Physics
1. A rubber cord has a cross-sectional area \(1~\text{mm}^2\) and the total unstretched length \(10~\text{cm}.\) It is stretched to \(12~\text{cm}\) and then released to project a mass of \(80~\text g.\) The Young's modulus for rubber is \(5\times10^{8}~\text{N-m}^2.\) What would be the velocity of mass when the rubber cord is unstretched?
1. \(5~\text{m/s}\)
2. \(3~\text{m/s}\)
3. \(7~\text{m/s}\)
4. \(2~\text{m/s}\)
2. If the length of a wire is doubled and its radius is halved compared to their respective initial values, then, Young’s modulus of the material of the wire will:
| 1. |
remain the same. |
| 2. |
become \(8\) times its initial value. |
| 3. |
become \({1 \over 4}\)th of its initial value. |
| 4. |
become \(4\) times its initial value. |
3. Mercury, with a coefficient of thermal expansion
\(\gamma\), is poured into a thin glass tube, which does not expand on heating. The length of the mercury column is
\(L.\) If the temperature is raised by
\(\theta,\) the new length of the mercury column will be:
| 1. |
\(L(1+\gamma\theta)\) |
2. |
\(L\left(1+\dfrac\gamma2\theta\right)\) |
| 3. |
\(L\left(1+\dfrac\gamma3\theta\right)\) |
4. |
\(L\left(1+\dfrac{2\gamma}3\theta\right)\) |
4. A block of mass
\(m\) slides down a smooth plane inclined at an angle of
\(60^\circ\) with the horizontal. The normal reaction of the incline acting on the block equals:
| 1. |
\(mg\sin60^\circ\) |
2. |
\(mg\cos60^\circ\) |
| 3. |
\(mg\tan60^\circ\) |
4. |
\(mg\cot60^\circ\) |
5. A moving steel ball of mass
\(m\) collides elastically with another steel ball of mass
\(2m\) that is initially at rest. If the kinetic energy of the moving ball before the collision is
\(100\) J, then after the collision it will have a kinetic energy of:
| 1. |
\(\dfrac{100}{3}\) J |
2. |
\(\dfrac{100}{9}\) J |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{200}{3}\) J |
4. |
\(\dfrac{800}{9}\) J |
6.
A particle is moving along a straight line such that its position depends on time as \(x=1-at+bt^{2} \), where \(a=2~\text{m/s}\), \(b=1~\text{m/s}^2\). The distance covered by the particle during the first \(3\) seconds from start of the motion will be:
| 1. |
\(2~\text{m}\) |
2. |
\(5~\text{m}\) |
| 3. |
\(7~\text{m}\) |
4. |
\(4~\text{m}\) |
7. The position of a particle with respect to time \(t\) along the \({x}\)-axis is given by \(x=9t^{2}-t^{3}\) where \(x\) is in metres and \(t\) in seconds. What will be the position of this particle when it achieves maximum speed along the \(+{x} \text-\text{direction}?\)
1. \(32~\text m\)
2. \(54~\text m\)
3. \(81~\text m\)
4. \(24~\text m\)
8. Which, of the following materials, is the most elastic?
| 1. |
Steel |
2. |
Rubber |
| 3. |
Charcoal |
4. |
Chalk |
9. Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
During an adiabatic expansion, a gas \(A\) cools faster than another gas \(B:\) during adiabatic compression, the gas \(A\) would heat faster than gas \(B.\) |
| Reason (R): |
The rate of cooling or heating during an adiabatic process has the same magnitude, at any given point of the process. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
(A) is False but (R) is True. |
10. A horizontal force
\(F\) is applied to a block of mass
\(m\) resting on a plane, where the coefficient of friction is
\(\mu.\) As the value of
\(F\) is slowly increased, the force of friction:

| 1. |
is constant and equals \(\mu mg.\) |
| 2. |
is greater than \(F\) until \(F\) reaches \(\mu mg.\) |
| 3. |
is less than \(F,\) until \(F\) equals \(\mu mg.\) |
| 4. |
is equal to \(F,\) until \(F\) equals \(\mu mg.\) |
11. A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen has a volume of
\(2000\) cm
3, temperature
\(300\) K, pressure
\(100\) kPa and mass
\(0.76\) g. The ratio of the number of moles of hydrogen to the number of moles of oxygen in the mixture will be:
| 1. |
\( 1 \over 3\) |
2. |
\(3 \over 1\) |
| 3. |
\( 1 \over 16\) |
4. |
\( 16 \over 1\) |
12. A string is wrapped along the rim of a wheel of the moment of inertia \(0.10~\text{kg-m}^2\) and radius \(10~\text{cm}.\) If the string is now pulled by a force of \(10~\text N,\) then the wheel starts to rotate about its axis from rest. The angular velocity of the wheel after \(2~\text s\) will be:
| 1. |
\(40~\text{rad/s}\) |
2. |
\(80~\text{rad/s}\) |
| 3. |
\(10~\text{rad/s}\) |
4. |
\(20~\text{rad/s}\) |
13. The ice-point reading on a thermometer scale is found to be \(20^\circ,\) while the steam point is found to be \(70^\circ.\) When this thermometer reads \(100^\circ ,\) the actual temperature is:
1. \(80^\circ\text{C}\)
2. \(130^\circ\text{C}\)
3. \(160^\circ\text{C}\)
4. \(200^\circ\text{C}\)
14. A gas is compressed isothermally to half its initial volume. The same gas is compressed separately through an adiabatic process until its volume is again reduced to half. Then,
| 1. |
compressing the gas through an adiabatic process will require more work to be done. |
| 2. |
compressing the gas isothermally or adiabatically will require the same amount of work. |
| 3. |
which of the case (whether compression through isothermal or through the adiabatic process) requires more work will depend upon the atomicity of the gas. |
| 4. |
compressing the gas isothermally will require more work to be done. |
15. A body of mass \(0.5\) kg travels on a straight line path with velocity \(v=(3x^{2}+4)\) m/s. The net work done by the force during its displacement from \(x = 0\) to \(x = 2\) m is:
1. \(64\) J
2. \(60\) J
3. \(120\) J
4. \(128\) J
16. Given below are two statements:
| Statement I: |
The speed of sound waves in a medium depends on the elastic modulus and the density of the medium. |
| Statement II: |
The speed of sound in a gas is independent of its temperature. |
| 1. |
Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is correct. |
| 2. |
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct. |
| 3. |
Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect. |
| 4. |
Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect. |
17. Surface tension is the force per unit length, acting on a line which is attached to the free surface of a liquid. The dimensions of surface tension are:
| 1. |
\([ML^2T^{-2}]\) |
2. |
\([ML^{-2}T^{-2}]\) |
| 3. |
\([M^{-1}L^{-1}T^{-1}]\) |
4. |
\([MT^{-2}]\) |
18. Which of the following statements is not true?
| 1. |
The coefficient of viscosity is a scalar quantity. |
| 2. |
Surface tension is a scalar quantity. |
| 3. |
Pressure is a vector quantity. |
| 4. |
Relative density is a scalar quantity. |
19. The displacement of the point
\(P\) on the wheel (see figure) as the wheel completes half revolution while rolling on the ground is:

1.
\(2\pi r\)
2.
\(\pi r\)
3.
\(\pi r+2r\)
4.
\(r\sqrt{\pi^2+4}\)
20. What is the maximum acceleration of a train that allows a box resting on its floor to remain stationary? (given that the coefficient of static friction between the box and the train's floor is \(0.2,\) and the acceleration due to gravity is \(10\) ms-2)
1. zero
2. \(1.0\) ms-2
3. \(2.0\) ms-2
4. \(4.0\) ms-2
21. Which one of the following relationships between acceleration, \(a\) and the displacement, \(x\) of a particle involves simple harmonic motion?
1. \( a = -50x^3\)
2. \(a = 50x^2\)
3. \(a = 50x\)
4. \(a = -50x\)
22. Consider the following statements:
| (A) |
Planets revolve around the Sun with constant linear speed. |
| (B) |
The energy of a planet in an elliptical orbit is constant. |
| (C) |
A satellite in circular motion has constant energy. |
| (D) |
A body falling towards the Earth results in negligible displacement of the Earth. |
Choose the incorrect statement from the given ones:
1.
(A) only
2.
(B) only
3.
(C) only
4.
(D) only
23. Two forces of magnitude
\(A\) and
\({A\over 2}\) act perpendicular to each other. The magnitude of the resultant force is equal to:
| 1. |
\(\dfrac A2\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac {\sqrt {5}A} { 2}\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac {3A} {2}\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac {5A} {2}\) |
24. If vectors \(\overrightarrow{{A}}=\cos \omega t \hat{{i}}+\sin \omega t \hat{j}\) and \(\overrightarrow{{B}}=\cos \left(\frac{\omega t}{2}\right)\hat{{i}}+\sin \left(\frac{\omega t}{2}\right) \hat{j}\) are functions of time. Then, at what value of \(t\) are they orthogonal to one another?
| 1. |
\(t = \frac{\pi}{4\omega}\) |
2. |
\(t = \frac{\pi}{2\omega}\) |
| 3. |
\(t = \frac{\pi}{\omega}\) |
4. |
\(t = 0\) |
25. A ball is dropped from a spacecraft revolving around the earth at a height of
\(120~\text{km}\). What will happen to the ball?
| 1. |
It will go very far in the space. |
| 2. |
It will fall down on the earth gradually. |
| 3. |
It will move with the same speed, tangentially to the spacecraft. |
| 4. |
It will continue to move with the same speed along the original orbit of the spacecraft. |
26. The density of water at
\(20^\circ \text{C}\) is
\(998~\text{kg/m}^3\) and at
\(40^\circ \text{C}\) is
\(992~\text{kg/m}^3.\) The coefficient of volume expansion of water is:
| 1. |
\(3 \times 10^{-4} / ^\circ\text C\) |
2. |
\(2 \times 10^{-4} / ^\circ\text C\) |
| 3. |
\(6 \times 10^{-4} / ^\circ\text C\) |
4. |
\(10^{-4} / ^\circ\text C\) |
27. Two persons of masses \(55~\text{kg}\) and \(65~\text{kg}\) respectively, are at the opposite ends of a boat. The length of the boat is \(3.0~\text{m}\) and weighs \(100~\text{kg}.\) The \(55~\text{kg}\) man walks up to the \(65~\text{kg}\) man and sits with him. If the boat is in still water, the centre of mass of the system shifts by:
1. \(3.0~\text{m}\)
2. \(2.3~\text{m}\)
3. zero
4. \(0.75~\text{m}\)
28. A uniform rod
\(AB\) of mass
\(1~\text{kg}\) and length
\(3~\text m\) is suspended from one end
\((A),\) so that it can freely rotate about it. It is given an impulse of
\(6~\text{N-s}\) horizontally at its lowest end
\(B.\)

During the subsequent rotational motion of the rod under gravity:
| 1. |
momentum is conserved |
| 2. |
total energy is conserved |
| 3. |
angular momentum is conserved |
| 4. |
centre-of-mass moves in a straight line |
29. In the given \({(V\text{-}T)}\) diagram, what is the relation between pressure \({P_1}\) and \({P_2}\)?

| 1. |
\(P_2>P_1\) |
2. |
\(P_2<P_1\) |
| 3. |
cannot be predicted |
4. |
\(P_2=P_1\) |
30. The velocity of a particle at any instant is given by the equation \(\vec{v}=(2t \hat{i}+3t^2\hat{j}) ~\text{m/s},\) and the radius of the curvature of the path is \(2~\text{m}.\) The centripetal acceleration of the particle at \(t=2\) s will be:
1. \(80\) m/s2
2. \(160\) m/s2
3. \(40\) m/s2
4. \(100\) m/s2
31. If the ratio of the number density per cm3 of the two gases is \(5:3\) and the ratio of the diameters of the molecules of the two gases is \(4:5,\) then, the ratio of the mean free path of molecules of two gases is:
| 1. |
\(\dfrac{16}{15}\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac{15}{16}\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{3}{4}\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{4}{3}\) |
32. The frequency
\((\nu)\) of oscillations of a simple pendulum of length
\(l\) is given by:
\(\nu=\dfrac1k\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{l}},\) where
\(g\) is the acceleration due to gravity. The dimensional formula of the quantity
\(k\) can be written as:
| 1. |
\(\left[M^0L^0T^0\right]\) |
2. |
\(\left[M^1L^0T^0\right]\) |
| 3. |
\(\left[M^0L^0T^1\right]\) |
4. |
\(\left[M^0L^1T^0\right]\) |
33. A block
\(A\) is placed on a spring and causes it to be compressed; when another
block \(B\) is placed on top of the first one the compression increases by
\(125\%.\) The time period of small oscillations is
\(T_A\) when
\(A\) is present, and is
\(T_{AB},\) when both
\(A~\&~B\) are present. Then,

| 1. |
\(T_{AB}=\dfrac{3}{2}~T_A\) |
2. |
\(T_{AB}=\dfrac{\sqrt5}{2}~T_A\) |
| 3. |
\(T_{AB}=\dfrac{1}{2}~T_A\) |
4. |
\(T_{AB}=\dfrac{2}{3}~T_A\) |
34. A wooden block floats submerged at the interface of two liquids, the upper one of specific gravity \(0.4\) and the lower one being water (density: \(1\) g/cc). It is observed that the block has \(\dfrac{1}{3}\) of its volume in water and \(\dfrac{2}{3}\) of it in the upper liquid. The density of the block(in g/cc) is:
1. \(0.5\)
2. \(0.6\)
3. \(0.8\)
4. \(0.9\)
35. Which one of the following is not a vector quantity?
1. Velocity
2. Weight
3. Electric charge
4. Electric field
36. For the wave equation,
\(y=A\sin(Bt-Cx)\) , match
Column I with
Column II:
| Column I |
Column II |
| (a) |
Wave speed |
(p) |
\(\large\frac{B}{2\pi}\) |
| (b) |
Maximum particle speed |
(q) |
\(\large\frac{C}{2\pi}\) |
| (c) |
Wave frequency |
(r) |
\(\large\frac{B}{C}\) |
| (d) |
Wavelength |
(s) |
None of these |
Codes:
| 1. |
a - s, b - p, c - q, d - r |
| 2. |
a - r, b - p, c - q, d - s |
| 3. |
a - s, b - q, c - p, d - r |
| 4. |
a - r, b - s, c - p, d - s |
37. If the gravitational constant
\(G\) were twice as large, the time period of the earth's orbital motion (i.e.,
\(1\) year) would be: (other parameters remaining the same)
| 1. |
the same |
| 2. |
halved |
| 3. |
\(\Large\frac{1}{\sqrt2}\) times the present value |
| 4. |
\({\sqrt2}\) times the present value |
38. The velocity of projection of an oblique projectile is \(\vec{v}=\left(3 \hat{i}+2 \hat{j}\right)\) ms-1. The speed of the projectile at the highest point of the trajectory is:
1. \(3\) ms-1
2. \(2\) ms-1
3. \(1\) ms-1
4. zero
39. A transverse wave travels along a uniform wire with a length of
\(50\) cm and a mass of
\(10~\text{grams}\) at a speed of
\(60\) m/s. If the wire has a cross-sectional area of
\(2.0\) mm
2 and a Young's modulus of
\(1.2\times 10^{11}\) N/m
2, the extension of the wire over its natural length due to its tension will be:
| 1. |
\(0.12\) mm |
2. |
\(0.15\) mm |
| 3. |
\(0.20\) mm |
4. |
\(0.25\) mm |
40. Which of the following, is dimensionless?
| 1. |
\(\dfrac{\text{pressure}}{\text{density}\times\text{acceleration}}\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac{\text{density}\times\text{pressure}}{\text{speed}}\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{\text{viscosity}\times\text{speed}}{\text{surface tension}}\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{\text{surface tension}}{\text{(speed)}^2}\) |
41. A body floats in a liquid contained in a beaker. The whole system as shown in the figure is falling under gravity. The upthrust on the body due to liquid is:

| 1. |
zero. |
| 2. |
equal to the weight of liquid displaced. |
| 3. |
equal to the weight of the body in air. |
| 4. |
equal to the weight of the immersed body. |
42. Which of the following statements is true about the motion depicted in the diagram?

| 1. |
The acceleration is constant and non-zero. |
| 2. |
The velocity changes suddenly during the motion. |
| 3. |
The velocity is positive throughout. |
| 4. |
All of the above are true. |
43. Two gases are said to be in thermal equilibrium when they have the same:
1. pressure
2. volume
3. temperature
4. area
44. A force defined by;
\(F = \alpha t^2 + \beta t\) acts on a particle at a given time
\(t.\) The factor which is dimensionless, if
\(\alpha\) and
\(\beta\) are constants, is:
| 1. |
\(\alpha t / \beta \) |
2. |
\(\alpha \beta t \) |
| 3. |
\(\alpha \beta / t \) |
4. |
\(\beta t / \alpha\) |
45. A car starts from rest along straight horizontal road under the action of an engine that delivers constant power,
\(P.\) The velocity,
\(v,\) as a function of time
\(t\) varies as given by:
| 1. |
\(v\propto t\) |
2. |
\(v\propto \sqrt t\) |
| 3. |
\(v\propto {\Large\frac{1}{\sqrt t}}\) |
4. |
\(v\propto t^{3/2}\) |
Biology
46. Which classes of algae possess pigment fucoxanthin and pigment phycoerythrin, respectively?
1. Phaeophyceae and Chlorophyceae
2. Phaeophyceae and Rhodophyceae
3. Chlorophyceae and Rhodophyceae
4. Rhodophyceae and Phaeophyceae
47. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The spread of living pteridophytes is limited and restricted to narrow geographical regions. |
| Reason (R): |
Pteridophytes are not dependent on water for fertilisation. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) does not explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False but (R) is True |
48. Which characteristic feature is common to both Bryophytes and Pteridophytes?
| 1. |
Presence of flowers |
| 2. |
Production of seeds |
| 3. |
Dependence on water for fertilization |
| 4. |
Presence of vascular tissues |
49. Which of the following algae produce Carrageen?
| 1. |
Red algae |
2. |
Blue-green algae |
| 3. |
Green algae |
4. |
Brown algae |
50. Which of the following is a correct statement regarding heterospory in the plant kingdom?
| 1. |
Heterospory is the condition where microspores and megaspores develop into male and female gametophytes respectively. |
| 2. |
Heterospory is the production of two types of male gametes within a single gametophyte. |
| 3. |
Heterospory is exclusive to gymnosperms and is absent in pteridophytes like Selaginella. |
| 4. |
The presence of heterospory has no relevance to seed habit in plants. |
51. Besides paddy fields, cyanobacteria are also found inside vegetative part of:
| 1. |
Cycas |
2. |
Equisetum |
| 3. |
Psilotum |
4. |
Pinus |
52. Match each item in
Column-I with one in
Column-II and select the correct match from the codes given:
|
Column-I |
|
Column-II |
| A. |
Phylogenetic classification |
P. |
based on cytological information like chromosome number, structure, behaviour |
| B. |
Chemotaxonomy |
Q. |
based on evolutionary relationships |
| C. |
Cytotaxonomy |
R. |
uses the chemical constituents of the plant |
Codes:
|
A |
B |
C |
| 1. |
Q |
R |
P |
| 2. |
Q |
P |
R |
| 3. |
P |
Q |
R |
| 4. |
R |
Q |
P |
53. Classification of organisms based on measurable similarities and differences rather than genetic makeup and evolutionary descent is called phenetics. What type of biological classification system does it belong to?
| 1. | Artificial | 2. | Phylogenetic |
| 3. | Cytotaxonomy | 4. | Numerical taxonomy
|
54. You do not expect to see flagella during the life cycle of:
| 1. | Spirogyra | 2. | Dictyota |
| 3. | Sargassum | 4. | Polysiphonia
|
55. One of the commercial products obtained from Gelidium and Gracilaria and which is used to grow microbes and in preparations of ice-creams and jellies is:
1. Agar
2. Algin
3. Carrageen
4. Inulin
56. Consider the following statements:
| I: |
Pteridophytes are the first terrestrial plants to possess vascular bundles. |
| II: |
Main plant body in pteridophytes is sporophyte which is differentiated into true stem and leaves. |
| III: |
Genera like Selaginella and Salvinia are heterosporous. |
Which of the above statements are true?
1. I and II only
2. I and III only
3. II and III only
4. I, II and III
57. What will be A, B and C in the given table?
|
Stored food |
Cell wall |
Flagellar insertions |
| Green algae |
Starch |
A |
2 – 8, equal, apical |
| Brown algae |
B |
Algin |
2, unequal lateral |
| Red algae |
C |
Polysulphate esters |
D |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1 |
Cellulose |
Laminarin and
Mannitol |
Laminarin and
Mannitol |
2, unequal, apical |
| 2 |
Cellulose |
Laminarin and
Mannitol |
Floridean
starch |
Absent |
| 3 |
Cellulose |
Floridean starch |
Laminarin and
Mannitol |
4, equal, apical
or lateral |
| 4 |
Algin |
Floridean starch |
Floridean starch |
Absent |
58. The life cycle of a moss includes two distinct phases. Which of the following is the correct description of these phases?
| 1. |
Protonema and gametophyte stage, both of which are diploid. |
| 2. |
Sporophyte and gametophyte stages, with the gametophyte being diploid. |
| 3. |
Protonema stage and leafy stage, both being parts of the gametophyte. |
| 4. |
Leafy stage and sporophyte stage, both independent and diploid. |
59. What is common in all the three,
Funaria,
Dryopteris and Ginkgo?
| 1. |
Presence of archegonia |
| 2. |
Well-developed vascular tissues |
| 3. |
Independent gametophyte |
| 4. |
Independent sporophyte |
60. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Equal weightage to vegetative and sexual characteristics in the artificial systems is not acceptable. |
| Reason (R): |
The sexual characters are more easily affected by environment. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) does not explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False but (R) is True |
61. Fucoxanthin is an important pigment in:
1. Red algae
2. Blue-green algae
3. Green algae
4. Brown algae
62. Consider the given two statements:
| Statement I: |
In Cycas, the pinnate leaves persist for a few years. |
| Statement II: |
In conifers, the needle-like leaves reduce the surface area helping to reduce water loss. |
1.
