Select Question Set:
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
Nickel contributes to the formation of one of the following
1.
urease
2.
dehydrogenase
3.
rubisco protein
4.
nitrate reductase
Subtopic: Enzymes Classification |
Level 3: 35%-60%
AIIMS - 2011
Hints
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
Thiamine (B1) deficiency resuits in
| 1. | Wernickes’ syndromes |
| 2. | Korsakoffs’ syndromes |
| 3. | osteonecrosis |
| 4. | tunnel vission |
Subtopic: Enzyme Cofactors |
63%
Level 2: 60%+
AIIMS - 2009
Hints
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
FAD is a coenzyme derived from
| 1. | riboflavin |
| 2. | vitamin-B12 |
| 3. | thiamine |
| 4. | niacin |
Subtopic: Enzyme Cofactors |
53%
Level 3: 35%-60%
AIIMS - 2009
Hints
Proteins are
| 1. | homopolymer |
| 2. | heteropolymer |
| 3. | homogenous mixture of amino acids |
| 4. | heterogenous mixture of amino acids |
Subtopic: Proteins |
77%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Links
Amino acid is a:
| 1. | Substituted methane |
| 2. | Substituted ethane |
| 3. | Any acid having amino group |
| 4. | Derivative of indol acetic acid |
Subtopic: Introduction to Proteins |
76%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Links
A.
B.
C.
Which of the above is Zwitterionic form?
(1) B
(2) C
(3) A
(4) All are correct
Subtopic: Zwitter ion & Peptide Bond |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
Links
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
The quaternary structure of a protein:
| 1. | Consists of 4 subunits - hence the name quaternary |
| 2. | Is unrelated to the function of the protein |
| 3. | Both (a) and (b) |
| 4. | Depends on the 1° structure of subunits |
Subtopic: Structural Organisation of Proteins |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
Links
Adult human haemoglobin consists of:
| 1. | 2 subunits (β, β) |
| 2. | 2 subunits (α, α) |
| 3. | 4 subunits (2α, 2β) |
| 4. | 3 subunits (2α, 1β) |
Subtopic: Structural Organisation of Proteins |
92%
Level 1: 80%+
Hints
Links
Lecithin is:
(1) Phospholipid
(2) Carbohydrate
(3) Protein
(4) Amino acid
Subtopic: Lipids: Glycerolipids, Phospholipids & Glycerol |
93%
Level 1: 80%+
Hints
Links
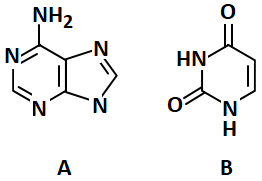
The above diagram represent the nitrogenous bases. Identify the correct combination:
1. A = Adenine; B = Thymine
2. A = Guanine; B = Thymine
3. A = Adenine; B = Uracil
4. A = Guanine; B = Uracil
Subtopic: Double Helix : Watson & Crick Part 1 | Double Helix : Watson & Crick |
77%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Links
Select Question Set:









