What is the percentage of photosynthetic active radiation [PAR] in the incident solar radiation?
1. 100 %
2. 50%
3. 1-5%
4. 2-10%
Given below is a simplified model of phosphorus cycling in a terrestrial ecosystem with
four blanks (A-D). Identify the blanks.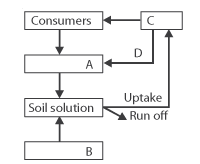
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1. | Rock minerals | Detritus | Litterfall | Producers |
| 2. | Litterfall | Producer | Rock minerals | Detritus |
| 3. | Detritus | Rock minerals | Producer | Litterfall |
| 4. | Producer | Litterfall | Rock minerals | Detritus |
Which one of the following is not a functional unit of an ecosystem?
1. Energy flow
2. Decomposition
3. Productivity
4. Stratification
Of the total incident solar radiation the proportion of PAR is
1. about 60%
2. less than 50%
3. more than 80%
4. about 70%
Which of the following is false?
I. Quantity of biomass in a trophical level at a particular period is called standing crop.
II. The energy content in a trophic level is determined by considering a few individuals of a species in that trophic level.
III. The succession that occurs in nearly cooled lava is called primary succession.
IV. Rate of succession is faster in the secondary succession
V. Phytoplankton are the pioneers in aquatic succession
1. Only II
2. Only III
3. Only V
4. Only I and IV
Read the following statements carefully.
(i) Primary succession is a very slow process taking thousands of years for the climax to reach.
(ii) Energy at a higher trophic level is always more than that at a lower level.
(iii) Bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances. This process is called fragmentation.
(iv) All succession, whether taking place in water or on land, proceeds to a similar climax community - the mesic.
Which of the two above statements are correct?
1. (i) and (ii)
2. (ii) and (iii)
3. (i) and (iv)
4. (iii) and (iv)
Primary productivity of an terrestrial ecosystem depends upon
1. Photosynthetic capacity of plants.
2. A variety of environmental factors,
3. Availability of nutrients
4. All of the above.
What is the process by which Detritivores break down the detritus into smaller particles.?
1. Degradation
2. Decomposition
3. Fragmentation
4. Leaching
“Detritus food chain may be connected with the grazing food chain at some levels”. This is evident from
| i: | Some of the organisms of DFC are prey to the GFC animals |
| ii: | In a natural ecosystem, some animals like cockroaches, crows, etc., are omnivores. |
| iii: | Some of the organisms of GFC are facultative decomposers |
1. i and iii
2. i and ii
3. ii and iii
4. i only
Why does the pyramid of energy always upright?
1. Because energy cannot be destroyed.
2. Smaller organisms have more potential energy than larger ones
3. Because when energy flows from a particular trophic level to the next trophic level, some energy is always lost as heat at each step.
4. More than one statement is correct.
Standing state does not vary in-
1. Different kinds of ecosystems
2. A seasonal basis
3. Different kinds of soil
4. Same kind of ecosystem.
In the hydrosere the reed-swamp stage is followed by
1. Marsh-meadow stage
2. Submerged free floating plant stage
3. Submerged plant stage
Organisms that are capable of conversion of inorganic material into organic material with the help of the radiant energy of the sun include:
| I: | Plants |
| II: | Photosynthetic bacteria |
| III: | Chemosynthetic bacteria |
| 1. | I only | 2. | I and II only |
| 3. | I and III only | 4. | I, II, and III |
Approximately, what percent of energy is transferred to each trophic level from the lower trophic level in an ecosystem?
| 1. | 1 | 2. | 10 |
| 3. | 50 | 4. | 90 |
Regarding phosphorus cycle:
| I: | There is no respiratory release of phosphorus into atmosphere |
| II: | Atmospheric inputs of phosphorus through rainfall of phosphorus is small |
1. Only I is true.
2. Only II is true.
3. Both I and II are true.
4. Both I and II are false.
Approximately how much of the solar energy that falls on the leaves of a plant is converted to chemical energy by photosynthesis?
| 1. | Less than 1% | 2. | 2-10 % |
| 3. | 30 % | 4. | 50 % |
In any ecological pyramid, an organism can occupy how many trophic levels?
1. Only one trophic level
2. More than one trophic level simultaneously
3. Can occupy more than one trophic level but not simultaneously
4. Very difficult to say in a precise manner
Consider the two statements:
| I: | Food chains rarely extend for more than 4 or 5 levels. |
| II: | Consumers at each level convert, on an average, only about 10% of the chemical energy in their food to their own organic tissue. |
1. Both I and II are correct and II explains I.
2. Both I and II are correct but II does not explain I.
3. Only I is correct.
4. Both I and II are incorrect.
In a food chain, the transition from an earlier trophic level to the next trophic level will lead to:
| 1. | a gain of 50% of energy | 2. | a gain of 1% of energy |
| 3. | a loss of 90% of energy | 4. | a loss of 10% of energy |
Select the correct statement
1. The number of trophic levels in the GFC is never restricted
2. GFC is major conduit of energy flow in a terrestrial ecosystem
3. Some of the organisms of DFC are prey to the animals of GFC
4. In a natural ecosystem, some organisms are omnivores, like fungi and actinomycetes
Primary consumers in the pioneer community of hydrarch succession are
(1) Cyanobacteria
(2) Small fishes
(3) Zooplanktons
(4) Aquatic fungi
| 1. | It occurs only through the process of photosynthesis. |
| 2. | Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. |
| 3. | Net primary production is available for consumption by herbivores. |
| 4. | Gross primary productivity minus the respiratory loss is the net primary productivity. |
| 1. | begins with primary producers like grass |
| 2. | is the major conduit for energy flow in an aquatic ecosystem |
| 3. | is not made up of any decomposers |
| 4. | may be connected with the grazing food chain at some levels |
| Statement I: | Standing state is the amount of inorganic nutrients found in an ecosystem and it varies on a seasonal basis |
| Statement II: | Standing crop is the mass of living matter in an ecosystem and it tends to be more readily apparent in terrestrial environment as compared to aquatic environment |
| 1. | Standing state | 2. | Standing crop |
| 3. | Humus | 4. | Detritus |
| Assertion (A): | Pyramid of energy is always upright, can never be inverted. |
| Reason (R): | When energy flows from a particular trophic level to the next trophic level, some energy is always lost as heat at each step. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |
| 1. | 25 | 2. | 33 |
| 3. | 66 | 4. | 70 |

| I: | It represents an ideal pyramid of energy in an ecosystem. |
| II: | Primary producers convert only 1% of the energy in the sunlight available to them into NPP. |
| 1. | Only I | 2. | Only II |
| 3. | Both I and II | 4. | Neither I nor II |
| 1. | Pyramid of numbers |
| 2. | Pyramid of biomass |
| 3. | Pyramid of energy |
| 4. | All ecological pyramids can be inverted |