Statement I is correct but
Statement II is incorrect
2.
Statement I is incorrect but
Statement II is correct
3.
Statement I and
Statement II are correct
4.
Statement I and
Statement II are incorrect
63. Biflagellate zoospores that are pear-shaped and have two unequal laterally attached flagella are involved in:
| 1. |
Asexual reproduction in brown algae |
| 2. |
Asexual reproduction in red algae |
| 3. |
Sexual reproduction in brown algae |
| 4. |
Sexual reproduction in red algae |
64. Consider the two statements:
| Statement I: |
Systematics takes into account evolutionary relationships between organisms. |
| Statement II: |
Taxonomy takes into account only some easily observable external characters of organisms. |
1.
Statement I is correct;
Statement II is correct
2.
Statement I is incorrect;
Statement II is correct
3.
Statement I is correct;
Statement II is incorrect
4.
Statement I is incorrect;
Statement II is incorrect
65. Fragmentation and budding in the secondary protonema are means
of vegetative reproduction in:
1. Mosses
2. Liverworts
3. Vascular cryptogams
4. Thalloid green algae
66. Regarding pteridophytes:
| I: |
They are the first terrestrial plants to possess true vascular tissue |
| II: |
Main plant is sporophyte |
| III: |
Water is required for transfer of antherozoids |
1. Only
II is incorrect
2. Only
I is correct
3.
I and
II are incorrect
4.
I,
II and
III are correct
67. The leafy stage in the life cycle of mosses:
| 1. |
is a stage of the sporophytic generation. |
| 2. |
is a creeping, green, branched and frequently filamentous stage. |
| 3. |
develops directly from a spore. |
| 4. |
bears sex organs. |
68. Match the correct features with Pinus:
| I: |
Needle like Leaves |
| II: |
Reproduce by spores |
| III: |
Male and female cones on the same plant |
1. Only
I and
II
2. Only
I and
III
3. Only
II and
III
4.
I,
II and
III
69. Pteridophytes are considered important in the plant kingdom because they were the first plants to:
| 1. |
Develop seeds |
| 2. |
Form flowers |
| 3. |
Develop vascular tissue |
| 4. |
Produce fruits |
70. A ‘protonema’ stage in the life cycle of a moss is the:
| 1. |
first stage in gametophyte generation |
| 2. |
second stage in gametophyte generation |
| 3. |
first stage in sporophyte generation |
| 4. |
second stage in sporophyte generation |
71. Examine the figures A, B, C and D. In which one of the four options all the items, A, B, C and D are correct?

Options :
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1. |
Equisetum |
Ginkgo |
Selaginella |
Lycopodium |
| 2. |
Selaginella |
Equisetum |
Salvinia |
Ginkgo |
| 3. |
Funaria |
Adiantum |
Salvinia |
Riccia |
| 4. |
Chara |
Marchantia |
Fucus |
Pinus |
72. Bryophytes are often referred to as the amphibians of the plant kingdom because they:
1. Can live in soil but require water for reproduction
2. Have vascular tissues
3. Are exclusively aquatic
4. Can reproduce asexually via spores
73. Match each item in Column I with one in Column II and select the correct match from the codes given:
|
Column I
[Pteridophyte class] |
|
Column II
[Example] |
| A |
Psilopsida |
P |
Psilotum |
| B |
Lycopsida |
Q |
Adiantum |
| C |
Sphenopsida |
R |
Selaginella |
| D |
Pteropsida |
S |
Equisetum |
Codes:
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1. |
P |
R |
Q |
S |
| 2. |
P |
R |
S |
Q |
| 3. |
P |
S |
R |
Q |
| 4. |
Q |
S |
R |
P |
74. Consider the two statements:
| Statement I: |
Green algae are usually grass green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and b. |
| Statement II: |
Red algae vary in colour from olive green to various shades of brown depending upon the amount of fucoxanthin. |
1.
Statement I is correct;
Statement II is correct
2.
Statement I is incorrect;
Statement II is correct
3.
Statement I is correct;
Statement II is incorrect
4.
Statement I is incorrect;
Statement II is incorrect
75. How many of the given statements regarding the life cycle of mosses are true?
| I: |
The predominant stage of the life cycle of a moss is the gametophyte. |
| II: |
Protonema stage develops directly from a spore. |
| III: |
Leafy stage bears the sex organs. |
1. 0
2. 1
3. 2
4. 3
76. Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The leaves in gymnosperms are well-adapted to withstand extremes of temperature, humidity and wind |
| Reason (R): |
Unlike bryophytes and pteridophytes, in gymnosperms, the male and female gametophytes do not have an independent, free-living existence |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
77. Which of the following is not a feature of Red Algae?
| 1. |
r-phycoerythrin is a major pigment. |
| 2. |
Floridean starch is stored food. |
| 3. |
Cell wall contains poly sulphate esters. |
| 4. |
There are 2, unequal, lateral flagellar insertions. |
78. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Algae can reproduce by fragmentation, a type of vegetative reproduction. |
| Reason (R): |
Fragmentation involves the body of the algae breaking into pieces, each of which can develop into a complete organism. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
(A) is False but (R) is True. |
79. In Bryophytes, the __________ is the dominant phase, whereas in Pteridophytes, the __________ is the dominant phase.
1. sporophyte, gametophyte
2. gametophyte, sporophyte
3. zygote, spore
4. spore, zygote
80. Pteridophytes:
| I: |
evolutionarily are the first terrestrial plants to possess vascular tissues – xylem and phloem. |
| II: |
have gametophytes as the dominant generation in their life cycle. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
81. Match
List-I with
List-II
|
List-I |
|
List-II |
| (A) |
Pteropsida |
(I) |
Psilotum |
| (B) |
Lycopsida |
(II) |
Equisetum |
| (C) |
Psilopsida |
(III) |
Adiantum |
| (D) |
Sphenopsida |
(IV) |
Selaginella |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| Options: |
(A) |
(B) |
(C) |
(D) |
| 1. |
II |
III |
I |
IV |
| 2. |
III |
I |
IV |
II |
| 3. |
II |
III |
IV |
I |
| 4. |
III |
IV |
I |
II |
82. The correct statements regarding the life cycle seen in various algae will be:
| I. |
Most algal genera are haplontic |
| II. |
Genera such as Ectocarpus, Polysiphonia, and kelps are diplontic |
| III. |
Fucus is diplontic |
1. Only
I
2. Only
III
3. Only
I and
III
4.
