The number of structural isomers of alcohol of formula C5H12O are:
| 1. | 4 | 2. | 6 |
| 3. | 8 | 4. | 10 |
The number of monohydric phenols that can have the molecular formula, \(\mathrm{C}_7 \mathrm{H}_8 \mathrm{O}\) are:
| 1. | 2 | 2. | 3 |
| 3. | 4 | 4. | 5 |
Propanol has a higher boiling point than that of butane because:
1. Butane undergoes intermolecular ionic bonding
2. Propanol undergoes intermolecular H-bonding
3. Propanol undergoes intramolecular hydrogen bonding
4. Butane undergoes intermolecular H-bonding
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses because:
| 1. | Alcohols form van der waal bonds with water while hydrocarbons do not |
| 2. | Alcohols form covalent bonds with water while hydrocarbons do not |
| 3. | Alcohols form ionic bonds with water while hydrocarbons do not |
| 4. | Alcohols form H-bonds with water while hydrocarbons do not |
The hydroboration-oxidation reaction is:
1. The addition of borane followed by oxidation
2. The addition of propane followed by oxidation
3. The addition of propane followed by reduction
4. The addition of borane followed by reduction
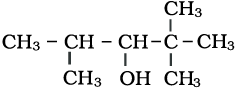
The IUPAC name of the above compound is:
1. 2, 2, 2-Trimethylpentan-3-ol
2. 2, 2, 4-Trimethylpentan-3-ol
3. 2, 2, 3-Trimethylpentan-3-ol
4. 1, 1, 3-Trimethylpentan-3-ol
The IUPAC name of the below compound is:

| 1. | 1-Phenylpropan-2-ol | 2. | 2-Phenylpropan-2-ol |
| 3. | 1-Phenylpropan-1-ol | 4. | 2-Phenylpropan-1-ol |
The IUPAC name of the below compound is:

1. 3,4-Dimethylhexane –1,3,5-triol
2. 3,5-Dimethylhexane –1,1,5-triol
3. 3,5-Dimethylhexane –1,3,5-triol
4. 3,1-Dimethylhexane –1,3,5-triol

The IUPAC name of the above compound is:
| 1. | 4 – Ethoxypropane | 2. | 3 – Ethoxypropane |
| 3. | 1 – Ethoxypropane | 4. | 2 – Ethoxypropane |
The IUPAC name of the following compound is:

1. 1-Ethoxy-3-methylpentane
2. 3-Ethoxy-1-methylpentane
3. 2-Ethoxy-3-methylpentane
4. 3-Ethoxy-2-methylpentane






