The temperature of an open room of volume \(30~\text{m}^3\) increases from \(17^\circ \text{C}\) to \(27^\circ \text{C}\) due to the sunshine. The atmospheric pressure in the room remains \(1\times 10^{5}~\text{Pa}\). In \(n_i\) and \(n_f\) are the number of molecules in the room before and after heating, the \(n_f\text-n_i \) will be:
1. \( -1.61 \times 10^{23} \)
2. \( 1.38 \times 10^{23} \)
3. \( 2.5 \times 10^{25} \)
4. \( -2.5 \times 10^{25}\)

| 1. |  |
3. |  |
| 2. |  |
4. |  |
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process in which pressure and volume are related by the equation:
\(P=P_0\left[1-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{V_0}{V}\right)^2\right] \)
where \(P_0\) and \(V_0\) are constants. If the volume of the gas increases from \(V=V_0\) to \(V=2V_0,\) what is the resulting change in temperature?
1. \( \frac{3}{4} \frac{P_o V_o}{R} \)
2. \(\frac{1}{2} \frac{P_o V_o}{R} \)
3. \(\frac{5}{4} \frac{P_o V_o}{R} \)
4. \(\frac{1}{4} \frac{P_o V_o}{R}\)
Number of molecules in a volume of \(4~\text{cm}^3\) of a perfect monoatomic gas at some temperature \(T\) and at a pressure of \(2~\text{cm}\) of mercury is close to ? (Given, mean kinetic energy of a molecule (at \(T\)) is \(4 \times 10^{-14}\)erg, \(g=980\) cm/s2 , density of mercury = \(13.6~ \text{g/cm}^3\))
1. \( 5.8 \times 10^{18} \)
2. \( 5.8 \times 10^{16} \)
3. \( 4.0 \times 10^{18} \)
4. \( 4.0 \times 10^{16}\)
Initially, a gas of diatomic molecules is contained in a cylinder of volume \(V_1\) at a pressure \(P_1\) and temperature \(250~\text{K}.\) Assume that \(25\%\) of the molecules get dissociated, causing a change in the number of moles. The pressure of the resulting gas at temperature \(2000~\text{K},\) when contained in a volume \(2V_1\) is given by \(P_2.\) The ratio \(P_2/P_1\) is:
1. \(2\)
2. \(3\)
3. \(5\)
4. \(9\)
On the basis of kinetic theory of gases, the gas exerts pressure because its molecules:
| 1. | continuously lose their energy till it reaches wall. |
| 2. | are attracted by the walls of container. |
| 3. | continuously stick to the walls of container. |
| 4. | suffer change in momentum when impinge on the walls of container. |
\(0.76\) g. The ratio of the number of moles of hydrogen to the number of moles of oxygen in the mixture will be:
1. \( 1 \over 3\)
2. \(3 \over 1\)
3. \( 1 \over 16\)
4. \( 16 \over 1\)
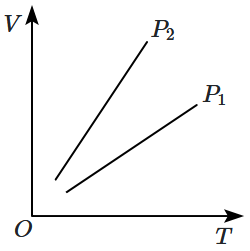
1. \(P_1 > P_2\)
2. \(P_1 < P_2\)
3. \(P_1 = P_2\)
4. Insufficient data to draw any conclusion
1. \(72\times10^{5}\)
2. \(32\times10^{5}\)
3. \(27\times10^{4}\)
4. \(54\times10^{4}\)
1. 2
2. 4
3. 6
4. 8