I,
II and
III
83. Which group of plants is characterized by the presence of naked seeds, typically found on cones, and
lacks fruits and flowers?
1. Angiosperms
2. Pteridophytes
3. Gymnosperms
4. Bryophytes
84. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion(A): |
Artificial systems of classification of organisms are simple and acceptable to most scientists. |
| Reason (R): |
Artificial classification systems take into account the evolutionary relationships between living organisms. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True; (R) is False |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False |
85. In plant life cycle, the gametophyte is the generation that:
1. is diploid in genetic constitution
2. produces the gametes
3. produces the spores
4. has vascular tissue
86. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The artificial systems used for classification of living organisms are not very acceptable to taxonomists. |
| Reason (R): |
The artificial systems give more weightage to vegetative characteristics and no weightage to sexual characteristics and the sexual characteristics are easily affected by environment. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A). |
87. A dominant gametophyte will be seen in the life cycle of:
1. Marchantia
2. Sequoia
3. Adiantum
4. Eucalyptus
88. Regarding gymnosperms:
| I: |
Ovules are not enclosed by any ovary wall and remain exposed, both before and after fertilisation. |
| II: |
The seeds that develop post-fertilisation, are not covered, i.e., are naked. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
89. The giant redwood tree Sequoia, one of the tallest tree species, belongs to:
1. Pteridophytes
2. Gymnosperms
3. Angiosperms
4. Bryophytes
90. The sporophyte of mosses is more elaborate than that in:
| 1. |
Pteridophytes |
2. |
Gymnosperms |
| 3. |
Angiosperms |
4. |
Liverworts |
91. The leaves in pteridophyta are:
| 1. |
microphylls in Selaginella or macrophylls in ferns. |
| 2. |
macrophylls in Selaginella or microphylls in ferns. |
| 3. |
microphylls in Selaginella and ferns. |
| 4. |
macrophylls in Selaginella and ferns. |
92. Column I shows characteristics of members of Red algae. Match each item in Column I with the one in Column II and select the correct match from the codes given:
|
Column I |
|
Column II |
| A. |
Pigment |
P. |
Fucoxanthin |
| B. |
Stored food |
Q. |
Phycoerythrin |
| C. |
Cell wall |
R. |
Floridean starch |
| D. |
Flagella |
S. |
Laminarin |
|
|
T. |
Polysulfate esters |
|
|
U. |
Algin |
|
|
V. |
2-8. equal, apical |
|
|
W. |
Absent |
Codes:
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1. |
Q |
R |
T |
W |
| 2. |
P |
S |
U |
V |
| 3. |
Q |
R |
U |
W |
| 4. |
P |
S |
T |
V |
93. The classification system given by Bentham and Hooker is a/an:
| 1. |
Artificial system |
2. |
Natural system |
| 3. |
Phylogenetic system |
4. |
Useless system |
94. Unlike bryophytes and pteridophytes, in gymnosperms:
| I: |
the male and the female gametophytes do not have an independent free-living existence. |
| II: |
vascular tissues [xylem and phloem] are present. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
95. Porphyra, Sargassum and Laminaria are all:
| I: |
brown algae |
| II: |
marine edible algae |
1. Only I is correct
2. Only II is correct
3. Both I and II are correct
4. Both I and II are incorrect
96. In ferns, Meiosis takes place at the time of:
1. Spore formation
2. Spore germination
3. Gamete formation
4. Antheridia and archegonia formation
97. In angiosperms, the phylogenetic system of classification considers evolutionary relationships, assuming that organisms belonging to the same ________ share a common ________.
1. taxa, ancestor
2. family, habitat
3. class, species
4. order, trait
98. Which of the following is true regarding the classes of Bryophytes?
| 1. |
The thallus of mosses is dorsiventral and closely appressed to the surface |
| 2. |
In the life cycle of liverworts, the predominant gametophytic stage is divided into two stages - the protonema and the leafy stage |
| 3. |
The sporophyte in liverworts is more elaborate than in mosses |
| 4. |
Asexual reproduction in liverworts takes place by fragmentation of thalli, or by the formation of specialised structures called gemmae |
99. Identify the correct statement regarding the given figure:
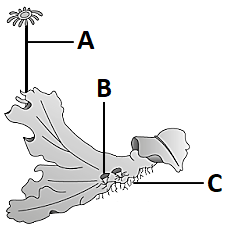
1. It shows the male thallus of
Marchantia.
