Select Question Set:
Which of the following characteristics differentiate bryophytes from algae
A.
Attachment to a substratum by unicellular rhizoids
B.
Haploid condition
C.
Filamentous body
D.
Unicellularity and colonial habitat
E.
Lack of true roots and stem
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, C, D only
2. A, B, C, D only
3. A, B, E only
4. B, C, D, E only
Subtopic: Algae | Bryophytes |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Match List I with List II:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
2. A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
3. A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
4. A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
| List I | List II |
| A. Isogamous | I. Cycas |
| B. Heterosporous | II. Spirogyra |
| C. Gemmae | III. Selaginella |
| D. Coralloid root | IV. Marchantia |
1. A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
2. A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
3. A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
4. A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
Subtopic: Bryophytes | Bryophytes (Liverworts) | Chlorophyceae: Green Algae | Gymnosperms |
87%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Given below are two statements
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
| Statement I: | In Phaephyceae, laminarin is the stored food and major pigments are chlorophyll a & b |
| Statement II: | In Rhodophyceae, Floridean starch is the sored food and the major pigments are chlorophyll-a, b and Phycoerythrin |
| 1. | Both statement I and statement II are correct |
| 2. | Both statement I and statement II are incorrect |
| 3. | Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect |
| 4. | Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct |
Subtopic: Pheophyceae: Brown Algae | Rhodophyceae: Red Algae and Importance of Algae |
79%
Level 2: 60%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The spread of living pteridophytes is limited and restricted to narrow geographical regions because
| 1. | Gametophytes are dependent on sporophytes |
| 2. | Sporophytes require cool, damp place to produce gametes |
| 3. | Gametophytes require cool, damp and shady places to grow. |
| 4. | They do not need water for fertilisation |
Subtopic: Pteridophytes |
70%
Level 2: 60%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Which of the following statement is/are correct regarding red algae?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A,B,C only
2. A,B,D,E only
3. B,E only
4. C,D,E only
| A. | Asexual reproduction takes place by motile spores |
| B. | Sexual reproduction may be isogamous, anisogamous, or oogamous |
| C. | Food is stored in the form of floridean starch |
| D. | They are called red algae because of the predominance of the red pigment, r-phycoerythrin in their body |
| E. | They possess chlorophyll a and d |
1. A,B,C only
2. A,B,D,E only
3. B,E only
4. C,D,E only
Subtopic: Rhodophyceae: Red Algae and Importance of Algae |
87%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Bryophytes are also called amphibians of plant kingdom because they can live in soil are not dependent on water for sexual reproduction
Statement II: The main plant body of bryophytes is diploid and is called sporophyte
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
2. Both Statement and Statement II are false
3. Statement I is true but statement II is false
4. Statement I is false but statement II is true
Statement I: Bryophytes are also called amphibians of plant kingdom because they can live in soil are not dependent on water for sexual reproduction
Statement II: The main plant body of bryophytes is diploid and is called sporophyte
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
2. Both Statement and Statement II are false
3. Statement I is true but statement II is false
4. Statement I is false but statement II is true
Subtopic: Bryophytes |
78%
Level 2: 60%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Match List-I with List-II:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| List-I | List-II | ||
| (a) | Chlamydomonas | (i) | Moss |
| (b) | Cycas | (ii) | Pteridophyte |
| (c) | Selaginella | (iii) | Alga |
| (d) | Sphagnum | (iv) | Gymnosperm |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| 1. | (iii) | (i) | (ii) | (iv) |
| 2. | (iii) | (iv) | (ii) | (i) |
| 3. | (iii) | (ii) | (i) | (iv) |
| 4. | (ii) | (iii) | (i) | (iv) |
Subtopic: Algae | Bryophytes | Pteridophytes | Gymnosperms |
91%
Level 1: 80%+
NEET - 2022
Hints
Read the following statements and identify the characters related to the alga shown in the diagram:
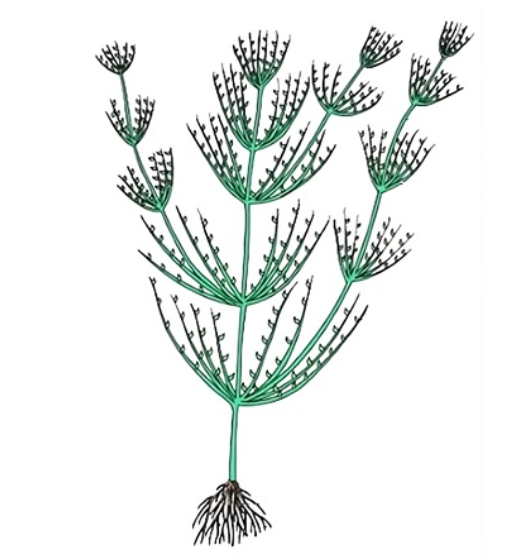
| a. | It is a member of Chlorophyceae. |
| b. | Food is stored in the form of starch. |
| c. | It is a monoecious plant showing oogonium and antheridium. |
| d. | Food is stored in the form of laminarin or mannitol. |
| e. | It shows dominance of pigments chlorophyll a, c and Fucoxanthin. |
| 1. | (a) and (b) only | 2. | (a), (b) and (c) only |
| 3. | (a), (c) and (d) only | 4. | (c), (d) and (e) only |
Subtopic: Chlorophyceae: Green Algae: I |
51%
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2022
Hints
Select the incorrect statement with respect to algae.
| 1. | The food stored in red algae is in the form of floridean starch |
| 2. | Pyrenoids in green algae contain protein besides starch |
| 3. | Asexual reproduction in most brown algae is by non-motile spores |
| 4. | Brown algae show great variation in size and form |
Subtopic: Algae |
82%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
In gymnosperms:
| 1. | The female gametophyte has independent free-living existence. |
| 2. | Two different types of spores are produced. |
| 3. | Ovules are enclosed by an ovary wall. |
| 4. | Pollen grains are carried to the ovule by water currents. |
Subtopic: Gymnosperms |
77%
Level 2: 60%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Select Question Set:






