\(n\) moles of a perfect gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA (see figure) consisting of the following processes.
| \(A\rightarrow B\) | Isothermal expansion at temperature \(T\) so that the volume is doubled from \(V_1\) to \(V_2=2V_1\) and pressure changes from \(P_1\) to \(P_2.\) |
| \(B\rightarrow C\) | Isobaric compression at pressure \(P_2\) to initial volume \(V_1\). |
| \(C\rightarrow A\) | Isochoric change leading to change of pressure from \(P_2\) to \(P_1\). |
Total work done in the complete cycle \(ABCA\) is:
1. \(0\)
2. \(nRT(\ln 2-\frac{1}{2})\)
3. \(nRT\ln 2\)
4. \(nRT(\ln 2+\frac{1}{2})\)
| 1. | \(W_1>W_2\) |
| 2. | \(W_1<W_2\) |
| 3. | \(W_1=W_2\) |
| 4. | \(W_1\) and \(W_2\) cannot be compared unless the temperatures are known. |
| 1. | \({\dfrac{3}{2}}R\) | 2. | \({\dfrac{5}{2}}R\) |
| 3. | \({\dfrac{1}{2}}R\) | 4. | zero |
The quantity of heat required to take a system from \(\mathrm{A}\) to \(\mathrm{C}\) through the process \(\mathrm{ABC}\) is \(20\) cal. The quantity of heat required to go from \(\mathrm{A}\) to \(\mathrm{C}\) directly is:
1. \(20\) cal
2. \(24.2\) cal
3. \(21\) cal
4. \(23\) cal
1. \(166.7\) K
2. \(255.1\) K
3. \(266.7\) K
4. \(367.7\) K
| 1. | \(300\) K | 2. | \(\dfrac{300}{2^{5/3}}\) K |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{300}{2^{2/3}}\) K | 4. | \(600\) K |

1. \(450~\text K\)
2. \(400~\text K\)
3. \(500~\text K\)
4. \(550~\text K\)
In the first case, a Carnot engine operates between temperatures of \(300~\text{K}\) and \(100~\text{K}.\) In the second case, as shown in the figure, two heat engines are connected in series (i.e., the output of the first engine becomes the input for the second engine).
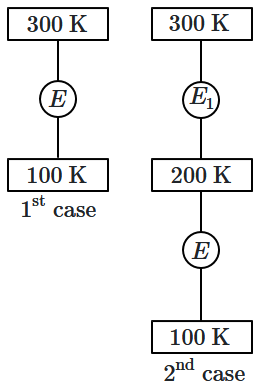
What is the overall efficiency of the combined engine system in the second case?
| 1. | Same as the first case. |
| 2. | Always greater than the first case. |
| 3. | Always less than the first case. |
| 4. | May increase or decrease with respect to the first case. |
The two gases \(A,B\) are allowed to expand adiabatically until their volumes are doubled. The final temperatures are \(\theta_A\) (for gas \(A\)) and \(\theta_B\) (for gas \(B\)). Then:
| 1. | \(\theta_A=\theta_B\) |
| 2. | \(\theta_A<\theta_B\) |
| 3. | \(\theta_A>\theta_B\) |
| 4. | the relationship between \(\theta_A,\theta_B\) depends on the molecular weights of \(A\) and \(B\) |
where \(dQ\) is the heat supplied to the gas and \(T\) is the temperature of the gas. The integral is evaluated over the entire cycle. The value of the integral \(I\) is:
| 1. | zero |
| 2. | negative |
| 3. | positive |
| 4. | non-negative(positive or zero) |