2. A is antheridiophore.
3. B are used as asexual buds.
4. C are true roots and multicellular in organisation.
100. What is a critical difference between liverworts and mosses?
| 1. |
Presence of flagellated sperm cells in liverworts |
| 2. |
Presence of a cuticle in mosses |
| 3. |
Liverworts typically have a simple, flat body called a thallus that is often undifferentiated, whereas mosses have more complex, differentiated structures. |
| 4. |
Liverworts are vascular plants, mosses are not. |
101. Match the alga with the type of life cycle and select the correct match from the codes given:
|
Alga |
|
Type of life cycle |
| A. |
Spirogyra |
P. |
Haplontic |
| B. |
Fucus |
Q. |
Diplontic |
| C. |
Polysiphonia |
R. |
Haplo-diplontic |
Codes:
|
A |
B |
C |
| 1. |
P |
Q |
R |
| 2. |
P |
R |
Q |
| 3. |
Q |
P |
R |
| 4. |
R |
Q |
P |
102. Given are the following five statements (I - V) for your consideration:
| I: |
In Equisetum, the female gametophyte is retained on the parent sporophyte |
| II: |
In Ginkgo, the male gametophyte is not independent |
| III: |
The sporophyte in Marchantia is more developed than that in Polytrichum |
| IV: |
Sexual reproduction in Volvox is isogamous |
| V: |
The spores of slime moulds lack cell walls |
How many of the above statements is/are correct?
| 1. |
Three |
2. |
Four |
| 3. |
One |
4. |
Two |
103. An example of colonial alga is:
| 1. |
Volvox |
2. |
Ulothrix |
| 3. |
Spirogyra |
4. |
Chlorella |
104. The pattern where a dominant, independent, photosynthetic, thalloid or erect phase is represented by a haploid gametophyte and it alternates with the short-lived multicellular sporophyte totally or partially dependent on the gametophyte for its anchorage and nutrition is seen in:
1. Pteridophytes
2. Bryophytes
3. Gymnosperms
4. Angiosperms
105. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic feature of bryophytes?
A: Presence of vascular tissues.
B: Gametophyte dominance in the life cycle.
C: Water is necessary for fertilization.
1. Only A
2. Only A and B
3. Only C
4. A, B and C
106. Which statement accurately describes the difference between artificial and natural systems of classification?
| 1. |
Artificial systems utilize genetic similarities, whereas natural systems use morphological characteristics. |
| 2. |
Artificial systems classify organisms based on a few characteristics, while natural systems consider a large number of characteristics. |
| 3. |
Artificial systems classify organisms based on evolutionary relationships, while natural systems focus on ecological roles. |
| 4. |
Artificial systems are based on observable characteristics, while natural systems are more theoretical. |
107. Select the option where the given characters are correct match for members of Rhodophyceae:
|
Major pigments |
Stored food |
Cell wall |
Flagella |
| 1. |
Chlorophyll a, d; phycoerythrin |
Mannitol. Laminarin |
Cellulose, pectin, polysulphate esters |
2-8, equal, apical |
| 2. |
Chlorophyll a, d; phycoerythrin |
Floridean starch |
Cellulose, pectin, polysulphate esters |
Absent |
| 3. |
Chlorophyll a, c; Fucoxanthin |
Mannitol. Laminarin |
Cellulose and algin |
2, unequal, lateral |
| 4. |
Chlorophyll a, b; |
Starch |
Cellulose |
2-8, equal, apical |
108. What is incorrect regarding the prothallus of pteridophytes?
1. Inconspicuous, small but multicellular
2. Free-living
3. Mostly photosynthetic
4. Thalloid sporophyte
109. Match List-I with List-II:
|
List-I |
|
List-II |
| a. |
Cedrus |
(i) |
Pteridophyte |
| b. |
Adiantum |
(ii) |
Gymnosperm |
| c. |
Sphagnum |
(iii) |
Liverwort |
| d. |
Marchantia |
(iv) |
Moss |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
|
a |
b |
c |
d |
| 1. |
(ii) |
(iii) |
(i) |
(iv) |
| 2. |
(iii) |
(i) |
(iv) |
(ii) |
| 3. |
(ii) |
(i) |
(iv) |
(iii) |
| 4. |
(iii) |
(iv) |
(ii) |
(i) |
110. Unlike in bryophytes and pteridophytes, in gymnosperms:
| 1. |
vascular bundles are not present and hence they are limited to shady and moist habitats. |
| 2. |
water is needed for fertilisation and seed formation does not take place. |
| 3. |
all members are homosporous. |
| 4. |
the male and female gametophytes do not have an independent free-living existence. |
111. The term ‘strobilus’ in a gymnosperm defines a:
| 1. |
collection of megasporophylls |
| 2. |
collection of microsporophylls |
| 3. |
site of sporangial development |
| 4. |
collection of megasporophylls, microsporophylls and/or a site of sporangial development |
112. Isogamous sexual reproduction by non-flagellated gametes is seen in which of the following alga?
1. Chlamydomonas
2. Volvox
3. Spirogyra
4. Udorina
113. Identify the correct statement regarding gymnosperms:
1. They are always unisexual and never monoecious.
2. They bear flowers and fruits.
3. Their seeds are enclosed within an ovary wall.
4. They are heterosporous and produce naked seeds.
114. All the following are example of green alga except:
1. Ectocarpus
2. Chara
3. Ulothrix
4. Spirogyra
115. In gymnosperms:
| 1. |
gametophytes have an independent free-living existence |
| 2. |
pollen grains are transported by water |
| 3. |
pollen tubes are not seen |
| 4. |
seeds are not covered |
116.
