Three resistors are connected to a \(20\) V battery with a constant voltage supply. One of the resistors is a variable resistor. The resistance of the variable resistor is gradually increased from \(0~\Omega\) to \(5\) \(\Omega.\)
Which graph correctly represents how the current drawn from the battery varies with the resistance \((R)\) of the variable resistor?
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
The dependence of resistivity \((\rho)\) on the temperature \((T)\) of a semiconductor is, roughly, represented by:
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Which of the following graph represents the variation of resistivity () with temperature (\(T\)) for copper?
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Which of the following \(({I\text-V})\) graphs represents ohmic conductors?
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Figure (i) and figure (ii) both are showing the variation of resistivity \((\rho)\) with a temperature \((T)\) for some materials. Identify the type of these materials.

1. Conductor and semiconductor
2. Conductor and Insulator
3. Insulator and semiconductor
4. Both are conductors
| Assertion (A): | Resistance of a conducting metallic wire depends on the voltage applied across it and current passing through it. |
| Reason (R): | Ohm's law is also valid for semiconductors. |
In the light of the above statements choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |

1. \(T_{1}=T_{2}\)
2. \(T_{2}>T_{1}\)
3. \(T_{1}>T_{2}\)
4. Insufficient information to conclude.

| 1. |  |
2. | 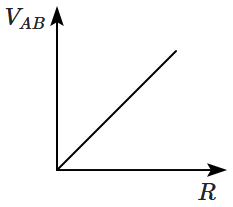 |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
The plot of current \(I~\text{(A)}\) flowing through a metallic conductor versus the applied voltage \(V~\text{(volt)}\) across the ends of a conductor is:
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |







