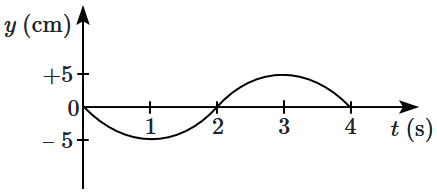Physics
1. The number of possible natural oscillations of the air column in a pipe closed at one end of length \(85\) cm whose frequencies lie below \(1250\) Hz are:
(velocity of sound= \(340~\text{m/s}\))
| 1. |
\(4\) |
2. |
\(5\) |
| 3. |
\(7\) |
4. |
\(6\) |
2. Two dipoles are placed along the
\(x\)-axis, as shown in the figure, in two different configurations:
\(A\) and
\(B.\) Then, they will:

| 1. |
attract in \((A),\) repel in \((B)\) |
| 2. |
repel in \((A),\) attract in \((B)\) |
| 3. |
attract in both \((A)~\text{and}~(B)\) |
| 4. |
repel in both \((A)~\text{and}~(B)\) |
3. A pendulum oscillates about its mean position \(\mathrm{C}.\) The position where the speed of the bob becomes maximum is: (ignore all dissipative forces)

| 1. |
\(\mathrm{A}\) |
2. |
\(\mathrm{B}\) |
| 3. |
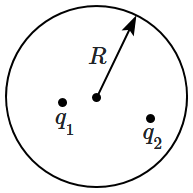
\(\mathrm{C}\) |
4. |
\(\mathrm{D}\) |
4. A positive charge \(Q=1.1\times 10^{-11}~\text{C}\) is located \(10^{-2}\) m away from a negative charge of equal magnitude. Point \(P\) is exactly between them. What is the magnitude of the electric field intensity at the point \(P?\)
1. \(10^3~\text{N/C}\)
2. \(2\times 10^3~\text{N/C}\)
3. \(4\times 10^3~\text{N/C}\)
4. \(8\times 10^3~\text{N/C}\)
5. An electric dipole with dipole moment \(\vec{p}=\left({{3}\hat{i}+{4}\hat{j}} \right)\) C-m, is kept in electric field \(\vec{E}=0.4~{\text{kN}}{/}{\text{C}} \hat{i}\). What is the torque acting on it & the potential energy of the dipole?
1. \(1600\) \(\left({{\text{N}}\times{\text{m}}}\right)\hat{k}\), \(-1200\) J
2. \(-1600\) \(\left({{\text{N}}\times{\text{m}}}\right)\hat{k}\), \(1200\) J
3. \(-1600\) \(\left({{\text{N}}\times{\text{m}}}\right)\hat{k}\), \(-1200\) J
4. \(1600\) \(\left({{\text{N}}\times{\text{m}}}\right)\hat{k}\), \(1200\) J
6. For a particle performing linear SHM, its position
\((x)\) as a function of time
\((t)\) is given by
\(x = A \sin (\omega t + \delta)\). If, at
\(t=0\), particle is at +
\(\dfrac{A}{2}\) and is moving towards
\(x = +A \), then
\(\delta=\)
| 1. |
\(\dfrac{\pi}{3}~ \text{rad}\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac{\pi}{6}~ \text{rad}\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{\pi}{4} ~\text{rad}\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{5\pi}{6}~\text{rad}\) |
7. A sonometer wire supports a \(5\) kg load and vibrates in fundamental mode with a tuning fork of frequency \(420\) Hz. The length of the wire between the bridges is now doubled. In order to maintain fundamental mode with same frequency, the load should be changed to:
1. \(1\) kg
2. \(2\) kg
3. \(8\) kg
4. \(20\) kg
8. A sinusoidal waveform whose displacement is given
by:
\(y(x,t)=(5~\text{mm})\sin2\pi\)\(\large{\Big(\frac{x}{2~\text{m}}+\frac{t}{0.01~\text s}\Big)}\)
propagates along the
\(x\)-axis. The wavelength of the waveform is:
| 1. |
\(\large\frac{2\pi}{2}\)\(~\text m\) |
2. |
\(\large\frac{1}{2}\)\(~\text m\) |
| 3. |
\(\large\frac{2}{2\pi}\)\(~\text m\) |
4. |
\(2~\text m\) |
9. A uniform electric field \(\vec E=3\times10^3\hat i\) N/C interacts with a square surface of \(10~\text{cm}\) side, with its plane parallel to the \(YZ\)-plane. The electric flux through the square is:
1. \(60\) N-m2/C
2. \(30\) N-m2/C
3. \(15\) N-m2/C
4. zero
10. A particle performs SHM with frequency \(f.\) The frequencies of its velocity and acceleration are, respectively:
| 1. |
\(f,~f\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac{f}{2},~f\) |
| 3. |
\(2f,~f\) |
4. |
\(f,~2f\) |
11. Two point charges
\(q_A,q_B\) are placed at the opposite ends
\(A\) &
\(B\) of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle
\(ABC~(\angle C=90^\circ).\) The lengths of the sides are denoted by using the standard notation:
\(l~(AB)=c,l~(BC)=a\) &
\(l~(AC)=b.\) \(O\) is the mid-point of the hypotenuse
\(AB.\)
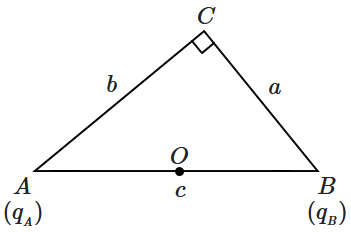
If the electric field at
\(C\) is parallel to
\(AB,\) then (considering the four statements given below):
| (p) |
\(q_{_A},q_{_B}\) are of the same sign |
| (q) |
\(q_{_A},q_{_B}\) are of opposite sign |
| (r) |
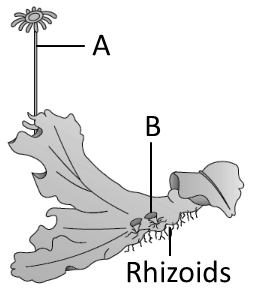
\({\Large\frac{|q_{_A}|}{b}}={\Large\frac{|q_{_B}|}{a}}\) |
| (s) |
\({\Large\frac{|q_{_A}|}{b^3}}={\Large\frac{|q_{_B}|}{a^3}}\) |
1. p & r are true
2. p & s are true
3. q & r are true
4. q & s are true
12. An electric dipole is placed at an angle of
\(30^\circ\) with an electric field intensity
\(2\times10^5~ \text{N/C}\). It experiences a torque equal to
\(4~\text{N-m}\). The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is
\(2~ \text{cm}\), is:
| 1. |
\(8~\text{mC}\) |
2. |
\(2~\text{mC}\) |
| 3. |
\(5~\text{mC}\) |
4. |
\(7~\mu \text{C}\) |
13. A string is stretched between fixed points separated by
\(75.0~\text{cm}\). It is observed to have resonant frequencies of
\(420~\text{Hz}\) and
\(315~\text{Hz}\). There are no other resonant frequencies between these two. The lowest resonant frequency for this string is:
| 1. |
\( 155~\text{Hz} \) |
2. |
\( 205~\text{Hz} \) |
| 3. |
\( 10.5~\text{Hz} \) |
4. |
\( 105~\text{Hz} \) |
14. The figure shows the snapshot of a travelling sine wave in a string. Four elemental portions \(a,b,c\) and \(d\) are indicated on the string. The elemental portion with maximum potential energy is/are:
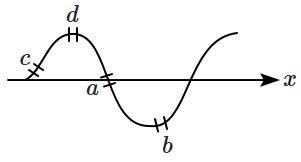
1. \(a\)
2. \(b\)
3. \(c\)
4. \(b \text{ and } d\)
15. A travelling wave pulse is given by the equation;
\(y=\dfrac{4}{3x^2+48 t^2+24xt+2},\)
where \(x\) and \(y\) are in metres and \(t\) is in seconds. The velocity of the wave is:
1. \(4~\text{m/s}\)
2. \(2~\text{m/s}\)
3. \(8~\text{m/s}\)
4. \(12~\text{m/s}\)
16. The electric field inside a uniformly charged thin spherical shell having radius
\(R\) and total charge
\(Q\) is:
(
\( \varepsilon_0\) is the permittivity of free space)
| 1. |
\(\frac{Q}{4\pi \varepsilon_0R^2}\) |
2. |
\(\frac{Q}{4\pi \varepsilon_0R}\) |
| 3. |
zero |
4. |
\(\frac{Q}{2\pi \varepsilon_0R^2}\) |
17. If the electric lines of force in a region are depicted as shown in the figure, one can conclude that the electric field is:

| 1. |
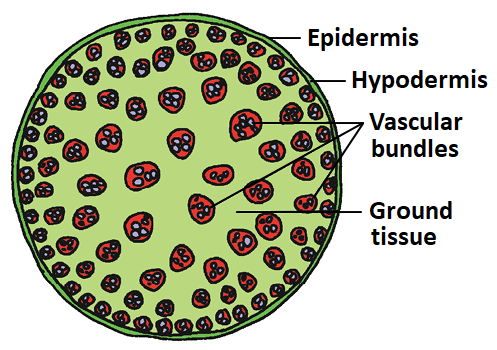
non-uniform |
| 2. |
uniform |
| 3. |
both uniform and non-uniform |
| 4. |
zero everywhere |
18. Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
When an electric dipole is completely enclosed by a closed Gaussian surface, the total electric flux through the surface is zero. |
| Reason (R): |
The net charge enclosed within the surface is zero. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
19. The displacement of a particle varies according to the relation:
\(x=4\left({\cos{\pi t}+\sin{\pi t}}\right) \)
The amplitude of the particle is:
| 1. |
\(8\) |
2. |
\(-4 \) |
| 3. |
\(4\) |
4. |
\(4\sqrt{2} \) |
20. A tuning fork \(\mathrm A\) of unknown frequency produces \(5\) beats per second with a fork of known frequency of \(340\) Hz. When fork \(\mathrm A\) is filed, the beat frequency decreases to \(2\) beats per second. What is the frequency of fork \(\mathrm A\)?
