1. Consider the given half-cell reactions:
\(\begin{array}{ll} \mathrm{Fe}^{2+} \rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}^{3+}+\mathrm{e}^{-} & \mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{Fe}^{3+} / \mathrm{Fe}^{2+}}^0=0.77 \mathrm{~V} \\ 2 \mathrm{I}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{I}_2+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} & \mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{I}_2 / \text{I}^-}^{\circ}=0.54 \mathrm{~V} \end{array}\)
The standard electrode potential for the spontaneous reaction in the cell is \(x\times 10^{-2}V~\text{at}~ 298~K.\)
The value of \(x\) is: (Nearest Integer)
1. 32
2. 23
3. 45
4. 17
2. Given the following reaction:
\(\mathrm{Zn}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}(\mathrm{aq}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Zn}^{2+}(\mathrm{aq})+\mathrm{Cu}(\mathrm{s})\)
E°cell = 2 V at 298 K
The standard Gibbs energy for the given cell reaction in kJ mol–1 at 298 K is:
(Faraday’s constant, F = 96000 C mol–1)
1. –384
2. 384
3. 192
4. –192
3. \(\Delta G^o \) for a reversible reaction having equilibrium constant 10–2 at 27°C will be:
1. 500R
2. 2.303 × 600R
3. 600R
4. 2.303 × 500R
4. The graph represents the variation of molar conductance (
\(\Lambda_m\)) with the square root of concentration (
\(\sqrt{C}\)) for two electrolytes, '
A' and '
B'. Based on the graph, the nature of both electrolytes is:
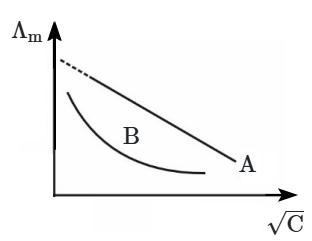
1.
A → Strong Electrolyte,
B→ Strong Electrolyte
2.
A → Weak Electrolyte,
B → Strong Electrolyte
3.
A → Strong Electrolyte,
B → Weak Electrolyte
4.
A → Weak electrolyte,
B → Weak Electrolyte
5. The resistance of a cell containing 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is 1500 Ω. The conductivity is 0.146 × 10–3 S cm–1. The cell constant would be:
| 1. |
|
2. |
|
| 3. |
|
4. |
|
6. Match column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice:
|
Column I |
|
Column II |
| (A) |
Electrochemical equivalent |
(i) |
Potential difference \(\times\) Quantity of charge |
| (B) |
Faraday |
(ii) |
Mass of substance deposited by one coulomb of charge |
| (C) |
Ampere |
(iii) |
Charge carried by one mole of electrons |
| (D) |
Electrical energy |
(iv) |
One coulomb of electric charge passed through one second |
1. (A) →(i), (B)→(ii), (C) →(iii), (D)→ (iv)
2. (A) →(ii), (B)→(iii), (C) →(iv), (D)→ (i)
3. (A) →(iii), (B)→(iv), (C) →(i), (D)→ (ii)
4. (A) →(iv), (B)→(i), (C) →(ii), (D)→ (iii)
7. Match the two lists and choose the correct option:
|
List-I |
|
List-II |
| (i) |
Ni-Cd cell |
(a) |
Rechargeable |
| (ii) |
Fuel cell |
(b) |
Anode \(\left(\mathrm{Zn} \rightarrow \mathrm{Zn}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-}\right)\) |
| (iii) |
Mercury cell |
(c) |
Used in hearing aid |
| (iv) |
Leclanché cell |
(d) |
Converts combustion energy into electrical energy |
1. (i)-(a); (ii)-(d); (iii)-(c), (iv)-(b)
2. (i)-(b); (ii)-(a); (iii)-(c), (iv)-(d)
3. (i)-(d); (ii)-(a); (iii)-(c), (iv)-(b)
4. (i)-(a); (ii)-(b); (iii)-(c), (iv)-(d)
8. The strongest reducing agent on the basis of E° values is:
1. \(\text A^+ / \text A ;~ E^o = -3.04 \text V \)
2. \(\text B^+ / \text B ;~ E^o = -2.71 \text V \)
3. \(\text C^+ / \text C ;~ E^o = -2.92 \text V \)
4. \(\text D^+ / \text D ;~ E^o = +0.79 \text V \)
9. Match Column I with Column II and mark the appropriate choice:
|
Column I |
|
Column II |
| (A) |
\(Pb_{(s)} + SO^{2-}_{4(aq)} \rightarrow\\ PbSO_{4(s)}+ 2 e^-\) |
(i) |
Rusting of iron |
| (B) |
\( SO^{2-}_{4(aq)} \rightarrow \\S_2O^{2-}_{8(aq)}+ 2 e^-\) |
(ii) |
Reaction at the anode in
lead storage battery |
| (C) |
\(2H_{2(g)} + 4OH^{-}_{(aq)} \rightarrow \\4 H_2O_{(l)}+ 4e^-\) |
(iii) |
Electrolysis of concentrated
\(H_2SO_4\) |
| (D) |
\(2Fe_{(s)} + O_{2(g)} + 4H^+_{(aq)} \rightarrow \\2Fe^{2+}_{(aq)}+ 2 H_2O_{(l)}\) |
(iv) |
Reaction at the anode in fuel cell |
1. (A) →(i), (B)→(ii), (C) →(iii), (D)→ (iv)
2. (A) →(ii), (B)→(iii), (C) →(iv), (D)→ (i)
3. (A) →(iii), (B)→(iv), (C) →(i), (D)→ (ii)
4. (A) →(iv), (B)→(i), (C) →(ii), (D)→ (iii)
10. The reduction potential of the hydrogen electrode when in contact with a solution having pH = 8 is:
(Given : \(\text {P}_{H_2} = 1~\text {atm} \))
1. –0.71 V
2. –0.47 V
3. –0.95 V
4. –0.36 V
*If above link doesn't work, please go to test link from where you got the pdf and fill OMR from there
CLICK HERE to get FREE ACCESS for 2 days of ANY NEETprep course
