1. Which of the following is expected to be the most soluble in hexane, \(\text{C}_6\text{H}_{14}?\)
1. \(\text{KCl}\)
2. \(\text{C}_2\text{H}_5\text{OH}\)
3. \(\text{C}_6\text{H}_6\)
4. \(\text{H}_2\text{O}\)
2. Determine the vapor pressure (in torr) of a MgCl
2 solution, given the following data:
a) molality: 1 m
b) vapor pressure of pure solvent: 100 torr
c)
\(\alpha \) (degree of dissociation) = 80 %
| 1. |
95.53 |
2. |
78.23 |
| 3. |
68.12 |
4. |
58.26 |
3. The density of a 3 M NaCl solution is 1 g/mL. The molality of the solution is ‘x’. The value of 2x is:
(Round off to the nearest integer.)
1. 7
2. 10
3. 13
4. 5
4. What is the partial pressure of helium when 8.0 grams of helium and 16 grams of oxygen are in a container with a total pressure of 5.00 atm?
| 1. |
0.25 atm |
2. |
1.00 atm |
| 3. |
1.50 atm |
4. |
4.00 atm |
5. Points A and B in the below-mentioned graph represent, respectively:

| 1. |
Partial pressures of first and second components |
| 2. |
Vapour pressures of the pure second and first components |
| 3. |
Partial pressures of second and first components |
| 4. |
Vapour pressures of the pure first and second components |
6. The vapour pressure of an aqueous solution obtained after mixing 900 g H2O with 120 g urea at 373.15 K will be:
1. 650 mm Hg
2. 760 mm Hg
3. 730.77 mm Hg
4. 855 mm Hg
7. Consider the two statements:
| Statement I: |
The value of Kf can be calculated by using \( K_{f} \ = \ \frac{R\times M_{1}\times T_{f}^{2}}{1000\times \Delta _{fus}H}\) |
| Statement II: |
Unit of Ebullioscopic constant (Kb) is K kg L-1. |
| 1. |
Statement I is True, Statement II is False. |
| 2. |
Statement I is False, Statement II is True. |
| 3. |
Both Statement I and Statement II are True. |
| 4. |
Both Statement I and Statement II are False. |
8. Two containers are taken, each holding a different non-volatile solute, X and Y, as depicted.
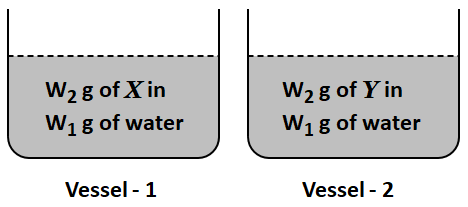
The molar mass of
\(X\) is
\(60\%\) of that of
\(Y\) and van't Hoff factor for
\(X\) is
\(1.2\) times of
\(Y.\) The ratio of depression in freezing point of
\(X\) and
\(Y\) is:
| 1. |
\( \dfrac {1} {2}\) |
2. |
\(2\) |
| 3. |
\(1.5\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac {2} {3}\) |
9. Which of the following pair of aqueous solutions will have the same value of osmotic pressure?
(Assume complete dissociation in aqueous solution)
1. \(0.1~ \mathrm{{M}~ {BaCl}_2} \text { and } 0.2 ~\mathrm{{M} ~{K}_2 {SO}_4}\)
2. \(0.1~ \mathrm{{M}~ {Na}_3 {PO}_4} \text { and } 0.1 ~\mathrm{{M}~ {K}_2 {SO}_4}\)
3. \(0.2~ \mathrm{{M}~ {NaCl}} \text { and } 0.1 ~\mathrm{{M} ~{K}_2 {SO}_4}\)
4. \(0.2 ~\mathrm{{M} ~{NaCl}} \text { and } 0.1~ \mathrm{{M} ~{K}_3\left[{Fe}({CN})_6\right]}\)
10. Consider the following statements:
| (A) |
Components of an azeotropic binary mixture cannot be separated by fractional distillation. |
| (B) |
Ethanol-water azeotropic mixture contains approximately 95% by volume of ethanol. |
| (C) |
A solution containing components A and B follows Raoult's law if A-B attraction force remains the same as A-A and B-B attraction forces. |
The correct statements are:
1.
A and
B only.
2.
B and
C only.
3.
A,
B, and
C.
4.
A and
C only.
*If above link doesn't work, please go to test link from where you got the pdf and fill OMR from there
CLICK HERE to get FREE ACCESS for 2 days of ANY NEETprep course
