Consider the following features:
| I. | Chlorophyll a and Chlorophyll c |
| II. | Fucoxanthin |
| III. | Floridean starch |
| IV. | Flagella 2 in number, unequal and lateral |
Which of these are seen in Phaeophyceae?
1. I, II, III
2. I, II, IV
3. II, III, IV
4. I, II, III, IV
Identify the incorrectly matched pair:
| 1. | Chlamydomonas: | Microscopic unicellular algae |
| 2. | Volvox: | Colonial algae |
| 3. | Ulothrix: | Filamentous algae |
| 4. | Fucus: | Isogamous algae |
Viroids differ from viruses in having
1. DNA molecules with protein coat
2. DNA molecules without protein coat
3. RNA molecules with protein coat
4. RNA molecules without protein coat
Life cycle of Ectocarpus and Fucus respectively are
(1) Haplontic, Diplontic
(2) Diplontic, Haplodiplontic
(3) Haplodiplontic, Diplontic
(4) Haplodiplontic, Haplontic
Read the following statements (IV) and answer the question which follows them
| I. | In liverworts, mosses and ferns gametophytes are free living. |
| II. | Gymnosperms and some ferns are heterospores. |
| III. | Sexual reproduction in Fucus, Volvox and Albugo is oogamous. |
| IV. | The sporophyte in liverworts is more elaborate than that in mosses. |
How many of the above statements are correct?
1. One
2. Two
3. Three
4. Four
If you are asked to classify the various algae into distinct groups, which of the following characters you should choose?
1. Types of pigments present in the cell
2. Nature of stored food materials in the cell
3. Structural organisation of thallus
4. Chemical composition of the cell wall
The fruiting bodies of Agaricus are also known as
1. cleistothecium
2. fairy rings
3. basidiocarp
4. ascocarp
SER and RER can be distinguished with its presence in
| 1. | protein synthesising cells |
| 2. | protein and fat synthesising cells |
| 3. | carbohydrates and fat synthesising cells |
| 4. | lipid and protein synthesising cells |
The total DNA content of each daughter cell is reduced during meiosis because:
| 1. | Chromosomes do not replicate during the interphase preceding meiosis I |
| 2. | Chromosomes do not replicate between meiosis I and II |
| 3. | Half of the chromosomes from each gamete are lost during fertilization |
| 4. | Chromosome arms are lost during crossing over |
In membranes, the lipids are arranged within the membrane with the ______heads towards the outer sides and the _________ tails towards the inner part.
(1)polar, charged
(2)polar, hydrophobic
(3)polar, nonpolar
(4)Both B and C
If meiosis in zygote results in haploid spores, then ploidy of adult cells should be-
a. Haploid
b. Diploid
c. Dikaryon
d. None of the above
Dikaryophase of fungus is-
| 1. | Two nuclei per cell |
| 2. | Diploid nucleus |
| 3. | Two nuclei per mycelium |
| 4. | More than one options are correct. |
Read the following statements :
| A. | The male or female cones or strobili may be borne on same tree in Pinus. |
| B. | In Cycas male cones and megasporophylls are borne on different trees. |
| C. | Stem of Cycas is branched and of Pinus and Cedrus is unbranched. |
| D. | In gymnosperms generally tap roots are found. |
Select the correct statements.
1. A, B
2. A, B, D
3. A, B, C
4. C, D
Read the following statements.
(a) Gymnosperms are heterosporous.
(b) Bryophytes have well developed vessels and sieve tubes.
(c) Strobilus is found in the main plant body of Equisetum.
(d) Antheridia are absent but archegonia are present in female storobil of gymnosperms.
Choose the correct option.
