1. The rate constant of a zero-order reaction is 2.0 × 10–2 mol L–1 s–1. The concentration of the reactant after 25 seconds is 0.5 M. What is the initial concentration?
1. 0.5 M
2. 1.25 M
3. 12.5 M
4. 1.0 M
2. Match the rate law given in column I with the dimensions of rate constants given in column II and mark the appropriate choice.
|
Column I |
|
Column II |
| (A) |
Rate=\(k[NH_3]^0\) |
(i) |
\(\text {mol L}^{-1} \text s^{-1}\) |
| (B) |
Rate=\(k[H_2O_2] [I^-]\) |
(ii) |
\(\text {L mol }^{-1}~ \text s^{-1}\) |
| (C) |
Rate=\(k[CH_3CHO]^{3/2}\) |
(iii) |
\( \text s^{-1}\) |
| (D) |
Rate=\(k[C_2H_5Cl]\) |
(iv) |
\(\text {L}^{1/2} \text {mol}^{-1/2}~\text s^{-1}\) |
1. (A) →(iv), (B)→(iii), (C) →(ii), (D)→ (i)
2. (A) →(i), (B)→(ii), (C) →(iii), (D)→ (iv)
3. (A) →(ii), (B)→(i), (C) →(iv), (D)→ (iii)
4. (A) →(i), (B)→(ii), (C) →(iv), (D)→ (iii)
3. In the reaction A + 2B → C, the rate law is experimentally determined to be rate = k[B]2. What happens to the initial rate of reaction when the concentration of A is doubled?
1. The rate doubles.
2. The rate quadruples.
3. The rate halves.
4. The rate is unchanged.
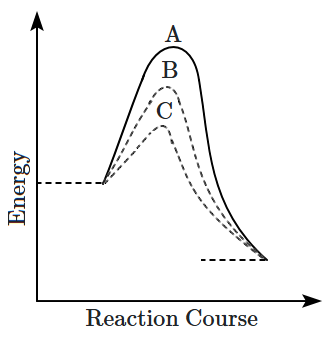
4. A homogeneous catalytic reaction takes place through the three alternative plots A, B, and C shown in the given figure. Which one of the following indicates the relative ease with which the reaction can take place?
1.
\(A>B>C\)
2.
\(C>B>A\)
3.
\(A>C>B\)
4.
\(A=B=C\)
5. For a 1
st order reaction, following graph is obtained between lnk and
\({1000 \over T}\). Then, the activation energy of the reaction in kcal is:

1. 37 kcal
2. 40 kcal
3. 42 kcal
4. 34 kcal
6. A first-order reaction with a half-life of 85 seconds will have what fraction of the reactant remaining after 255 seconds?
| 1. |
\(\frac{1}{2}\) |
2. |
\(\frac{1}{4}\) |
| 3. |
\(\frac{1}{8}\) |
4. |
\(\frac{1}{3}\) |
7. If 75% of A is converted to B in 60 minutes (irreversible first-order reaction, A → B), the half-life of the given reaction will be:
1. 30 minutes
2. 45 minutes
3. 60 minutes
4. 80 minutes
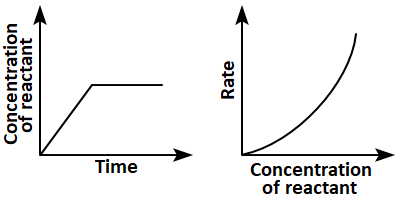
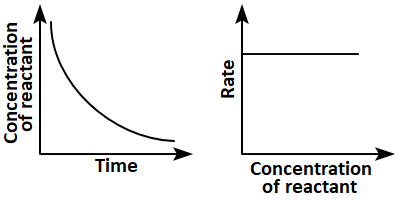
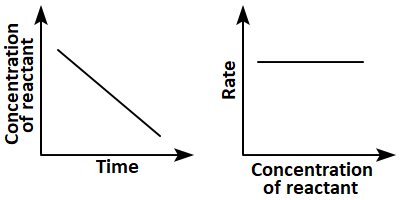
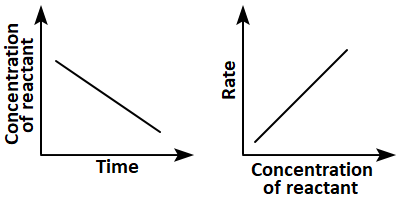
8. Which of the following pairs of graphs do not represent the same order of reaction?
1. (a) Only
2. (b),(c), and (d)
3. (c) and (d)
4. (a),(b),and (d)
9. Select the correct option for the function of a catalyst in a chemical reaction:
| 1. |
Reduces enthalpy of reaction. |
| 2. |
Decrease the rate constant of the reaction. |
| 3. |
Increases activation energy of the reaction. |
| 4. |
Does not affect the equilibrium constant of the reaction. |
10. Consider the equilibrium reaction: A(g) ⇌ B(g) with an enthalpy change (ΔH) of -42 kJ/mol.
Determine the activation energies for the forward and backward reactions, given that the ratio of the activation energy of the forward reaction to the activation energy of the backward reaction is 2 : 3.
| 1. |
84 kJ/mole, 126 kJ/mole |
2. |
24 kJ/mole, 36 kJ/mole |
| 3. |
48 kJ/mole, 72 kJ/mole |
4. |
90 kJ/mole, 135 kJ/mole |
*If above link doesn't work, please go to test link from where you got the pdf and fill OMR from there
CLICK HERE to get FREE ACCESS for 2 days of ANY NEETprep course