| 1. |
\(342\) Hz |
2. |
\(345\) Hz |
| 3. |
\(335\) Hz |
4. |
\(338\) Hz |
21. A particle undergoes simple harmonic motion, oscillating vertically. The graph of its height
\(y\) as a function of time
\(t\) is provided.
At what time
\(t\) does the particle achieve its maximum positive acceleration?
| 1. |
\(1~\text{s}\) |
2. |
\(2~\text{s}\) |
| 3. |
\(3~\text{s}\) |
4. |
\(4~\text{s}\) |
22. A simple pendulum is vibrating in an evacuated chamber. It will oscillate with:
| 1. |
constant amplitude |
2. |
decreasing amplitude |
| 3. |
increasing amplitude |
4. |
none of these |
23. The phase difference between velocity and displacement in a simple harmonic motion is:
1. \(\pi\)
2. \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
3. \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
4. zero
24. A heavy uniform rope hanging under its own weight from the ceiling of a room, can propagate small disturbances along its length as it is under tension. Let the mass per unit length of the rope be
\(\mu,\) and its total length
\(L.\)

The speed of a wave-like transverse disturbance along the rope is given by
\(\sqrt{\dfrac{T}{\mu}},\) where
\(T\) is the tension at the location. The speed of waves, at a distance
\(x\) from the bottom, is:
| 1. |
\(\sqrt{g(L-x)}\) |
2. |
\(\sqrt{gx}\) |
| 3. |
\(\sqrt{2g(L-x)}\) |
4. |
\(\sqrt{2gx}\) |
25. A clock \(S\) operates based on the oscillations of a spring, while a clock \(P\) operates based on pendulum motion. Both clocks run at the same rate on Earth. On a planet with the same density as Earth but twice the radius, which of the following will be true?
| 1. |
\(S\) will run faster than \(P.\) |
| 2. |
\(P\) will run faster than \(S.\) |
| 3. |
Both will run at the same rate. |
| 4. |
Both will run at the same rate but different from their rates on Earth. |
26. An infinitely long straight line carries a uniform positive charge
\(\lambda\) per unit length. A negative point charge
\((-q)\) moves in a circular path with the charge
\(\lambda\) as its axis, under the action of its electric field. The kinetic energy of the point charge is:

| 1. |
\({\dfrac{q\lambda}{4\pi\varepsilon_0}}\) |
2. |
\({\dfrac{q\lambda}{2\pi\varepsilon_0}}\) |
| 3. |
\({\dfrac{2q\lambda}{\pi\varepsilon_0}}\) |
4. |
\({\dfrac{q\lambda}{8\pi\varepsilon_0}}\) |
27. Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Sound waves cannot propagate through a vacuum but light waves can. |
| Reason (R): |
Sound waves cannot be polarised but light waves can be. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
28. If the displacement
\((x)\) and velocity
\((v)\) of a particle executing simple harmonic motion are related by the expression
\(4v^2=25-x^2,\) then its time period is:
| 1. |
\(\mathit{\pi}\) |
2. |
\({2}\mathit{\pi}\) |
| 3. |
\({4}\mathit{\pi}\) |
4. |
\({6}\mathit{\pi}\) |
29. An uncharged spherical conducting shell of outer
radius \(R\) has two point charges
\(q_1,q_2\) placed within it. The flux of the electric field due to all charges from the outer surface of the sphere is
\(\phi_0\) while the potential of the sphere is
\(V_0.\) The ratio
\(\dfrac{\phi_0}{V_0}\) is proportional to:
| 1. |
\(\sqrt R\) |
2. |
\(R\) |
| 3. |
\(R^2\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{1}{R^2}\) |
30. The wire of a sonometer \(180\) cm long is divided into three parts by two bridges. The fundamental frequencies of the parts are in the ratio \(3:4:6.\) The positions of bridges are:
1. \(41.5, 97\) cm
2. \(80, 140\) cm
3. \(50, 120\) cm
4. \(30,140\) cm
31. A
\(100\) cm wire of mass
\(40\) g is fixed at both ends. A tuning fork, vibrating at a frequency of
\(50\) Hz, sets the wire into resonance in its fundamental mode. Then, the tension in the wire is:
| 1. |
\(400\) N |
2. |
\(100\) N |
| 3. |
\(25\) N |
4. |
\(1600\) N |
32. A spring has spring constant
\(400\) N/m. When mass of
\(M\) kg is attached to it and the other end is fixed to the ceiling, it executes simple harmonic motion with a frequency
\(f.\) The spring is cut into four equal parts, and all the parts are placed side by side and hung from the same point, with the same mass attached to the other end (as shown in the figure). The new frequency of oscillation will be:
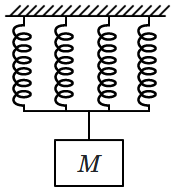
| 1. |
\(f\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac{f}{2}\) |
| 3. |
\(2f\) |
4. |
\(4f\) |
33. Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
In simple harmonic motion, the velocity is maximum when the displacement is minimum. |
| Reason (R): |
Displacement and velocity of simple harmonic motion differ in phase by \(\pi /2.\) |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
34. A block connected to a spring undergoes a displacement given by: \(x=(2~\text{cm})\sin\big\{(5~\text s^{-1})t+{\large\frac{\pi}{6}}\big\}~\)
The time period of the motion is:
1. \(5~\text{s}\)
2. \(10~\text{s}\)
3. \(\large\frac{5}{2\pi}\)\(~\text{s}\)
4. \(\large\frac{2\pi}{5}\)\(~\text{s}\)
35. A toy car with charge \(q\) moves on a frictionless horizontal plane surface under the influence of a uniform electric field \(\vec {E}.\) Due to the force \(q\vec {E},\) its velocity increases from \(0\) to \(6~\text{m/s}\) in a one-second duration. At that instant, the direction of the field is reversed. The car continues to move for two more seconds under the influence of this field. The average velocity and the average speed of the toy car between \(0\) to \(3\) seconds are respectively:
| 1. |
\(2~\text{m/s}, ~4~\text{m/s}\) |
2. |
\(1~\text{m/s}, ~3~\text{m/s}\) |
| 3. |
\(1~\text{m/s}, ~3.5~\text{m/s}\) |
4. |
\(1.5~\text{m/s},~ 3~\text{m/s}\) |
36. A spring pendulum is placed on a rotating table. The initial angular velocity of the table is \(\omega_{0}\) and the time period of the pendulum is \(T_{0}.\) If the the angular velocity of the table becomes \(2\omega_{0},\) then the new time period of the pendulum will be:
| 1. |
\(2T_{0}\) |
2. |
\(T_0\sqrt{2}\) |
| 3. |
the same |
4. |
\(\dfrac{T_0}{\sqrt{2}}\) |
37. A block is suspended from a spring and allowed to oscillate vertically, giving a time period
\(T.\) If the block is suspended from the same spring, the elongation produced will be:
| 1. |
\(\dfrac12gT^2\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac14gT^2\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{1}{2\pi}gT^2\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{1}{4\pi^2}gT^2\) |
38. A string \(180~\text{cm}\) long resonates in three segments with transverse waves produced by a \(270~\text{Hz}\) vibrator. What is the speed of the waves on the string?