1. All of these 2. (a), (c) and (d)
3. Only (a) 4. (b) and (c)
The most dramatic period of the cell cycle is
| 1. | Prophase | 2. | M phase |
| 3. | S phase | 4. | G1 phase |
Algae is not
| 1. | Chlorophyll-bearing |
| 2. | Simple Thalloid |
| 3. | Mainly Fresh water |
| 4. | Largely Aquatic |
Asexual reproduction is by the production of different types of spores. Out of that most common is
| 1. | Carpospore | 2. | Zoospores |
| 3. | Basidiospores | 4. | Akinetes |
| 1. | Pachytene | 2. | Diplotene |
| 3. | Diakinesis | 4. | Zygotene |
State True (T) or False (F) to the given statements and select the correct option
| (A) | Abundance of lichens in any area indicates that the area is highly polluted with SO2. |
| (B) | Mycobiont partner of lichens is always heterotrophic. |
| (C) | Body of lichens is made up of phycobionts only. |
(A) (B) (C)
1. T T F
2. F T F
3. F F F
4. T F F
Which one of the following living organisms completely lacks a cell wall?
1. Cyanobacteria
2. Sea- fan (Gorgonia)
3. Saccharomyces
4. Green algae
Which of the following is the correct sequence / route of the secretory product?
| 1. | ER Vesicles Cis region of GB Trans region of GB Vesicle Plasma membrane. |
| 2. | RER GB Lysosome Nuclear membrane Plasma membrane. |
| 3. | ER Vesicles Trans region of GB Cis region of GB Vesicles Plasma membrane. |
| 4. | Lysosome ER GB Vesicles Cell membrane. |
Consider the following statements:
| I: | G0 phase is viewed as either an extended G1 phase where the cell is neither dividing nor preparing to divide or as a distinct quiescent stage which occurs outside of the cell cycle. |
| II: | In gamete production interphase is succeeded by meiosis. |
| III: | In programmed cell death interphase is followed or preempted by apoptosis. |
The correct statements include:
| 1. | II and III | 2. | I and III |
| 3. | I, II, and III | 4. | I only |
Each pole receives half the chromosome number of the
parent cell, is true for which stage?
1. Anaphase - II
2. Anaphase - I
3. Telophase-I
4. Telophase-II
According to the five-kingdom classification system, which of the following kingdom has multicellular/loose tissue level body organization?
1. Protista
2. Plantae
3. Animalia
4. Fungi
Which of the following is not associated with chloroplast of higher plants?
1. Thylakoid
2. Grana
3. Quantasome
4. Pyrenoids
Chromatin condensation and movement of duplicated centriole towards opposite pole can be observed during -
| 1. | Prophase | 2. | Metaphase |
| 3. | Anaphase | 4. | Telophase |
The synthesis of spindle proteins occurs during
1. -phase
2. S-phase
3. -phase
4. M-phase
Movement of ions or molecules against the prevailing direction of the electrochemical gradient is
| 1. | Diffusion |
| 2. | Passive transport |
| 3. | Active transport |
| 4. | Pinocytosis |
X-ray crystallography is useful in the study of
| 1. | Lipid structure |
| 2. | Three-dimensional structure of proteins |
| 3. | Arrangement of proteins |
| 4. | Composition of nucleic acids and proteins |
The characteristic pigment found in brown algae is
| 1. | Phycocyanin |
| 2. | Fucoxanthin |
| 3. | Phycoerytherin |
| 4. | Haematochrome |
The primary cell wall is the part of a eukaryotic cell wall which is
| 1. | closest to the inside of the cell |
| 2. | in the middle of the cell wall |
| 3. | the farthest outside of the cell |
| 4. | the strongest of the three layers |
Consider the following statements:
| I: | The centromere is termed as the primary constriction of a chromosome |
| II: | The secondary constrictions are always constant in their positions |
| III: | The chromosomes having a satellite are marker chromosomes |
| IV: | The chromosomes bend at the secondary constrictions when they are pulled at anaphase |
Which of the above statements are true?
1. I, II and III
2. I and III
3. II, III and IV
4. I, II, III and IV
Which stage of the mitotic division in a cell shown in the options depicts a ‘transition’ to metaphase?
