An element X being with oxygen and CO present in air as
When X at 1 atm is treated with air, 25% of it is bound to CO(g). The partial pressure of CO(g) in air at equilibrium, if partial pressure of O2(g) in air at equilibrium is 0.2 atm, would be
1.
2.
3.
4.
For the reaction (i) and (ii)
Given, If degree of dissociation of A(g) and X(g) are same then the ratio of total pressure in equilibrium (i) and (ii) will be
1. 36:1
2. 0.5:1
3. 1:1
4. 3:1
For the reaction the value of Kp is when the partial pressure are measured in atmosphere. The value of Kc with concentration in mol L-1 is
1.
2.
3.
4.
The degree of dissociation of PCl5 at one atmosphere is 0.3. The pressure at which PCl5 is dissociated to 50% is:
1. 0.273 atm
2. 0.3 atm
3. 1.34 atm
4. 2.73 atm
At 550 K, Kc for the following reaction is \(10^4 \rm { ~mol^{-1} ~L}\).
\(X(g) + Y(g) \rightleftharpoons Z(g)\)
At equilibrium, it was observed that,
\(\rm{[X] = \dfrac{1}{2}[Y] = \dfrac{1}{2} [Z]}\)
What is the value of [Z] at equilibrium?
| 1. | \(10^{-4} \mathrm{{~mol} {~L}^{-1}} \) | 2. | \(2 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{{~mol} {~L}^{-1}} \) |
| 3. | \(2 \times 10^4 \mathrm{{~mol} {~L}^{-1}} \) | 4. | \(10^4 \mathrm{{~mol} {~L}^{-1}}\) |
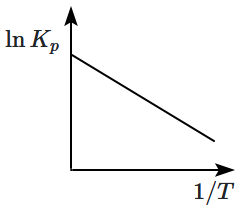
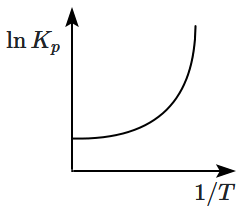
An exothermic reaction is represented by the graph:
| 1. | 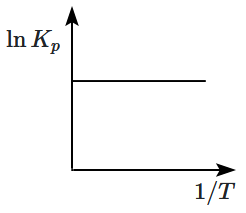 |
2. |  |
| 3. | 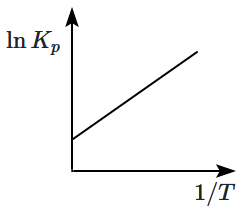 |
4. |  |
For the reversible system the relationship between degree of dissociation of PCl5 and the equilibrium constant Kp of the above equilibrium is
1.
2.
3.
4.
One mole of N2O4(g) at 300 K is kept in a closed container under one atmospheric pressure. It is heated to 600 K when 20% by mass of N2O4(g) decomposes to NO2(g).
The resultant pressure will be:
| 1. | 1.0 atm | 2. | 2.4 atm |
| 3. | 2.0 atm | 4. | 1.2 atm |
The equilibrium constant (K) of the reaction, at 298 K is 100. If the rate constant of the forward reaction is , the rate constant of the reverse reaction is
1. 4
2.
3.
4.
One mole of N2O4(g) at 310 K is 25% dissociated at 1 atm pressure. The percentage dissociation at 0.1 atm and 310 K is
1. 25%
2. 50%
3. 76%
4. 63%