| Statement I: |
Red algae do not occur in well-lighted regions close to the surface of water. |
| Statement II: |
Red algae reproduce by non-motile spores and non-motile gametes. |
| 1. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is correct |
| 2. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect |
| 3. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct |
| 4. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is incorrect |
117. Floridian starch has structure similar to :
1. Amylopectin and glycogen
2. Mannitol and algin
3. Laminarin and cellulose
4. Starch and cellulose
118. Red algae are characterized by:
| 1. |
Having chlorophyll a and b |
| 2. |
Storing food as starch |
| 3. |
Their red color due to the pigment phycoerythrin |
| 4. |
Floating freely in fresh water habitats |
119. Match each item in
Column-I with one in
Column-II and select the correct match from the codes given:
|
Column-I |
|
Column-II |
| A. |
The gametes are flagellated and similar in size |
P. |
Eudorina |
| B. |
The gametes are non-flagellated (non-motile) but similar in size |
Q. |
Ulothrix |
| C. |
The female gametes are larger and flagellated, while the male gametes are smaller and flagellated |
R. |
Fucus |
| D. |
One large, non-motile (static) female gamete and a smaller, motile male gamete |
S. |
Spirogyra
|
Codes:
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1. |
S |
Q |
P |
R |
| 2. |
Q |
S |
P |
R |
| 3. |
Q |
S |
R |
P |
| 4. |
S |
Q |
R |
P |
120. The given diagram shows:

1. Female gametophyte of
Marchantia
2. Male gametophyte of
Marchantia
3. Female gametophyte of
Funaria
4. Male gametophyte of
Funaria
121. From an evolutionary point of view, retention of the female gametophyte with developing young embryo on the parent sporophyte for some time, is first observed in:
| 1. |
Gymnosperms |
2. |
Liverworts |
| 3. |
Mosses |
4. |
Pteridophytes |
122. What would be correct for the members of green algae?
| 1. |
Main photosynthetic pigments are chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. |
| 2. |
Cell wall has a deposition of algin. |
| 3. |
Stored food is laminarin and mannitol. |
| 4. |
There are no flagella in the life cycle of green algae. |
123. What term is used to describe the diploid, spore-producing phase of the plant life cycle that alternates with the haploid, gamete-producing phase?
| 1. |
Gametophyte |
2. |
Sporophyte |
| 3. |
Protonema |
4. |
Thallus |
124. In
Cycas:
| I: |
coralloid roots are associated with N2-fixing cyanobacteria |
| II: |
the stems are unbranched |
| III: |
the pinnate leaves persist for a few years |
| 1. |
Only I and II are correct |
| 2. |
Only I and III are correct |
| 3. |
Only II and III are correct |
| 4. |
I, II and III are correct |
125. Asexual reproduction in brown algae is by:
| 1. |
biflagellate biconcave disc shaped zoospores |
| 2. |
non-motile spherical aplanogametes |
| 3. |
biflagellate pear shaped zoospores |
| 4. |
non-motile zoospores produced in zoosporangia |
126. Which pigment is predominantly found in red algae and contributes to their distinctive coloration?
1. Chlorophyll a
2. Phycoerythrin
3. Carotenoids
4. Xanthophylls
127. Which of the following distinguishes the life cycle of pteridophytes from that of bryophytes?
| 1. |
The main plant body in pteridophytes is haploid, while in bryophytes it is diploid. |
| 2. |
In pteridophytes, the gametophyte is independent, while in bryophytes the sporophyte is independent. |
| 3. |
Pteridophytes have a dominant sporophyte generation, while bryophytes have a dominant gametophyte generation. |
| 4. |
Bryophytes possess well-differentiated vascular tissues, unlike pteridophytes. |
128. The class of pteridophytes to which Selaginella belongs is:
1. Psilopsida
2. Sphenopsida
3. Lycopsida
4. Pteropsida
129. Consider the two statements:
| Statement I: |
The gymnosperms are plants in which the ovules are not enclosed by any ovary wall and remain exposed, both before and after fertilisation. |
| Statement II: |
The seeds that develop post-fertilisation, are not covered, i.e., are naked. |
1.
Statement I is correct;
Statement II is incorrect
2.
Statement I is incorrect;
Statement II is incorrect
3.
Statement I is correct;
Statement II is correct
4.
Statement I is incorrect;
Statement II is correct
130. Identify the algal group:
| I: |
They possess chlorophyll a, c, carotenoids and xanthophylls. |
| II: |
Food is stored as complex carbohydrates, which may be in the form of laminarin or mannitol. |
1. Green algae
2. Brown algae
3. Red algae
4. Blue-green algae
131. The reduced male gametophyte in a gymnosperm is called a:
| 1. |
pollen grain |
2. |
microsporangium |
| 3. |
microsporophyll |
4. |
antheridium |
132. Which of the following pairs is of unicellular algae?
1. Gelidium and Gracilaria
2. Anabaena and Volvox
3. Chlorella and Spirulina
4. Laminaria and Sargassum
133. Identify the incorrectly matched pair:
|
Pteridophyte class |
Example |
| 1. |
Psilopsida |
Adiantum |
| 2. |
Lycopsida |
Lycopodium |
| 3. |
Sphenopsida |
Equisetum |
| 4. |
Pteropsida |
Dryopteris |
134. Identify the incorrectly matched pair:
| 1. |
Phylogenetic classification systems |
Based on evolutionary relationships |
| 2. |
Numerical Taxonomy |
Based on all observable characteristics |
| 3. |
Cytotaxonomy |
Based on a few vegetative characters only. |
| 4. |
Chemotaxonomy |
Uses the chemical constituents of the plant |
135. Which of the following is a comparison between Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms?
| 1. |
Both reproduce sexually through seeds. |
| 2. |
Pteridophytes have a well-developed vascular system, whereas gymnosperms do not. |
| 3. |
Pteridophytes reproduce through spores, while gymnosperms reproduce through seeds. |
| 4. |
Both are non-flowering plants that reproduce asexually. |
*If above link doesn't work, please go to test link from where you got the pdf and fill OMR from there
CLICK HERE to get FREE ACCESS for 2 days of ANY NEETprep course







