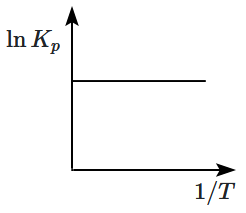
An exothermic reaction is represented by the graph:
1.
2.
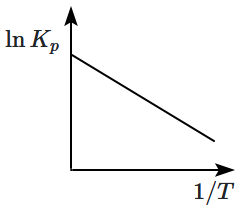
3.
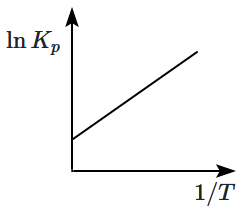
4.
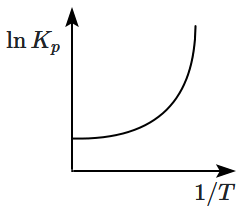




For the reversible system the relationship between degree of dissociation of PCl5 and the equilibrium constant Kp of the above equilibrium is
1.
2.
3.
4.
One mole of N2O4(g) at 300 K is kept in a closed container under one atmospheric pressure. It is heated to 600 K when 20% by mass of N2O4(g) decomposes to NO2(g).
The resultant pressure will be:
| 1. | 1.0 atm | 2. | 2.4 atm |
| 3. | 2.0 atm | 4. | 1.2 atm |
The equilibrium constant (K) of the reaction, at 298 K is 100. If the rate constant of the forward reaction is , the rate constant of the reverse reaction is
1. 4
2.
3.
4.
One mole of N2O4(g) at 310 K is 25% dissociated at 1 atm pressure. The percentage dissociation at 0.1 atm and 310 K is
1. 25%
2. 50%
3. 76%
4. 63%
Kp has the value of 10-6 atm3 and 10-4 atm3 at 298 K and 323 K respectively for the reaction:
\(\mathrm{CuSO}_4 \cdot 3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{~s}) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{CuSO}_4(\mathrm{~s})+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{~g})\)
\(\Delta_{\mathrm{r}} \mathrm{H}^{\circ} \text { for the reaction is: }\)
| 1. | 7.7 kJ/mol | 2. | -147.41 kJ/mol |
| 3. | 147.41 kJ/mol | 4. | None of the above |
Assume that the decomposition of HNO3 can be represented by the following equation
and the reaction approaches equilibrium at 400K temperature and 30 atm pressure. At equilibrium, partial pressure of HNO3 is 2 atm. Calculate Kc in (mol/L)3 at 400 K:
(Use : R=0.08 atm-L/mol-K)
1. 4
2. 8
3. 16
4. 32
A 250 ml flask containing NO(g) at 0.46 atm is connected to a 100 ml flask containing oxygen gas at 0.86 atm by means of a stop cock at 350 K, the gases are mixed by opening the stop cock where the following equilibrium is established.
The first reaction is complete while the second is at equilibrium. If the total pressure is 0.37 atm, Kp is:
1. 0.645 atm-1
2. 1.290 atm-1
3. 20 atm-1
4. 5.46 atm-1
The equilibrium constant for the reactions
are K1 and K2 respectively. The correct relationship between K1 and K2 is
1.
2.
3.
4.
One mole of N2(g) is mixed with 2 moles of H2(g) in a 4 litre vessel. 50% of N2(g) is converted to NH3(g) by the following reaction:
What will be the value of Kc for the following equilibrium?
1. 256
2. 16
3.
4. None of the above






