Select Chapter Topics:
De-Broglie wavelength of an electron orbiting in the \(n=2\) state of hydrogen atom is close to: (Given: Bohr radius \(=0.052~ \text{nm}\))
1. \(1.67~ \text{nm}\)
2. \(2.67~ \text{nm}\)
3. \(0.067~ \text{nm}\)
4. \(0.67~ \text{nm}\)
1. \(1.67~ \text{nm}\)
2. \(2.67~ \text{nm}\)
3. \(0.067~ \text{nm}\)
4. \(0.67~ \text{nm}\)
Subtopic: De-broglie Wavelength |
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2025
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Which of the following options represents the variation of photoelectric current with the property of light shown on the \(x \text{-}\)axis?
1. \(\mathrm{(A)}\) and \(\mathrm{(D)}\)
2. \(\mathrm{(B)}\) and \(\mathrm{(D)}\)
3. \(\mathrm{(A)}\) only
4. \(\mathrm{(A)}\) and \(\mathrm{(C)}\)
| \(\mathrm{(A)}\) |  |
\(\mathrm{(B)}\) | 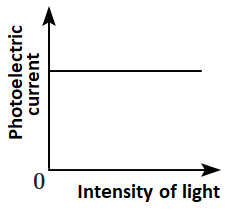 |
| \(\mathrm{(C)}\) |  |
\(\mathrm{(D)}\) |  |
1. \(\mathrm{(A)}\) and \(\mathrm{(D)}\)
2. \(\mathrm{(B)}\) and \(\mathrm{(D)}\)
3. \(\mathrm{(A)}\) only
4. \(\mathrm{(A)}\) and \(\mathrm{(C)}\)
Subtopic: Photoelectric Effect: Experiment |
50%
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2025
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
A photon and an electron (mass \(m\)) have the same energy \(E.\) The ratio \((\lambda_{\text{photon}}/\lambda_{\text{electron}})\) of their de Broglie wavelengths is: (\(c\) is the speed of light)
| 1. | \(c\sqrt{\dfrac{2m}{E}}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{1}{c}\sqrt{\dfrac{E}{2m}}\) |
| 3. | \(\sqrt{\dfrac{E}{2m}}\) | 4. | \(c\sqrt{2mE}\) |
Subtopic: De-broglie Wavelength |
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2025
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
If \(c\) is the velocity of light in free space, the correct statements about photons among the following are:
| (A) | The energy of a photon is \(E=h\nu.\) |
| (B) | The velocity of a photon is \(c.\) |
| (C) | The momentum of a photon, \(p={\dfrac{h\nu}{c}}.\) |
| (D) | In a photon-electron collision, both total energy and total momentum are conserved. |
| (E) | Photon possesses a positive electric charge. |
| 1. | (A), (B), (C) and (D) only |
| 2. | (A), (C) and (D) only |
| 3. | (A), (B), (D) and (E) only |
| 4. | (A) and (B) only |
Subtopic: Particle Nature of Light |
64%
Level 2: 60%+
NEET - 2024
Hints
The graph that shows the variation of \({\dfrac{1}{\lambda^2}}\) with the kinetic energy \(E\) (where \(\lambda\) is the de-Broglie wavelength of a free particle) is:
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Subtopic: De-broglie Wavelength |
57%
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2024
Hints
Radiation of wavelength \(280~\text{nm}\) is used in an experiment of photoelectric effect with cathode of work function, \(2.5~\text{eV}.\) The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is:
(take \(h=6.62\times10^{-34}~\text{J s}\) and \(c=3\times10^{8}~\text{ms}^{-1}\))
(take \(h=6.62\times10^{-34}~\text{J s}\) and \(c=3\times10^{8}~\text{ms}^{-1}\))
| 1. | \(4.4~\text{eV}\) | 2. | \(7.103\times10^{-15}~\text{J}\) |
| 3. | \(1.9~\text{eV}\) | 4. | \(4.60~\text{eV}\) |
Subtopic: Einstein's Photoelectric Equation |
76%
Level 2: 60%+
NEET - 2024
Hints
Given below are two statements:
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
| Statement I: | The de Broglie wavelength associated with a material particle depends on its charge and nature. |
| Statement II: | The wave nature of particles in sub-atomic domain is significant and measurable. |
| 1. | Both Statement I and Statement II are correct. |
| 2. | Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect. |
| 3. | Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect. |
| 4. | Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct. |
Subtopic: De-broglie Wavelength |
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2024
Hints
An electron and an alpha particle are accelerated by the same potential difference. Let \(\lambda_\mathrm{e}\) and \(\lambda_\mathrm{\alpha}\) denote the de-Broglie wavelengths of the electron and the alpha particle, respectively, then:
| 1. | \(\lambda_{\mathrm{e}}>\lambda_{\alpha}\) | 2. | \(\lambda_{\mathrm{e}}=4\lambda_{\alpha}\) |
| 3. | \(\lambda_{\mathrm{e}}=\lambda_{\alpha}\) | 4. | \(\lambda_{\mathrm{e}}<\lambda_{\alpha}\) |
Subtopic: De-broglie Wavelength |
71%
Level 2: 60%+
NEET - 2024
Hints
If \(\phi\) is the work function of photosensitive material in electron-volts and light of a wavelength of numerical value \(\lambda=\dfrac{{hc}}{{e}}\) metres is incident on it with energy above its threshold value at an instant, then the maximum kinetic energy of the photo-electron ejected by it at that instant is (in SI units):
(take \(h\) as Plank's constant and \(c\) as the velocity of light in free space)
(take \(h\) as Plank's constant and \(c\) as the velocity of light in free space)
| 1. | \({e}+2\phi \) | 2. | \(2{e}-\phi \) |
| 3. | \({e}-\phi \) | 4. | \({e}+\phi \) |
Subtopic: Einstein's Photoelectric Equation |
81%
Level 1: 80%+
NEET - 2024
Hints
The work functions of Caesium \((\mathrm{Cs}),\) Potassium \((\mathrm{K}),\) and Sodium \((\mathrm{Na})\) are \(2.14~\text{eV},\) \(2.30~\text{eV}\) and \(2.75~\text{eV}\) respectively. If incident electromagnetic radiation has an incident energy of \(2.20~\text{eV},\) which of these photosensitive surfaces may emit photoelectrons?
| 1. | \(\mathrm{Na}\) only | 2. | \(\mathrm{Cs}\) only |
| 3. | both \(\mathrm{Na}\) and \(\mathrm{K}\) | 4. | \(\mathrm{K}\) only |
Subtopic: Photoelectric Effect: Experiment |
68%
Level 2: 60%+
NEET - 2023
Hints






