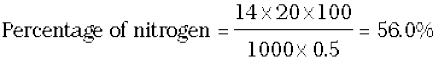There are two methods for estimation of nitrogen: (i) Dumas method and (ii) Kjeldahl’s method.
(i) Dumas method: The nitrogen containing organic compound, when heated with copper oxide in an atmosphere of carbon dioxide, yields free nitrogen in addition to carbon dioxide and water.
CxHyNz + (2x + y/2) CuO → x CO2 + y/2 H2O + z/2 N2 + (2x + y/2) Cu
Traces of nitrogen oxides formed, if any, are reduced to nitrogen by passing the gaseous mixture over a heated copper gauze. The mixture of gases so produced is collected over an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide which absorbs carbon dioxide. Nitrogen is collected in the upper part of the graduated tube (Fig.12.15).
Let the mass of organic compound = m g
Volume of nitrogen collected = V1 mL
Room temperature = T1K
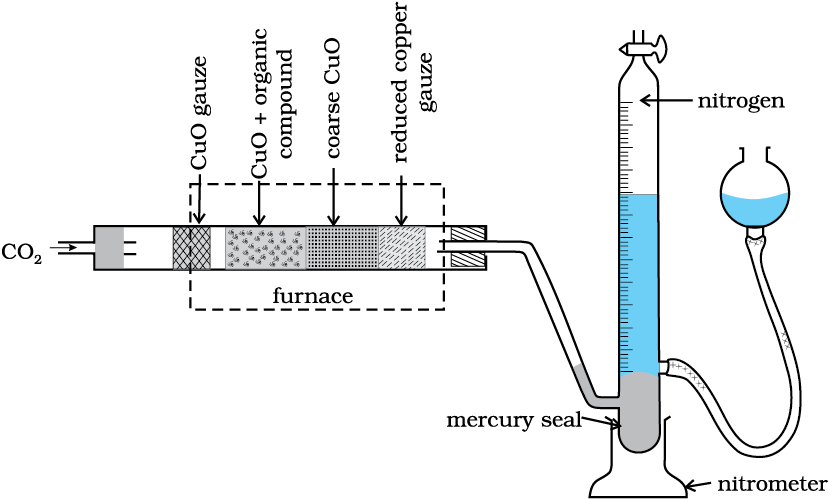
Fig.12.15 Dumas method. The organic compound yields nitrogen gas on heating it with copper(II) oxide in the presence of CO2 gas. The mixture of gases is collected over potassium hydroxide solution in which CO2 is absorbed and volume of nitrogen gas is determined.
(Let it be V mL)
Where p1 and V1 are the pressure and volume of nitrogen, p1 is different from the atmospheric pressure at which nitrogen gas is collected. The value of p1 is obtained by the relation;
p1= Atmospheric pressure – Aqueous tension
22400 mL N2 at STP weighs 28 g.
Percentage of nitrogen =
Problem 12.21
In Dumas’ method for estimation of nitrogen, 0.3g of an organic compound gave 50mL of nitrogen collected at 300K temperature and 715mm pressure. Calculate the percentage composition of nitrogen in the compound. (Aqueous tension at 300K=15 mm)
Solution
Volume of nitrogen collected at 300K and 715mm pressure is 50 mL
Actual pressure = 715-15 =700 mm
22,400 mL of N2 at STP weighs = 28 g
(ii) Kjeldahl’s method: The compound containing nitrogen is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid. Nitrogen in the compound gets converted to ammonium sulphate (Fig. 12.16). The resulting acid mixture is then heated with excess of sodium hydroxide. The liberated ammonia gas is absorbed in an excess of standard solution of sulphuric acid. The amount of ammonia produced is determined by estimating the amount of sulphuric acid consumed in the reaction. It is done by estimating unreacted sulphuric acid left after the absorption of ammonia by titrating it with standard alkali solution. The difference between the initial amount of acid taken and that left after the reaction gives the amount of acid reacted with ammonia.
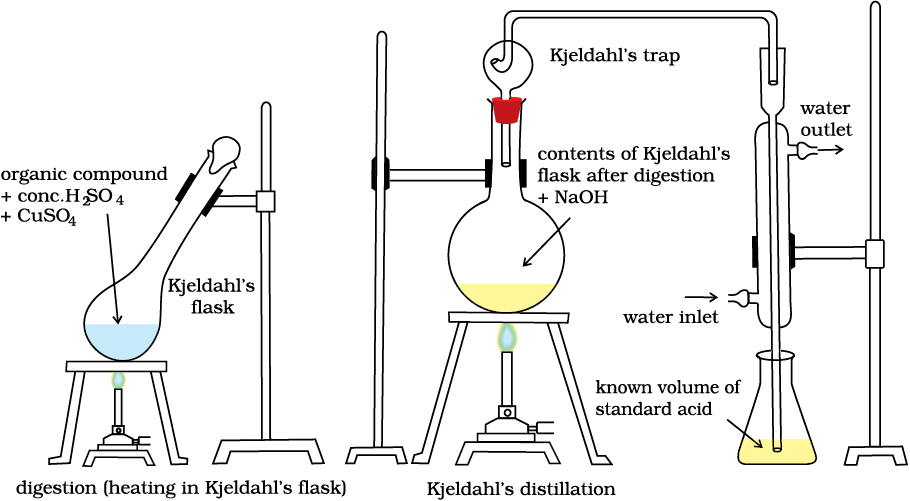
Fig.12.16 Kjeldahl method. Nitrogen-containing compound is treated with concentrated H2SO4 to get ammonium sulphate which liberates ammonia on treating with NaOH; ammonia is absorbed in known volume of standard acid.
Organic compound + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4
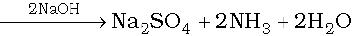
2NH3 + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4
Let the mass of organic compound taken = m g
Volume of H2SO4 of molarity, M,
taken = V mL
Volume of NaOH of molarity, M, used for titration of excess of H2SO4 = V1 mL
V1mL of NaOH of molarity M
= V1 /2 mL of H2SO4 of molarity M
Volume of H2SO4 of molarity M unused
= (V - V1/2) mL
(V- V1/2) mL of H2SO4 of molarity M
= 2(V-V1/2) mL of NH3 solution of molarity M.
1000 mL of 1 M NH3 solution contains
17g NH3 or 14 g of N
2(V-V1/2) mL of NH3 solution of molarity M contains:
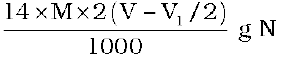
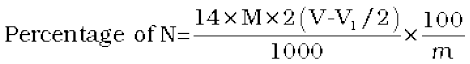
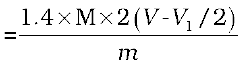
Kjeldahl method is not applicable to compounds containing nitrogen in nitro and azo groups and nitrogen present in the ring (e.g. pyridine) as nitrogen of these compounds does not change to ammonium sulphate under these conditions.
Problem 12.22
During estimation of nitrogen present in an organic compound by Kjeldahl’s method, the ammonia evolved from 0.5 g of the compound in Kjeldahl’s estimation of nitrogen, neutralized 10 mL of 1 M H2SO4. Find out the percentage of nitrogen in the compound.
Solution
1 M of 10 mL H2SO4=1M of 20 mL NH3
1000 mL of 1M ammonia contains 14 g nitrogen
Fig. 12.17 Carius method. Halogen containing
organic compound is heated with fuming nitric acid in the presence of silver nitrate.
20 mL of 1M ammonia contains 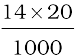 g nitrogen
g nitrogen