1. \(162~\text{m/s}\)
2. \(324~\text{m/s}\)
3. \(364~\text{m/s}\)
4. \(374~\text{m/s}\)
39. A small point mass carrying a positive charge is released from the edge of a table. There is a uniform electric field in the horizontal direction. Which of the following options correctly describes the trajectory of the mass?
(The curves are drawn schematically and are not to scale).

40. A tuning fork vibrates at a frequency of \(256\) Hz. What would be the minimum length of a closed organ pipe that resonates with the tuning fork?
(take the speed of sound in air \(=360\) ms-1)
1. \(35.1\) cm
2. \(38.1\) cm
3. \(70.2\) cm
4. \(82.2\) cm
41. Consider the force \(F\) on a charge \(q\) due to a uniformly charged spherical shell of radius \(R\) carrying charge \(Q\) distributed uniformly over it. Which one of the following statements is true for \(F\), if \(q\) is placed at a distance \(r\) from the centre of the shell?
| 1. |
\( F=\dfrac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_0} \dfrac{Q q}{r^2} \text { for } r>R \) |
| 2. |
\( \dfrac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_0} \dfrac{Q q}{R^2}>F>0 \text { for } r<R \) |
| 3. |
\( F=\dfrac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_0} \dfrac{Q q}{r^2} \text { for all } r \) |
| 4. |
\(F=\dfrac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_0} \dfrac{Q q}{r^2} \text { for } r<R \) |
42. A charge of
\(10~\mathrm{\mu C}\) is placed at the origin. Where should a charge of
\(40~\mathrm{\mu C}\) be placed on the
\(x\text-\)axis so that the electric field at
\(x = 2\) units is zero?
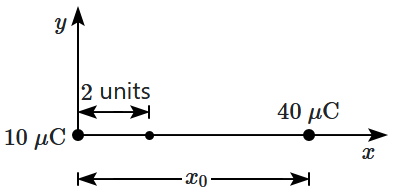
| 1. |
\(-2\) units |
2. |
\(4\) units |
| 3. |
\(6\) units |
4. |
\(2\) units |
43. When sound waves produced under water emerge into the air, then:
| 1. |
the frequency increases, and wavelength decreases. |
| 2. |
the frequency remains constant, but the wavelength decreases. |
| 3. |
the frequency decreases, wavelength remains constant. |
| 4. |
the frequency remains constant but the wavelength increases. |
44. The displacement of a particle executing simple harmonic motion is given by,
\(x=(6+6 ~\mathrm{sin} ~\omega t+8~\mathrm{cos} ~\omega t)~\text{m}.\)
The amplitude of its oscillation is:
1. \(10\) m
2. \(16\) m
3. \(20\) m
4. \(14\) m
45. Two different sources of sound having slightly different periods of vibration: \(1~\text{ms}\) and \(1.01~\text{ms},\) are sounded together. The resulting beat frequency is nearly:
1. \(100~\text{Hz}\)
2. \(50~\text{Hz}\)
3. \(10~\text{Hz}\)
4. \(0.01~\text{Hz}\)
Chemistry
46. Select the correct order of magnitudes of the first electron gain enthalpy from the options provided:
1. Cl < F
2. O < S
3. Te < O
4. S < Se
47. Which of the following pairs is incorrect?
|
A |
B |
| 1. |
Snowfall |
Exothermic process |
| 2. |
Expansion of an ideal gas at constant temperature |
\(\Delta U=0 \) |
| 3. |
State of equilibrium |
\(\Delta G_{T,P} =0 \) |
| 4. |
Entropy change of a reaction at 0 K is equal to zero |
Third law of thermodynamics |
48. At 300K, \(\Delta rG \) and \(\Delta rG^\circ \) are - 12.8 KJ mol-1 and -11.5 KJ mol-1 respectively for the following reaction:
\(A(g) + B(g) \rightleftharpoons C(l) + D(aq)\)
If the reaction is at equilibrium, then the equilibrium constant K will be:
1. \(-2.0 \times 10^0\)
2. \(1.0 \times 10^2\)
3. \(1.0 \times 10^{-2}\)
4. \(1.69 \times 10^0\)
49. The species that by definition has zero standard molar enthalpy of formation at 298 \(K\) is:
1. \( \mathrm{Br}_2(\mathrm{~g})\)
2. \( \mathrm{Cl}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \)
3. \( \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g}) \)
4. \( \mathrm{CH}_4(\mathrm{~g}) \)
50. The species Ar, K+ and Ca2+ contain the same number of electrons. In which order do their radii increase?
1. Ar < K+ < Ca2+
2. Ca2+ < Ar < K+
3. Ca2+ < K+ < Ar
4. K+ < Ar < Ca2+
51. Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Electron gain enthalpy of oxygen is more than that of sulphur. |
| Reason (R): |
Oxygen is more electronegative than sulphur. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is False but (R) is True. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
52. Calcium reacts with element X to form an ionic compound. If the ground-state electron configuration
of X is
\(1 s^2 2 s^2 2 p^4,\) what is the simplest formula for this compound?
| 1. |
\(\mathrm{CaX}\) |
2. |
\(\mathrm{CaX}_2 \) |
| 3. |
\(\mathrm{Ca}_4 X_2\) |
4. |
\(\mathrm{Ca}_2 \mathrm{X}_2\) |
53. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the element Unununium?
1. It is an inner transition element.
2. It belongs to the 8th period in the periodic table.
3. It is a transition element.
4. It is a non-transition element.
54. The electronic configuration of palladium is:
1. \([Ar]4d^95s^1\)
2. \([Kr]4d^85s^2\)
3. \([Kr]4d^86s^2\)
4. \([Kr]4d^{10}5s^0\)
55. Given the following standard heats of formation:
\(\begin{aligned} &\Delta_f H^{\ominus} \mathrm{P}_4 \mathrm{O}_{10}(s)=-3110 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol} \\ & \Delta_f H^{\ominus} \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(l)=-286 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol} \\ &\Delta_f H^{\ominus}\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_4(s)=-1279 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol} \end{aligned}\)
Calculate the change in enthalpy (
\(\Delta_r H^{\ominus}\)) for the following reaction:
\(\mathrm{P}_4 \mathrm{O}_{10}(s)+6 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(l) \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_4(s)\)
| 1. |
\(-290 \mathrm{~kJ}\) |
2. |
\(-1128 \mathrm{~kJ}\) |
| 3. |
\(-2117 \mathrm{~kJ}\) |
4. |
\(-3547 \mathrm{~kJ}\) |
56.
| Assertion (A): |
Oxygen has less negative electron gain enthalpy than sulphur. |
| Reason (R): |
The electronegativity of oxygen is higher than that of sulphur. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True, but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
(A) is False, but (R) is True. |
57. Given the following reaction:
Bond energy of is , and respectively. The enthalpy change for the above reaction will be:
1.
