Which of the following compounds can form a stable Grignard reagent?
1. a, b, d
2. b, c, a
3. b, d, c
4. None of the above
| a. |  |
b. | 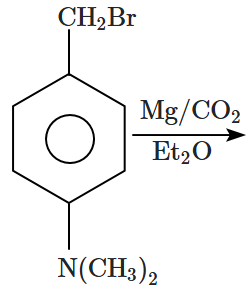 |
| c. |  |
d. |  |
2. b, c, a
3. b, d, c
4. None of the above
Subtopic: Mechanism of Reactions |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
Mark the appropriate reagent used to distinguish vicinal and geminal dihalides.:
| 1. | KOH (aq.) | 2. | KOH(alc.) |
| 3. | Zn dust | 4. | None of these |
Subtopic: Mechanism of Reactions |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
Wurtz reaction is not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing an odd number of carbon atoms because:
| 1. | Boiling points of alkanes obtained in the mixture are very close. |
| 2. | Melting points of alkanes obtained in the mixture are very close. |
| 3. | Lattice energy of alkanes obtained in the mixture are very close. |
| 4. | None of the above. |
Subtopic: Mechanism of Reactions | Chemical Properties |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
What is the major product (A) in the following reaction?

| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Subtopic: Mechanism of Reactions |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly

The product of the above mentioned reaction is:
1.
2.
3.
4. None of the above
Subtopic: Mechanism of Reactions |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints





