The dissociation energy of CH4 and C2H6 are respectively 360 and 620 Kcal/mole. The bond energy of C-C is-
1. 260 Kcal/mole
2. 180 Kcal/mole
3. 130 Kcal/mole
4. 80 Kcal/mole
CH4 और C2H6 की वियोजन ऊर्जा क्रमशः 360 और 620 Kcal/mole हैं। C-C की बंध ऊर्जा है-
1. 260 Kcal/mole
2. 180 Kcal/mole
3. 130 Kcal/mole
4. 80 Kcal/mole
Which of the following conditions should be satisfied for the given reaction to be spontaneous at 0C and 1 atm?
H2O(s) H2O(l)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सी शर्तों को 0°C और 1 atm पर स्वतः प्रवर्तित होने के लिए दी गई अभिक्रिया के लिए संतुष्ट होना चाहिए?
H2O(s) H2O(l)
The standard heat of combustion of a hydrocarbon compound is an/a-
1. Extensive property
2. Colligative property
3. Intensive property
4. Constitutive property
हाइड्रोकार्बन यौगिक के दहन की मानक ऊष्मा क्या है?
1. विस्तारी गुणधर्म
2. अणुसंख्य गुणधर्म
3. गहन गुणधर्म
4. संघटनी गुणधर्म
Heats of combustion of are -890, -1411 and -1560 kJ/mole respectively. Which has the lowest fuel value in kJ/gm ?
1.
2.
3.
4. All same
के दहन का ऊष्माएँ क्रमशः -890, -1411 और -1560 kJ/mole हैं। किसमें kJ/gm में सबसे कम ईंधन मान होता है?
1.
2.
3.
4. सभी समान
If (i) , (ii) , (iii) , the heats of reaction are Q, –12, –10 respectively. Then Q = [Orissa JEE 2004]
(1) – 2
(2) 2
(3) – 22
(4) – 16
यदि (i) , (ii) , (iii) , अभिक्रिया की ऊष्माएँ क्रमश: Q, –12, –10 हैं। तब Q = [Orissa JEE 2004]
(1) – 2
(2) 2
(3) – 22
(4) – 16
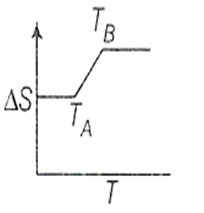
If for a given substance melting point is TB and freezing point is TA, then correct variation shown by graph between entropy change and temperature is [DCE 2001]
(1) 
(2)
(3)
(4)
यदि किसी दिए गए पदार्थ के लिए गलनांक TB और हिमांक TA है, फिर एंट्रॉपी परिवर्तन और तापमान के मध्य आरेख द्वारा दर्शाए गए सही परिवर्तन है: [DCE 2001]
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Among the following, the reaction for which is-
1.
2.
3.
4.
निम्नलिखित में से, अभिक्रिया जिसके लिए है-
1.
2.
3.
4.
For a given reaction, H =35.5 kJmol-1 and S = 83.6JK-1 mol-1. The reaction is spontaneous at: (Assume that H and S do not vary with temperature)
(1) T < 425 K
(2) T >425 K
(3) all temperatures
(4) T >298 K
एक दी गई अभिक्रिया के लिए, H= 35.5 kJmol-1 और S= 83.6 JK-1 mol-1है। किस ताप पर अभिक्रिया स्वतः होती है: (मान लीजिए किH और S तापमान के साथ परिवर्तित नहीं होते है)
(1) T < 425 K
(2) T > 425 K
(3) सभी तापमान
(4) T >298 K
Using only the following data:
(I)
(II)
the value, in kilojoules, for the reaction
is calculated to be:
1. -43.3
2. -10.3
3. +6.2
4. +10.3
केवल निम्नलिखित आकड़े का उपयोग करने पर:
(I)
(II)
अभिक्रिया के लिए मान की किलोजूल में गणना कीजिए:
1. -43.3
2. -10.3
3. +6.2
4. +10.3
When a liquid boils, there is [JIPMER 2002]
(1) An increase in entropy
(2) A decrease in entropy
(3) An increase in heat of vaporization
(4) An increase in free energy
जब एक द्रव उबला जाता है, वहाँ पर: [जिपमेर 2002]
(1) एंट्रॉपी में वृद्धि
(3) एंट्रॉपी में कमी
(3) वाष्पीकरण की ऊष्मा में वृद्धि
(4) मुक्त ऊर्जा में वृद्धि