2.
3.
4.
58. Which of the following elements is an unreactive metal?
| 1. |
Chlorine |
2. |
Gold |
| 3. |
Sodium |
4. |
Radon |
59. The ion having the highest value of ionic radius among the following is:
1. Li+
2. B3+
3. O2-
4. F-
60. A fixed mass '
\(m\)' of a gas is subjected to the transformation of states from
\(K\) to
\(L,\) \(L\) to
\(M,\) then
\(M\) to
\(N,\) and back to
\(K\) as shown in the figure:
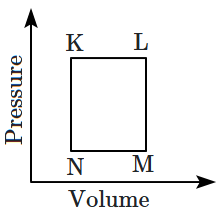
The succeeding operations that enable this transformation of states are:
1. Heating, cooling, heating, cooling
2. Cooling, heating, cooling, heating
3. Heating, cooling, cooling, heating
4. Cooling, heating, heating, cooling
61. Which option contains an inaccurate trend regarding periodic properties?
| 1. |
The Electronegativity of elements increases when moving from left to right in the periodic table. |
| 2. |
Ionisation enthalpy decreases in a group from top to bottom. |
| 3. |
Non-metallic character increases in moving from left to right in a period. |
| 4. |
Metallic character increases in moving from left to right in a period. |
62. Match the following reactions in
Column-I to the correct enthalpy associated with them given in
Column-II:
|
Column-I |
|
Column-II |
| A. |
\(\small{C_6H_6(l)+\frac{15}{2}O_2\rightarrow6CO_2(g)+3H_2O(l)}\) |
I. |
\(\Delta_{\text{lattice}}H^\circ\) |
| B. |
\(NaCl(s)\rightarrow Na^+(g)+Cl^-(g) \) |
II. |
\(\Delta_{\text{hyd}}H^\circ\) |
| C. |
\(AB(s)\rightarrow A^+(aq)+B^-(aq) \) |
III. |
\(\Delta_\text cH^\circ \) |
| D. |
\(\small{A^+(g)+B^-(g)\rightarrow A^+(aq)+B^-(aq)}\) |
IV. |
\(\Delta_{\text{sol}}H^\circ \) |
Choose the correct option from the following:
1. A - (III); B - (I); C - (IV); D - (II)
2. A - (III); B - (I); C - (II); D - (IV)
3. A - (II); B - (I); C - (IV); D - (III)
4. A - (III); B - (II); C - (I); D - (IV)
63. Match
Column-I with
Column-II and mark the appropriate choice:
|
Column-I
(Atomic number) |
|
Column-II
(Block) |
| (A) |
62 |
(i) |
d-block |
| (B) |
47 |
(ii) |
p-Block |
| (C) |
56 |
(iii) |
f-block |
| (D) |
53 |
(iv) |
s-block |
Codes:
1. (A) →(iii), (B)→(i), (C) →(iv), (D)→ (ii)
2. (A) →(i), (B)→(ii), (C) →(iii), (D)→ (iv)
3. (A) →(ii), (B)→(iv), (C) →(i), (D)→ (iii)
4. (A) →(iv), (B)→(i), (C) →(ii), (D)→ (iii)
64. Mark the correct observation regarding the entropy of freezing of water in a glass.
| 1. |
\(\Delta S_{system}\) decreases but \(\Delta S_{surroundings}\) remains the same |
| 2. |
\(\Delta S_{system}\) increases but \(\Delta S_{surroundings}\) decreases |
| 3. |
\(\Delta S_{system}\) decreases but \(\Delta S_{surroundings}\) increases |
| 4. |
\(\Delta S_{system}\) decreases but \(\Delta S_{surroundings}\) also decreases |
65. Factor among the following that does not affect the ionization enthalpy of an element is:
1. Effective nuclear charge
2. Atomic radius
3. Half-filled and completely filled sub-shell
4. Atomic number
66. Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Variables like P, V, and T are called state functions. |
| Reason (R): |
Their values depend solely on the system's state, and not on how it is reached.
|
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
67. For the spontaneous process at 268 K, the correct option is:
1.
2.
3.
4.
68. A piston filled with \(0.04 \mathrm{~mol}\) of an ideal gas expands reversibly from \(50.0 \mathrm{~mL}\) to \(375 \mathrm{~mL}\) at a constant temperature of \(37.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). As it does so, it absorbs \(208 \mathrm{~J}\) of heat. The values of \(q\) and \(w\) for the process will be:
\((\mathrm{R}=8.314 \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{mol} \mathrm{K})(\ln 7.5=2.01)\)
1. \( q=+208 J, w=-208 J \)
2. \( q=-208 J, w=-208 J \)
3. \( q=-208 J, w=+208 J\)
4. \( q=+208 J, w=+208 J \)
69. What is the boiling point of the liquid at 1 atm if the enthalpy of vaporization of a liquid is 30 \(\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}\) and entropy of vaporization is 75 \( \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}\)?
1. 250 \(K\)
2. 400 \(K\)
3. 450 \(K\)
4. 600 \(K\)
70. Identify the incorrect statement:
| 1. |
The oxidation state and coordination number (or covalency) of \(\mathrm{Al}\) in\( \left[\mathrm{AlCl}\left(\mathrm{{H}_2 {O}}\right)_5\right]^{2+} \) are +3 and 6, respectively. |
| 2. |
\(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{O}\) is a basic oxide and \(\mathrm{Cl}_2 \mathrm{O}_7\) is an acidic oxide |
| 3. |
The following four species are called isoelectronic species: \( \mathrm{O}^{2-}, \mathrm{F}^{-}, \mathrm{Na}^{+} \mathrm{and}~ \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}\) |
| 4. |
Among the four species \(\mathrm{Mg}, \mathrm{Al}, \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}\) and \(\mathrm{A l^{3+},}\) the smallest one is \(\mathrm{Al}.\) |
71. The value
\(|\Delta H| \) in kJ for the given reaction is:
\(\frac{1}{2} C l_2(g) → C l^{-}(a q) \)
(Given:
\(\Delta H_{\text {diss }} C l_2(g) → 2 C l(g) \quad 240 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{mol}^{-1} \)
\(\Delta H_{eg} Cl(g) + e^- → Cl^-(g) -320~ \mathrm{ kJmol}^{-1}\\ \Delta H_{hydration} Cl^-(g) + aq → Cl^-(aq) -340~\mathrm{ kJmol}^{-1} ) \)
| 1. |
540 |
2. |
620 |
| 3. |
450 |
4. |
470 |
72. Which of the following is not a state function?
| 1. |
H (Enthalpy) |
2. |
Q (Heat) |
| 3. |
S (Entropy) |
4. |
E (Internal Energy) |
73. Match the elements in Column I with their corresponding types in Column II.
|
Column I |
|
Column II |
| (a) |
Copper |
(i) |
Non-metal |
| (b) |
Fluorine |
(ii) |
Transition metal |
| (c) |
Silicon |
(iii) |
Lanthanoid |
| (d) |
Cerium |
(iv) |
Metalloid |
Identify the correct match:
1. (a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
2. (a)-(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
3. (a)-(iv), (b)-(iii), (c)-(i), (d)-(ii)
4. (a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv)
74. In which of the following processes entropy increases?
| A. |
A liquid evaporates to vapour. |
| B. |
Temperature of a crystalline solid lowered from \(130~\text{K}\) to \(0~\text{K}.\) |
| C. |
\(2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3(\mathrm{~s})} \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_{3(\mathrm{~s})}+\mathrm{CO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{g})}\) |
| D. |
\(\mathrm{Cl}_{2(\mathrm{~g})} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{g})}\) |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| 1. |
\(\text { A, B and D }\) |
2. |
\(\text { A, C and D }\) |
| 3. |
\(\text { C and D }\) |
4. |
\(\text { A and C }\) |
75. The heats of combustion of C, H
2, and C
2H
6 are -94 Kcal, -68 Kcal, and -372 Kcal, respectively. The enthalpy of the formation of C
2H
6 will be:
| 1. |
+20 K cal |
2. |
-40 K cal |
| 3. |
-20 K cal |
4. |
+40 K cal |
76. Identify the INCORRECT match.
|
Name |
|
IUPAC Official Name |
| a. |
Unnilunium |
(i) |
Mendelevium |
| b. |
Unniltrium |
(ii) |
Lawrecium |
| c. |
Unnilhexium |
(iii) |
Seaborgium |
| d. |
Unununnium |
(iv) |
Darmstadtium |
| 1. |
(b)- (ii) |
2. |
(c)- (iii) |
| 3. |
(d) -(iv) |
4. |
(a)- (i) |
77. The enthalpy of fusion of water is 1.435 kcal/mol. The molar entropy change for the melting of ice at 0 oC is:
| 1. |
10.52 cal/(mol K) |
2. |
21.04 cal/(mol K) |
| 3. |
5.260 cal/(mol K) |
4. |
0.526 cal/(mol K) |
78. The standard enthalpy of vaporization for water at 100 oC is 40.66 kJ mol–1. The internal energy of vaporization of water at 100 oC (in kJ mol–1) is:
(Assume water vapour behaves like an ideal gas.)
| 1. |
+37.56 |
2. |
–43.76 |
| 3. |
+43.76 |
4. |
+40.66 |
79. Which of the following oxide is basic in nature?
| 1. |
SiO2 |
2. |
CaO |
| 3. |
Al2O3 |
4. |
SO2 |
80. The heat required (in kJ) to raise the temperature of 54 g of Al from 30 °C to 50 °C is:
(Given: Molar heat capacity of Al is 24 J K-1 mol-1)
1. 960
2. 0.73
3. 0.96
4. 9.25
81. Which among the following species has the highest ionization potential?
1. \(F^-\)
2. \(Cl^-\)
3. \(O^-\)
4. \(S^-\)
82. Which of the following represents the correct ground-state electronic configuration of a gas-phase Mn2+ ion?
1. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5
2. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2
3. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d7
4. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 4s2
83. Which of the following statements is correct for a spontaneous process?
1. The entropy of the system always increases.
2. The free energy of the system always increases.
3. The total entropy change is always negative.
4. The total entropy change is always positive.
84. Given the following reaction:
\(\mathrm{Ag}_2 \mathrm{O}(s) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Ag}(s)+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_2(g)\)
The values of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) are 30.56 kJ/mol and 66.00 J/Kmol, respectively.
The temperature at which the free energy change (\(\Delta G\)) for the reaction will be zero is:
1. 563 K
2. 463 K
3. 403 K
4. 544 K
85. If the ionic radii of K
+ and F
- are nearly the same (i.e., 1.34 Å), what are the atomic radii of K and F respectively?
| 1. |
1.34 , 1.34 |
2. |
0.72 , 1.96 |
| 3. |
1.96 , 0.72 |
4. |
1.96 , 1.34 |
86. For the reaction:
\(\mathrm{X}_2 \mathrm{O}_4(l) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{XO}_2(g)\)
with the given values \(\Delta U = 2.1 \, \text{kcal}\) and \(\Delta S = 20 \, \text{cal K}^{-1}\) at \(300 \, \text{K}\), what is the value of \(\Delta G\)?
1. +2.7 kcal
2. –2.7 kcal
3. +9.3 kcal
4. –9.3 kcal
87.
| Statement I: |
Elements like He, Ne, and Nitrogen show positive electron gain enthalpies. |
| Statement II: |
The formation of Cl- from Cl and O2- from O- are exothermic processes. |
1.
Statement I is correct;
Statement II is incorrect.
2.
Statement I is correct;
Statement II is correct.
3.
Statement I is incorrect;
Statement II is incorrect.
4.
Statement I is incorrect;
Statement II is correct.
88. Which of the following sequences accurately represents the correct order?
1. F>N>C>Si>Ga - non-metallic character
2. F>O>Cl >N - oxidising property
3. C<Si>P>N - electron affinity value
4. All of the above
89. The atomic number of Unnilunium is-
1. 111
2. 110
3. 101
4. 107
90. Match Column I (Reactions) with Column II (Enthalpy) and mark the appropriate choice:
|
Column I (Reactions) |
|
Column II (Enthalpy) |
| (A) |
\(\small{CH_{4(g)} + 2O_{2(g)} \rightarrow CO_{2(g)} + 2H_2O}\) |
(i) |
\(\Delta _{sol}H^o\) |
| (B) |
\( H_{2(g)} \rightarrow 2H_{(g)}\) |
(ii) |
\(\Delta _{lattice}H^o\) |
| (C) |
\(NaCl_{(s)} \rightarrow Na^+_{(g)} + Cl^-_{(g)} \) |
(iii) |
\(\Delta _{c}H^o\) |
| (D) |
\(NaCl_{(s)} \rightarrow Na^+_{(aq)} + Cl^-_{(aq)} \) |
(iv) |
\(\Delta _{bond}H^o\) |
1. (A) →(iv), (B)→(iii), (C) →(i), (D)→ (ii)
2. (A) →(ii), (B)→(i), (C) →(iv), (D)→ (iii)
3. (A) →(i), (B)→(ii), (C) →(iii), (D)→ (iv)
4. (A) →(iii), (B)→(iv), (C) →(ii), (D)→ (i)
Biology
91. Which event marks the beginning of anaphase I?
1. Separation of sister chromatids.
2. Splitting of centromeres.
3. Disintegration of the nuclear membrane.
4. Separation of homologous chromosomes.
92. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
According to Oparin, the chemical composition of the primordial environment was oxidising, consisting of oxygen and ozone and excluding methane, ammonia, free hydrogen and water vapour. |
| Reason (R): |
Oparin of Russia proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules and that formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution. |
| 1. |
(A) is False but (R) is True |
| 2. |
(A) is True but (R) is False |
| 3. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A) |
93. Consider the given two statements:
| Statement I: |
Meiosis is the mechanism by which conservation of specific chromosome number of each species is achieved across generations in sexually reproducing organisms. |
| Statement II: |
Meiosis results in reduction of chromosome number by half. |
| 1. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is correct; Statement II does not explain Statement I. |
| 2. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is correct; Statement II explains Statement I. |
| 3. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect |
| 4. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct |
94. In an isobilateral leaf:
| I: |
the stomata are present on both the surfaces of the epidermis |
| II: |
the mesophyll is not differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
95. The type of natural selection that operates to eliminate intermediate phenotypes in a population is known as:
| 1. |
Directional selection |
2. |
Disruptive selection |
| 3. |
Stabilizing selection |
4. |
Reverse selection
|
96. An interesting example of fungus that is also used as a fungicide is:
1. Trichoderma harzianum
2. Botrytis cinerea
3. Fusarium graminearum
4. Penicillium camemberti
97. Anatomical features of a dorsiventral leaf include:
| 1. |
Parallel venation and a single layer of palisade cells. |
| 2. |
Differentiated upper and lower epidermis, with the upper epidermis being thicker. |
| 3. |
Undifferentiated mesophyll and scattered vascular bundles. |
| 4. |
Differentiated mesophyll into palisade and spongy tissues. |
98. Identify the correct description of the structure shown in the given figure:

| 1. |
It shows stomatal apparatus of almost all plants except grasses where A represents guard cells and B represents subsidiary cells. |
| 2. |
It shows stomatal apparatus of almost all plants except grasses where A represents subsidiary cells and B represents guard cells. |
| 3. |
It shows stomatal apparatus of grasses where A represents subsidiary cells and B represents guard cells. |
| 4. |
It shows stomatal apparatus of grasses where A represents guard cells and B represents subsidiary cells. |
99. Which microbe is responsible for the holes and flavour in Swiss cheese?
1. Lactobacillus acidophilus
2. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
3. Propionibacterium shermanii
4. Aspergillus niger
100. The Neanderthal man was characterized by:
| 1. |
A brain capacity larger than that of modern humans. |
| 2. |
The use of sophisticated tools and the development of language. |
| 3. |
Erect posture and a brain capacity smaller than that of modern humans. |
| 4. |
A nomadic lifestyle with the use of simple stone tools. |
101. The leafy stage in the life cycle of mosses:
| 1. |
is a stage of the sporophytic generation. |
| 2. |
is a creeping, green, branched and frequently filamentous stage. |
| 3. |
develops directly from a spore. |
| 4. |
bears sex organs. |
102. After cytokinesis in a plant cell, which of the following is formed first?
| 1. |
The primary cell wall |
| 2. |
The middle lamella |
| 3. |
The secondary cell wall |
| 4. |
There is no particular chronology |
103. Select the mismatch
| 1. |
Cycas - Dioecious |
2. |
Salvinia - Heterosporous |
| 3. |
Equisetum - Homosporous |
4. |
Pinus - Dioecious |
104. Trichoderma has been used for the production of a/an:
1. Anticoagulant
2. Thrombolytic
3. Immunosuppressant
4. Blood glucose lowering drug
105. During Anaphase I of Meiosis I:
| 1. |
sister chromatids move toward opposite poles |
| 2. |
homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles |
| 3. |
homologues move toward the same pole |
| 4. |
homologous chromosomes move randomly toward either pole |
106. Study the given figure and select the correct statement/s:
| A: |
It is the male thallus of Marchantia. |
| B: |
A is antheridiophore and B are gemma cups. |
1. Only
A
2. Only
B
3. Both
A and
B
4. Neither
A nor
B
107. Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) is used as an indicator of water pollution. What does a high BOD value indicate about a water sample?
| 1. |
The water is low in organic matter and is safe for drinking. |
| 2. |
There is a high amount of organic waste, leading to increased microbial oxygen consumption. |
| 3. |
The oxygen levels in the water are high, supporting aquatic life. |
| 4. |
The water has no microbial activity, making it free from contamination. |
108. A cell decides not to divide and enters the Quiescent Stage (G0) exiting the cell cycle from:
1. G1 phase
2. S phase
3. G2 phase
4. M phase
109. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Lichens can be used as industrial pollution indicators. |
| Reason (R): |
Lichens grow profusely in polluted areas. |
| 1. |
(A) is True but (R) is False |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) |
| 3. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A) |
| 4. |
(A) is False but (R) is True |
110. Which of the following is an example of stabilizing selection?
| 1. |
Favors individuals with extreme traits |
| 2. |
Favors intermediate traits and selects against extreme traits |
| 3. |
Favors new mutations |
| 4. |
Favors both extremes of a trait |
111. Which of the following animals called evolved into the first amphibians that lived on both land and water?
1. Lobe fish
2. Cynagnathous
3. Seymouria
4. Megalodon
112. All the following are benefits of mycorrhizal association to vascular plants except:
1. Increasing its tolerance to drought
2. Enhancing its resistance to root pathogens
3. Enhancing its phosphorus uptake capacity
4. Biological nitrogen fixation
113. Consider the given statements:
| Statement I: |
Meiosis II resembles mitosis in its separation of sister chromatids. |
| Statement II: |
Meiosis II does not involve the formation of spindle fibers. |
| 1. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect |
| 2. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is correct |
| 3. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct |
| 4. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is incorrect |
114. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Collenchyma cells provide structural support to growing parts of the plant such as young stems and petioles. |
| Reason (R): |
Collenchyma cells have thickened secondary cell walls that are lignified. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False |
115. Majority of human newborns weigh around 7 pounds. What type of natural selection might be operative here?
1. directional
2. stabilizing
3. disruptive
4. reverse
116. Which of the following statements correctly describes an event that occurs during mitosis?
| 1. |
During prophase, the nuclear envelope reforms around the separated chromosomes. |
| 2. |
In metaphase, chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane, attached to spindle fibers from opposite poles. |
| 3. |
Telophase is characterized by the replication of DNA in preparation for cell division. |
| 4. |
Anaphase involves the breakdown of the nuclear membrane, allowing chromosomes to move freely in the cytoplasm. |
117. Which structure is responsible for the initiation of lateral roots and vascular cambium during secondary growth in dicot roots?
1. Cortex
2. Endodermis
3. Pericycle
4. Epiblema
118. Monascus purpureus is the yeast used commercially in the production of:
| 1. |
Ethanol |
| 2. |
Streptokinase for removing clots from the blood vessels |
| 3. |
Citric acid |
| 4. |
Blood cholesterol-lowering statins |
119. Which of the following statements correctly describes the role of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in enriching soil nitrogen content?
| 1. |
Symbiotic bacteria like Rhizobium fix atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds inside root nodules, while free-living bacteria like Azospirillum and Azotobacter independently fix nitrogen in the soil. |
| 2. |
Free-living nitrogen fixers like Azospirillum and Azotobacter depend on leguminous plants to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form. |
| 3. |
All nitrogen-fixing bacteria require a host plant for nitrogen fixation, as no bacteria can fix nitrogen independently. |
| 4. |
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen directly into nitrates, which are readily absorbed by plants. |
120. A high value of BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) indicates that:
| 1. |
water is pure |
| 2. |
water is highly polluted |
| 3. |
water is less polluted |
| 4. |
consumption of organic matter in the water is higher by the microbes |
121. Which of the following statement is not true for stomatal apparatus?
| 1. |
Guard cells invariably possess chloroplasts and mitochondria |
| 2. |
Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells |
| 3. |
Stomata are involved in gaseous exchange |
| 4. |
Inner walls of guard cells are thick |
122. What is a characteristic feature of the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
| 1. |
DNA replication occurs. |
| 2. |
Chromosomes are visible under a light microscope. |
| 3. |
The cell undergoes division. |
| 4. |
The cell grows in size and synthesizes mRNA and proteins. |
123. Which of the following is not true regarding comparison between the gymnosperms Pinus and Cycas?
|
Character |
Pinus |
Cycas |
| 1. |
Root symbiotic association |
Mycorrhiza |
Cyanobacteria |
| 2. |
Stem |
Branched |
Unbranched |
| 3. |
Reproductive parts |
Dioecious |
Monoecious |
| 4. |
Scale leaves |
Fall off as branches mature |
Persistent, protective |
124. Identify the incorrect statement:
| 1. |
In grasses, the guard cells are dumb-bell shaped. |
| 2. |
Trichomes in the shoot system are generally unicellular. |
| 3. |
Casparian strips are associated with endodermis in dicot roots. |
| 4. |
Endodermis in dicot stem is referred to as starch sheath. |
125. Why is the effluent from the primary treatment sent to aeration tanks during secondary treatment?
| 1. |
To remove suspended solids from the effluent. |
| 2. |
To promote the growth of anaerobic bacteria. |
| 3. |
To allow aerobic microbes to form flocs and reduce organic matter. |
| 4. |
To separate activated sludge from the effluent. |
126. The probability that recombination [crossing over] takes place between two genes located on the same chromosome is proportional to:
| 1. |
the distance of genes from the centromere |
| 2. |
the degree of contribution to the phenotype |
| 3. |
the distance between the two genes |
| 4. |
the distance of genes from the telomere |
127. The pattern where a dominant, independent, photosynthetic, thalloid or erect phase is represented by a haploid gametophyte and it alternates with the short-lived multicellular sporophyte totally or partially dependent on the gametophyte for its anchorage and nutrition is seen in:
