. | 3.14 m/s | 2. | 2.0 m/s |
| 3. | 1.0 m/s | 4. | Zero |
1.0 s में, एक कण 1.0 m त्रिज्या के अर्धवृत्त में गति करते हुए बिंदु A से B तक जाता है (चित्र देखें)। औसत वेग का परिमाण है-

| 1. | 3.14 m/s | 2. | 2.0 m/s |
| 3. | 1.0 m/s |
4. | शून्य |







