Identify the given structure:

(1) Adenylic acid
(2) Uracil
(3) Cholesterol
(4) Adenosine

Match the tissues/molecules mentioned in column I with those of their degrading enzymes mentioned in column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
Column I Column II
A. Cell wall (i) Proteases
B. RNA (ii) Pectinases
C. Histone (iii) Ribonucleases
D. Pectin (iv) Cellulase
(1) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(ii)
(2) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iv),D-(iii)
(3) A-(i),B-(ii),C-(iii),D-(iv)
(4) A-(iii),B-(iv),C-(ii), D-(i)
Excess carbohydrates and proteins are stored in the body as
(1) amino acids
(2) fats
(3) starch
(4) monosaccharides
Nickel contributes to the formation of one of the following
| 1. | urease |
| 2. | dehydrogenase |
| 3. | rubisco protein |
| 4. | nitrate reductase |
Amino acid is a:
| 1. | Substituted methane |
| 2. | Substituted ethane |
| 3. | Any acid having amino group |
| 4. | Derivative of indol acetic acid |
A.
B.
C.
Which of the above is Zwitterionic form?
(1) B
(2) C
(3) A
(4) All are correct
The quaternary structure of a protein:
| 1. | Consists of 4 subunits - hence the name quaternary |
| 2. | Is unrelated to the function of the protein |
| 3. | Both (a) and (b) |
| 4. | Depends on the 1° structure of subunits |
Adult human haemoglobin consists of:
| 1. | 2 subunits (β, β) |
| 2. | 2 subunits (α, α) |
| 3. | 4 subunits (2α, 2β) |
| 4. | 3 subunits (2α, 1β) |
Lecithin is:
(1) Phospholipid
(2) Carbohydrate
(3) Protein
(4) Amino acid
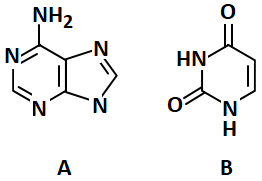
The above diagram represent the nitrogenous bases. Identify the correct combination:
1. A = Adenine; B = Thymine
2. A = Guanine; B = Thymine
3. A = Adenine; B = Uracil
4. A = Guanine; B = Uracil