1. Pteridophytes
2. Bryophytes
3. Gymnosperms
4. Angiosperms
128. Presence of exarch and polyarch vascular bundles is characteristically seen in:
| 1. |
Monocot stem |
2. |
Monocot root |
| 3. |
Dicot stem |
4. |
Dicot root |
129. Which of the following options most accurately describes algae in general?
| 1. |
Algae are chlorophyll-bearing, thalloid, autotrophic and largely aquatic (both fresh water and marine) organisms. |
| 2. |
Algae are chlorophyll-bearing, having highly differentiated body, autotrophic and exclusively found in fresh water organisms. |
| 3. |
Algae are chlorophyll-bearing or parasitic heterotrophic organisms, thalloid and largely marine organisms. |
| 4. |
Algae are chlorophyll-lacking, thalloid, autotrophic and largely saprophytic organisms found in both fresh and marine waters. |
130. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion(A): |
The presence of gill slits and a tail in the early stages of development of an embryo indicates that it can develop only as a fish. |
| Reason(R): |
Embryos pass through the adult stages of other animals. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) does not correctly explain (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) correctly explains (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is false and (R) is also false. |
| 4. |
(A) is true but (R) is false. |
131. In oogamy, fertilization involves:
| 1. |
A large non-motile female gamete and a small motile male gamete |
| 2. |
A large non-motile female gamete and a small non-motile male gamete |
| 3. |
A large motile female gamete and a small non-motile male gamete |
| 4. |
A small non-motile female gamete and a large motile male gamete |
132. Which gases were primarily present in the atmosphere of early Earth [according to Alexander I. Oparin] before the formation of the ozone layer?
1. Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Argon
2. Water vapor, Methane, Hydrogen, and Ammonia
3. Nitrogen, Helium, and Hydrogen
4. Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Ozone
133. In red algae:
| I: |
Phycoerythrin is a major photosynthetic pigment. |
| II: |
Floridean starch is stored food. |
| III: |
Cell wall contains polysulphate esters. |
| IV: |
Flagella are 2, unequal with lateral insertion. |
1. Only
I,
II and
III are correct
2. Only
I,
III and
IV are correct
3. Only
II,
III and
IV are correct
4.
I,
II,
III and
IV are correct
134. Match the following plant parts with their primary functions:
|
Column I |
|
Column II |
| A |
Stomata |
P |
Supports the leaf blade and connects it to the stem |
| B |
Xylem |
Q |
Involved in the transport of water and minerals from roots to leaves |
| C |
Phloem |
R |
Involved in the transport of food from leaves to other parts of the plant |
| D |
Petiole |
S |
Facilitates gas exchange and transpiration in plants |
Codes:
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1. |
S |
Q |
R |
P |
| 2. |
P |
Q |
R |
s |
| 3. |
P |
R |
Q |
S |
| 4. |
Q |
P |
S |
R |
135. The bottled juices are clarified by the use of:
1. lipases and proteases
2. lysozyme and chitinase
3. DNase and protease
4. Pectinases and proteases
136. Trichoderma harzianum is a free-living fungus used for:
| 1. |
killing insects |
| 2. |
biological control of fungal plant diseases |
| 3. |
controlling butterfly caterpillars |
| 4. |
producing antibiotics |
137. Consider the given two statements:
| Statement I: |
The large holes in ‘Swiss cheese’ are due to production of a large amount of CO2 by a bacterium named Propionibacterium shermanii. |
| Statement II: |
The ‘Roquefort cheese’ are ripened by growing a specific bacteria on them, which gives them a particular flavour. |
| 1. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect |
| 2. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is incorrect |
| 3. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct |
| 4. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is correct |
138. In gymnosperms, pollen grains:
| 1. |
develop outside microsporangia |
| 2. |
are a result of mitosis in certain pollen mother cells |
| 3. |
are carried in air currents |
| 4. |
do not form pollen tubes and the male gamete is released into water |
139. Biogas
| I: |
is a renewable energy source produced by the anaerobic decomposition of organic matter. |
| II: |
is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, and a small amount of hydrogen sulfide, and moisture. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
140. Bacillus thuringiensis has been used as:
1. Diazotroph
2. Bioinsecticide
3. Biofertilizer
4. Thrombolytic
141. Which of the following beverages is produced without distillation during the fermentation process?
| 1. |
Whisky and rum |
2. |
Brandy and rum |
| 3. |
Beer and wine |
4. |
Whisky and beer |
142. Meiosis in sexually reproducing organisms creates new variations by shuffling the available genetic material and leads to the formation of a recombinant DNA which is created at:
| 1. |
Pachytene of Prophase I |
| 2. |
Diplotene of Prophase I |
| 3. |
Anaphase I of Meiosis I |
| 4. |
Anaphase II of Meiosis II |
143. Consider the two statements:
| Statement I: |
Bryophytes usually occur in damp, humid and shaded localities and are not truly ‘successful’ on land. |
| Statement II: |
They are dependent on water for sexual reproduction. |
| 1. |
Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect |
| 2. |
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II explains Statement I |
| 3. |
Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is correct |
| 4. |
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II does not explain Statement I |
144. Cells in our body, that are not dividing, are said to be at which phase of the cell cycle?
| 1. |
G1 |
2. |
G2 |
| 3. |
G0 |
4. |
S phase |
145. Which of the following is missing in sieve tube elements when they attain maturity?
| 1. |
Nuclei |
2. |
Cytoplasm |
| 3. |
P-protein |
4. |
Callose |
146. The cell cycle in a typical eukaryotic cell is divided into:
| 1. |
Five phases |
2. |
Four phases |
| 3. |
Three phases |
4. |
Two phases |
147. Consider the following key events:
| I: |
Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete elements. |
| II: |
Nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reform |
The stage of mitosis characterized by these key events is:
| 1. |
Prophase |
2. |
Metaphase |
| 3. |
Anaphase |
4. |
Telophase |
148. What algae has been depicted in the given figure?
| 1. |
Laminaria |
2. |
Fucus |
| 3. |
Polysiphonia |
4. |
Volvox |
149. What is the significance of the kinetochore in chromosomes?
| 1. |
It serves as an attachment point for spindle fibres during cell division. |
| 2. |
It is the site where DNA replication begins. |
| 3. |
It forms the primary constriction of the chromosome. |
| 4. |
It connects chromatids to nuclear pores. |
150. Which is the correct set of options with respect to the following?
| 1. |
Dicot stem – Differentiated ground tissue. |
|
Monocot stem – Endarch xylem. |
|
Dicot leaf – Isobilateral leaf. |
|
Monocot leaf – Dorsiventral leaf. |
| 2. |
Dicot stem – Scattered vascular bundle. |
|
Monocot stem – Arranged vascular bundle. |
|
Dicot leaf – Amphistomatic. |
|
Monocot leaf – Hypostomatic. |
| 3. |
Dicot stem – Endodermis is called a starch sheath. |
|
Monocot stem – Vascular bundle surrounded by a sclerenchymatous sheath. |
|
Dicot leaf – Palisade and spongy parenchyma. |
|
Monocot leaf – Stomata present on both surfaces. |
| 4. |
Dicot stem – Arranged vascular bundle. |
|
Monocot stem – Endodermis is called a starch sheath. |
|
Dicot leaf – Amphistomatatic. |
|
Monocot leaf – Palisade and spongy parenchyma. |
151. A common biocontrol agent for the control of plant diseases is
1. Trichoderma
2. Baculovirus
3. Bacillus thuringiensis
4. Glomus
152. All the following events take place during the telophase stage of mitosis except:
| 1. |
Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete elements. |
| 2. |
Nuclear envelope develops around the chromosome clusters at each pole forming two daughter nuclei. |
| 3. |
Nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER re-form. |
| 4. |
Microtubules get organised into spindle fibres. |
153. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic feature of Bryophytes?
