1. \(60~\text{cm}\)
2. \(24~\text{cm}\)
3. \(30~\text{cm}\)
4. \(-24~\text{cm}\)

1. \({3f}\)
2. \({3\over 2}{f}\)
3. \({f}\)
4. \({2f}\)

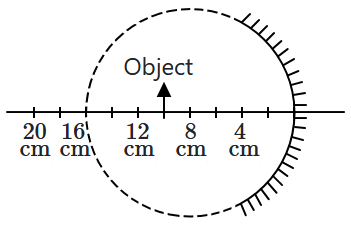
Identify the correct statements.
| A. | The image executes periodic motion |
| B. | The image executes non-periodic motion |
| C. | The turning points of the image are asymmetric w.r.t. the image of the point at \(x = 10~ \text{cm}.\) |
| D. | The distance between the turning points of the oscillation of the image is \(\frac{100} {21} ~\text{cm}.\) |
1. (B) and (C) only
2. (A), (C), and (D) only
3. (A) and (D) only
4. (B) and (D) only
A person wants to use a concave mirror of focal length \(0.4\text{ m}\) to view his face. The mirror produces an upright, magnified image that is five times larger than the actual face. What is the distance (magnitude) from the mirror at which the person should position his face to achieve this magnification?
| 1. | \(1.60~\text{m}\) | 2. | \(0.16~\text{m}\) |
| 3. | \(0.32~\text{m}\) | 4. | \(0.24~\text{m}\) |
A concave mirror with a radius of curvature of \(40~\text{cm}\) is placed at the bottom of a glass container. Water is filled in the container to a depth of \(5~\text{cm}\) above the mirror. A small particle floats on the surface of the water. When an observer looks at the particle from directly above (from air), they see an image at a distance \(d\) below the water surface due to the combined effect of reflection from the mirror and refraction at the water-air interface. The value of \(d\) is: (refractive index of water \(=1.33\))
1. \(11.7~\text{cm}\)
2. \(6.7~\text{cm}\)
3. \(13.4~\text{cm}\)
4. \(8.8~\text{cm}\)
A spherical mirror is obtained as shown in the figure from a hollow glass sphere. If an object is positioned in front of the mirror, what will be the nature and magnification of the image of the object? (Figure drawn as schematic and not to scale)
| 1. | Inverted, real and magnified |
| 2. | Erect, virtual and magnified |
| 3. | Erect, virtual and unmagnified |
| 4. | Inverted, real and unmagnified |
When an object is kept at a distance of \(30~\text{cm}\) from a concave mirror, the image is formed at a distance of \(10~\text{cm}\) from the mirror. If the object is moved with a speed of \(9~\text{cms}^{-1}\), the speed (\(\text{in cms}^{-1}\)) with which image moves at that instant is:
1. \(4\)
2. \(3\)
3. \(2\)
4. \(1\)
1. \(f=+\dfrac{1}{2}r\)
2. \(f=-r\)
3. \(f=-\dfrac{1}{2}r\)
4. \(f=r\)
A short straight object of height \(100\) cm lies before the central axis of a spherical mirror whose focal length has an absolute value \(|f|=40~\text{cm}\). The image of the object produced by the mirror is of height \(25\) cm and has the same orientation as the object. One may conclude from the information:
| 1. | The image is real, on the same side of the concave mirror. |
| 2. | The image is virtual, on the opposite side of the concave mirror. |
| 3. | The image is real, on the same side of the convex mirror. |
| 4. | The image is virtual, on the opposite side of the convex mirror. |
1. \(15~\text{cm}\)
2. \(25~\text{cm}\)
3. \(35~\text{cm}\)
4. \(30~\text{cm}\)







