1.28
(a) A conductor A with a cavity as shown in Fig. 1.36 (a) is given a charge Q. Show that the entire charge must appear on the outer surface of the conductor.
(b) Another conductor B with charge q is inserted into the cavity keeping B insulated from A. Show that the total charge on the outside surface of A is Q + q [Fig. 1.36(b)].
(c) A sensitive instrument is to be shielded from the strong electrostatic fields in its environment. Suggest a possible way.
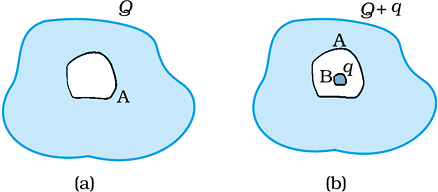
Figure 1.36
(a) Let us considera Gaussian surface that is lying wholly within a conductor and enclosing the cavity. The electric field intensity E inside the charged conductor is zero. Let q is the charge inside the conductor and is Eo the permittivity of free space.
According to Gauss's law, Flux,
Here,
Therefore, charge inside the conductor is zero.
The entire charge Q appears on the outer surface of the conductor.
(b) The outer surface of conductor A has a charge of amount Q. Another conductor B having charge tq is kept inside conductor A and it is insulated from A. Hence, a charge of the amount -q will be induced in the inner surface of conductor A and +q is induced on the outer surface of conductor A. Therefore, the total charge on the outer surface of conductor A is Q + q.
(c) A sensitive instrument can be environment by enclosing it fully inside a metallic surface. A closed metallic body acts as shielded from the strong electrostatic field in its electrostatic shield.

© 2026 GoodEd Technologies Pvt. Ltd.