If W1, W2 and W3 represent the work done in moving a particle from A to B along three different paths 1, 2 and 3 respectively (as shown) in the gravitational field of a point mass m, find the correct relation between W1, W2 and W3

(1) W1 > W2 > W3
(2) W1 = W2 = W3
(3) W1 < W2 < W3
(4) W2 > W1 > W3

The displacement x of a particle moving in one dimension under the action of a constant force is related to the time t by the equation , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. The work done by the force in the first 6 seconds is
(1) 9 J
(2) 6 J
(3) 0 J
(4) 3 J
A force \(F = -k(y\hat i +x\hat j)\) (where \(k\) is a positive constant) acts on a particle moving in the \(xy\text-\)plane. Starting from the origin, the particle is taken along the positive \(x\text-\)axis to the point \((a,0)\) and then parallel to the \(y\text-\)axis to the point \((a,a)\). The total work done by the force on the particle is:
1. \(-2ka^2\)
2. \(2ka^2\)
3. \(-ka^2\)
4. \(ka^2\)
A lorry and a car moving with the same K.E. are brought to rest by applying the same retarding force, then:
1. Lorry will come to rest in a shorter distance
2. Car will come to rest in a shorter distance
3. Both will come to rest in a same distance
4. None of the above
A particle free to move along the x-axis has potential energy given by for , where k is a positive constant of appropriate dimensions. Then
(1) At point away from the origin, the particle is in unstable equilibrium
(2) For any finite non-zero value of x, there is a force directed away from the origin
(3) If its total mechanical energy is k/2, it has its minimum kinetic energy at the origin
(4) For small displacements from x = 0, the motion is simple harmonic
The kinetic energy acquired by a mass m in travelling a certain distance d starting from rest under the action of a constant force is directly proportional to
(1)
(2) Independent of m
(3)
(4) m
An open knife edge of mass 'm' is dropped from a height 'h' on a wooden floor. If the blade penetrates upto the depth 'd' into the wood, the average resistance offered by the wood to the knife edge is
(1) mg
(2)
(3)
(4)
A body is moving along a straight line by a machine delivering constant power. The distance moved by the body in time t is proportional to
(1) t1/2
(2) t3/4
(3) t3/2
(4) t2
The relationship between force and position is shown in the given figure (in a one-dimensional case). The work done by the force in displacing a body from \(x = 1~\text{cm}\) to \(x = 5~\text{cm}\) is:

1. \(20~\text{ergs}\)
2. \(60~\text{ergs}\)
3. \(70~\text{ergs}\)
4. \(700~\text{ergs}\)
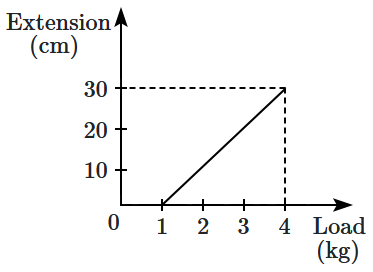
1. \(0.1\text{ N/cm}\)
2. \(5\text{ N/cm}\)
3. \(0.3\text{ N/cm}\)
4. \(1\text{ N/cm}\)






