Select Chapter Topics:
Which one of the following is a water-soluble vitamin, that is not excreted easily?
1.
Vitamin B2
2.
Vitamin B1
3.
Vitamin B6
4.
Vitamin B12
Subtopic: Vitamins, Hormones & Enzymes |
88%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Given below are two statements.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
| Assertion (A): | Amylose is a water-insoluble component. |
| Reason (R): | Amylose is a long linear molecule with more than 200 glucose units. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation for (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation for (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
Subtopic: Polysaccharides & their Importance |
57%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Given below are two statements:
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
| Statement I: | Maltose is formed by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage between two αD(+) glucose units that are reducing sugar. |
| Statement II: | Maltose is formed by C1-C6 glycosidic linkage between two αD(+) glucose & βD(+) glucose. |
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
| 1. | Both Statement I and Statement II are correct. |
| 2. | Both Statement I and Statement II are Incorrect. |
| 3. | Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect. |
| 4. | Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct. |
Subtopic: Polysaccharides & their Importance |
82%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Match List–I (Carbohydrates) with List – II (Cyclic Structures) and select the correct option:
1. A – 4; B – 1; C – 2; D – 3
2. A – 1; B – 4; C – 3; D – 2
3. A – 2; B – 3; C – 4; D – 1
4. A – 1; B – 3; C – 2; D – 4
| List - I (Carbohydrates) |
List - II (Cyclic Structures) |
||
| A. | α − D −Glucopyranose | 1. |  |
| B. | β −D − Glucopyranose | 2. |  |
| C. | α − D − Fructofuranose | 3. |  |
| D. | β − D −Fructofuranose | 4. |  |
1. A – 4; B – 1; C – 2; D – 3
2. A – 1; B – 4; C – 3; D – 2
3. A – 2; B – 3; C – 4; D – 1
4. A – 1; B – 3; C – 2; D – 4
Subtopic: Carbohydrates - Classification & D-L configuration |
73%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Which of the following cyclic forms represents the pyranose form of the linear carbohydrate shown in the image?

| 1. |  |
2. | 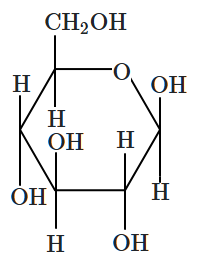 |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Subtopic: Carbohydrates - Classification & D-L configuration |
72%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
A biomolecule gives the following observations:
The correct structure of the biomolecule, from the following, is:
| (i) | With Br2/H2O, it gives monocarboxylic acid |
| (ii) | With acetate, it gives tetraacetate |
| (iii) | With HI/Red P, it gives isopentane |
The correct structure of the biomolecule, from the following, is:
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Subtopic: Carbohydrates - Classification & D-L configuration |
51%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The functional groups present in zwitter ion are:
1. -NH2 , -COOH
2. -NH2 , SO3H
3. Both (1) and (2)
4. None of the above
Subtopic: α - Amino Acids, Peptide Bond, Proteins & Structure |
53%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The term anomers of glucose refer to:
| 1. | Isomers of glucose that differ in configurations at carbons one and four (C-1 and C-4) |
| 2. | A mixture of (D)-glucose and (L)-glucose |
| 3. | Enantiomers of glucose |
| 4. | Isomers of glucose that differ in configuration at carbon one (C-1) |
Subtopic: Carbohydrates - Classification & D-L configuration |
68%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
In both DNA and RNA, heterocyclic base and phosphate ester linkages are at:
| 1. | C5' and C1' respectively of the sugar molecule. |
| 2. | C1' and C5' respectively of the sugar molecule. |
| 3. | C2' and C5' respectively of the sugar molecule. |
| 4. | C5' and C2' respectively of the sugar molecule. |
Subtopic: α - Amino Acids, Peptide Bond, Proteins & Structure |
79%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The secondary structure of a protein refers to:
1. α-Helical backbone
2. Hydrophobic interactions
3. Sequence of α-amino acids
4. Fixed configuration of the polypeptide backbone
Subtopic: α - Amino Acids, Peptide Bond, Proteins & Structure |
85%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.




