A block of mass \(m\) is placed on a smooth inclined surface of a wedge of mass \(M\). The system is placed on a smooth horizontal table and released.

| 1. | The acceleration of \(m\) is \(g\sin\theta\), and that of \(M\) is zero. |
| 2. | The acceleration of \(m\) is less than \(g\sin\theta\), and that of \(M\) is to the left. |
| 3. | The acceleration of \(m\) is greater than \(g\sin\theta\), and that of \(M\) is to the left. |
| 4. | Any of the above may be true depending on the values of \(m\) and \(M\). |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
The two blocks are at rest on a smooth horizontal plane and are connected by strings passing over a smooth light pulley as shown. The strings are vertical while the force \(F,\) applied to the pulley is vertical. For what minimum value of \(F\) will the \(2\) kg block be lifted off?
(\(g=10\) m/s2)
| 1. | \(20\) N | 2. | \(30\) N |
| 3. | \(25\) N | 4. | \(40\) N |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
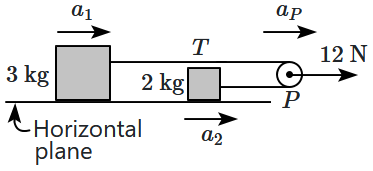
| Column I | Column II | ||
| \(\mathrm{(A)}\) | \(a_1\) | \(\mathrm{(I)}\) | \(2.5\) |
| \(\mathrm{(B)}\) | \(a_2\) | \(\mathrm{(II)}\) | \(2\) |
| \(\mathrm{(C)}\) | \(a_{\Large_P}\) | \(\mathrm{(III)}\) | \(6\) |
| \(\mathrm{(D)}\) | \(T\) | \(\mathrm{(IV)}\) | \(3\) |
| 1. | \(\mathrm{A\text-IV,B\text-III,C\text-II,D\text-I}\) |
| 2. | \(\mathrm{A\text-II,B\text-III,C\text-I,D\text-IV}\) |
| 3. | \(\mathrm{A\text-II,B\text-IV,C\text-I,D\text-III}\) |
| 4. | \(\mathrm{A\text-IV,B\text-II,C\text-III,D\text-I}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(F_1 < F_2\) |
| 2. | \(F_1 = F_2\) |
| 3. | \(F_1 >F_2\) |
| 4. | the relationship between \(F_1\) and \(F_2\) depends on the mass of the cylinder |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

1. \(100~\text N\)
2. \(60~\text N\)
3. \(40~\text N\)
4. \(20~\text N\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | \(45~\text{kg},~50~\text{kg}\) | 2. | \(50~\text{kg},~55~\text{kg}\) |
| 3. | \(47.5~\text{kg},~52.5~\text{kg}\) | 4. | \(45~\text{kg},~45~\text{kg}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(25~\text N\) | 2. | \(50~\text N\) |
| 3. | \(0~\text N\) | 4. | greater than \(100~\text N\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
\((A)\) a man pushes a block along a smooth horizontal plane with a force \(F\) (figure \(\mathrm A\))
\((B)\) a man pulls an identical block along a smooth horizontal plane, applying an equally inclined force \(F\) (figure \(\mathrm B\))

Normal reaction of the plane on the block:
| 1. | is greater in \((A)\) than in \((B)\) |
| 2. | is greater in \((B)\) than in \((A)\) |
| 3. | is equal for \((A)\) and \((B)\) |
| 4. | can be greater, lesser or equal for \(A\) compared to \(B\) depending on the magnitude of \(F.\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| Assertion (A): | When a block is placed on a fixed incline, the reaction of the plane is always smaller than the weight. |
| Reason (R): | The component of the weight of the block acts normal to the incline, and is smaller than the weight. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(T=mg\) | 2. | \(T=2mg\) |
| 3. | \(T={\Large\frac{mg}{2}}\) | 4. | \(T=\text{zero}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.







