\(AB\) is a \(20~\Omega\) resistor with a tapping point \(C\) that can be moved along \(AB\). The resistances in \(AC,BC\) are proportional to the lengths \(AC,BC\). Initially, \(C\) is at the mid-point of \(AB\) and the circuit is switched on.

If the tapping point \(C\) is moved so that the length \(BC\) is reduced to half its initial value, then the voltage across the \(15~\Omega\) resistor,

If the tapping point \(C\) is moved so that the length \(BC\) is reduced to half its initial value, then the voltage across the \(15~\Omega\) resistor,
| 1. | increases by \(1\) V |
| 2. | decreases by \(1\) V |
| 3. | increases by \(3\) V |
| 4. | decreases by \(3\) V |
Subtopic: Kirchoff's Voltage Law |
From NCERT
To view explanation, please take trial in the course.
NEET 2026 - Target Batch - Vital
Hints
To view explanation, please take trial in the course.
NEET 2026 - Target Batch - Vital
The current flowing through the left \(20~\Omega\) resistor is:


| 1. | \(1~\text A\) | 2. | \(0.5~\text A\) |
| 3. | \(2.5~\text A\) | 4. | \(3~\text A\) |
Subtopic: Kirchoff's Voltage Law |
58%
From NCERT
To view explanation, please take trial in the course.
NEET 2026 - Target Batch - Vital
Hints
To view explanation, please take trial in the course.
NEET 2026 - Target Batch - Vital
All the cells, shown in the figure below, are of \(2~\text V,\) and all the resistances are \(1~\Omega.\) When a potential difference \(V\) is applied between \(A\) and \(B,\) the current through the circuit doubles compared to the situation when the potential difference is made zero. Then;
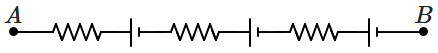
| 1. | \(V=2\) volts, positive at \(A.\) |
| 2. | \(V=2\) volts, negative at \(A.\) |
| 3. | \(V=6\) volts, positive at \(A.\) |
| 4. | \(V=6\) volts, negative at \(A.\) |
Subtopic: Kirchoff's Voltage Law |
From NCERT
To view explanation, please take trial in the course.
NEET 2026 - Target Batch - Vital
Hints
To view explanation, please take trial in the course.
NEET 2026 - Target Batch - Vital