1. Presence of vascular tissues
2. Dominant gametophyte phase
3. Multicellular sex organs
4. Requirement of water for sexual reproduction
154. How many of the given statements regarding gradual evolution of life forms as explained by Darwin are correct?
| I: |
Any population has built in variation in characteristics. |
| II: |
Those characteristics which enable some to survive better in natural conditions (climate, food, physical factors, etc.) would outbreed others that are less-endowed to survive under such natural conditions. |
| III: |
The fitness, according to Darwin, refers ultimately and only to reproductive fitness. |
| IV: |
Those who are better fit in an environment, leave more progeny than others. |
1. 1
2. 2
3. 3
4. 4
155. The role of the spindle apparatus during mitosis is to:
| 1. |
Control the timing of cell division |
| 2. |
Facilitate the movement of chromosomes |
| 3. |
Produce new DNA molecules |
| 4. |
Regulate cell growth |
156. What makes Red Algae different from Green Algae and Brown Algae?
| 1. |
Unlike Green Algae and Brown Algae, Red Algae do not have chlorophyll a. |
| 2. |
Unlike Green Algae and Brown Algae, Red Algae have no differentiated cells. |
| 3. |
Unlike Green Algae and Brown Algae, Red Algae are not photosynthetic. |
| 4. |
Unlike Green Algae and Brown Algae, Red Algae do not have any flagellated stages in their life cycles. |
157. An enzyme isolated from which of the following bacteria can be used to remove clots from blood vessels?
1. Bacillus thuringiensis
2. Clostridium butylicum
3. Streptococcus
4. Lactobacillus
158. In stems:
| 1. |
the primary xylem is endarch with protoxylem towards the center and metaxylem towards the periphery |
| 2. |
the primary xylem is endarch with metaxylem towards the center and protoxylem towards the periphery |
| 3. |
the primary xylem is exarch with protoxylem towards the center and metaxylem towards the periphery |
| 4. |
the primary xylem is exarch with metaxylem towards the center and protoxylem towards the periphery |
159. Sweet potato and potato are examples of:
1. Homology
2. Analogy
3. Vestigial organs
4. Atavism
160. If you are asked to classify the various algae into distinct groups, which of the following characters you should choose?
| 1. |
Types of pigments present in the cell |
| 2. |
Nature of stored food materials in the cell |
| 3. |
Structural organisation of thallus |
| 4. |
Chemical compositions of the cell wall |
161. Collenchyma in plants:
| I: |
occurs in layers below the epidermis in most of the dicotyledonous plants. |
| II: |
consists of cells that are much thickened at the corners due to deposition of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. |
| III: |
never contains chloroplasts. |
| IV: |
provides mechanical support to the growing parts of the plant such as the young stem and petiole of a leaf. |
1. Only
I,
II, and
III are correct
2. Only
I,
II, and
IV are correct
3. Only
II,
III, and
IV are correct
4. Only
I,
III, and
IV are correct
162. Identify the correct statements:
| I: |
Phylogenetic classification systems are based on evolutionary relationships. |
| II: |
Numerical Taxonomy is based on all observable characteristics. |
1. Only
I
2. Only
II
3. Both
I and
II
4. Neither
I nor
II
163. It is possible that Darwin was influenced by the essay on populations by:
| 1. |
Carl Correns |
2. |
Charles Lyell |
| 3. |
Thomas Malthus |
4. |
A. R. Wallace |
164. Convergent evolution describes the development of similar traits in unrelated organisms due to:
| 1. |
Inheritance of shared ancestral traits |
| 2. |
Selection for adaptations to similar environments |
| 3. |
Mutations in the same genes |
| 4. |
Interbreeding between different species |
165. The given figure represents the Transverse Section of a:
1. Monocot root
2. Dicot root
3. Dicot stem
4. Monocot stem
166. What is the term used for the short phase between meiosis I and meiosis II during which no DNA replication occurs?
| 1. |
Interkinesis |
2. |
Cytokinesis |
| 3. |
Diakinesis |
4. |
Telophase |
167. From an evolutionary point of view, retention of the female gametophyte with developing young embryo on the parent sporophyte for some time, is first observed in:
| 1. |
Gymnosperms |
2. |
Liverworts |
| 3. |
Mosses |
4. |
Pteridophytes |
168. Match the following microorganism with product
|
Column - I |
|
Column - II |
| (a) |
Clostridium butylicum |
(i) |
Cyclosporin A |
| (b) |
Trichoderma polysporunt |
(ii) |
Butyric acid |
| (c) |
Monascus purpureus |
(iii) |
Citric acid |
| (d) |
Aspergillus niger |
(iv) |
Blood cholesterol lowering agent |
|
(a) |
(b) |
(c) |
(d) |
| 1. |
(ii) |
(i) |
(iv) |
(iii) |
| 2. |
(i) |
(ii) |
(iv) |
(iii) |
| 3. |
(iv) |
(iii) |
(ii) |
(i) |
| 4. |
(iii) |
(iv) |
(ii) |
(i) |
169. In a eukaryotic cell which phase of the cell cycle can be regarded as the primary growth phase?
1. G0
2. G1
3. M
4. S
170. Consider the following statements regarding the epidermal tissue system:
| Statements A: |
The epidermis is a single-layered structure made up of compactly arranged cells with a large nucleus and no vacuole. |
| Statements B: |
The cuticle is a waxy layer present on the outer surface of the epidermis that helps in reducing water loss. |
| Statements C: |
Stomata are structures present in the epidermis of leaves that regulate transpiration and gaseous exchange. |
| Statements D: |
The guard cells of all plants are bean-shaped and regulate the opening and closing of stomata. |
How many of the above statements are correct?
| 1. |
Only one statement |
2. |
Only two statements |
| 3. |
Only three statements |
4. |
All four statements |
171. The cells of which tissue in plants are living, show angular wall thickening and provide mechanical support?
| 1. |
Xylem |
2. |
Sclerenchyma |
| 3. |
Collenchyma |
4. |
Epidermis |
172. The transverse section shown in the given figure is representative of:

1. Monocot stem
2. Monocot root
3. Dicot stem
4. Dicot root
173. The emergence of resistance to antibiotics in bacterial groups is due to:
| 1. |
adaptive radiation |
| 2. |
transduction |
| 3. |
pre-existing variation in the population |
| 4. |
mutations induced by antibiotics |
174. The frequency of recessive allele in a population of 500 at genetic equilibrium was found to be 0.4. What would be the number of heterozygotes in this population?
1. 40
2. 240
3. 200
4. 320
175. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The presence of a casparian strip is characteristic of the endodermis in plant roots. |
| Reason (R): |
The casparian strip is made up of cellulose and pectin which helps in regulating the flow of substances into the vascular tissue. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
(A) is False but (R) is True. |
176. The smallest units of natural selection and evolution respectively are:
1. Population, Species
2. Individual, Species
3. Family, Population
4. Individual, Population
177. Ichthyosaur was:
1. a marine retile
2. a marine amphibian
3. a fresh water amphibian
4. a flying reptile
178. G
1 phase in a cell cycle:
| I: |
corresponds to the interval between initiation of mitosis and DNA replication. |
| II: |
is characterised by a metabolically active cell that grows continuously and replicates its DNA. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
179. Bryophytes are often referred to as "amphibians of the plant kingdom" due to their dependence on water. Which of the following statements correctly describes the reason for this dependence?
| 1. |
Water is essential for bryophytes only during the sporophytic phase, as gametophytes are independent and produce seeds without water. |
| 2. |
Water is required for the movement of motile male gametes (antherozoids) to reach the archegonium for fertilization, as bryophytes lack vascular tissue for fluid transport. |
| 3. |
Bryophytes rely on water for absorbing nutrients directly from soil through specialized roots and not for fertilization. |
| 4. |
Water in bryophytes serves the same function as in gymnosperms, facilitating pollen transfer from male to female cones. |
180. All the following are example of green alga except:
1. Ectocarpus
2. Chara
3. Ulothrix
4. Spirogyra
*If above link doesn't work, please go to test link from where you got the pdf and fill OMR from there
CLICK HERE to get FREE ACCESS for 2 days of ANY NEETprep course