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Choose the incorrectly matched pair:
1. Ulothrix – Zygote is single celled diploid generation
2. Spirogyra – Zygote is a resistant structure
3. Cycas – Coralloid roots
4. Fucus – Isogametes
Identify the following statements as true (T) or false (F) and select the option accordingly
| (A) | Members of Rhodophyceae asexually reproduce by motile spores |
| (B) | Members of Phaeophyceae do not show isogamous type of sexual reproduction |
| (C) | In some green algae, food is stored in the form of oil droplets |
| (A) | (B) | (C) | |
| 1. | T | F | T |
| 2. | F | F | F |
| 3. | F | F | T |
| 4. | T | T | F |
Which disease of man is similar to cattle's, bovine spongiform encephalopathy:
| 1. | Encephalitis | 2. | Jacob-Creutzfeldt disease |
| 3. | Spongiocitis of cerebrum | 4. | Spondylitis |
The cell organelle capable of digesting carbohydrates, proteins & lipids
| (a) | is lysosomes |
| (b) | contains enzymes which are optimally active at acidic pH |
| (c) | is a type of microbody |
1. (a) and (b)
2. (b) and (c)
3. (a) and (c)
4. (a), (b) and (c)
| 1. | Anaphase I | 2. | Telophase I |
| 3. | Anaphase II | 4. | Telophase II |
Identify the fungi which do not belong to the group of other fungi among the following:
| 1. | Sac-fungi | 2. | Puffballs |
| 3. | Mushrooms | 4. | Bracket Fungi |
| 1. | anaphase in Meiosis I |
| 2. | anaphase in Mitosis |
| 3. | metaphase in Mitosis |
| 4. | metaphase in Meiosis II |
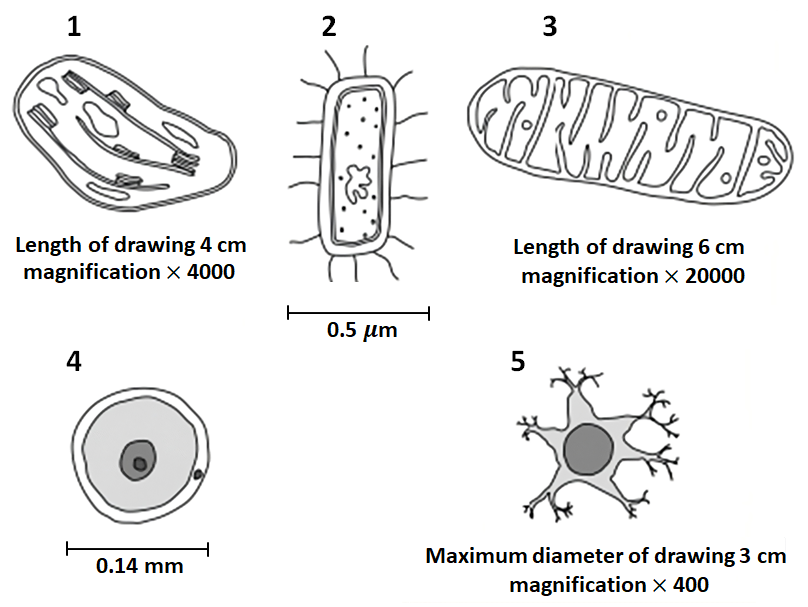
| 1. | 4 | 2. | 5 |
| 3. | 1 | 4. | 2 |
| a. | Polymerisation of amino acids |
| b. | Formation of glycoproteins |
| c. | Modification of proteins |
| Assertion (A): | Plant and animal kingdoms have been constant under all different classification systems. |
| Reason (R): | The understanding of what groups/organisms are included under these kingdoms have been changing over the time. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
| Phycomycetes | Basidiomycetes | ||
| 1. | Mycelium | Branched and septate | Aseptate and coenocytic |
| 2. | Asexual spores | Zoospores or aplanospores | Generally not found |
| 3. | Notable examples | Bread mould and Albugo | Rust and Smut fungi |
| 4. | Dikaryon stage |
Not seen | Present |
| Assertion (A): | In anaphase stage chromatids move to opposite poles. |
| Reason (R): | Anaphase is the shortest phase. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |
| A | B | |
| 1. | Respiration | Photosynthesis |
| 2. | Cell wall formation | DNA replication |
| 3. | Photosynthesis | Respiration |
| 4. | DNA replication | Secretion process |
| Assertion (A): | In basidiomycetes, basidiospores are produced endogenously in the basidium |
| Reason (R): | In ascomycetes, ascospores are produced exogenously in ascus |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
| Statement I: | At Metaphase I the chromosomes align at the equator and the microtubules from opposite poles of the spindle get attached to the kinetochores of sister chromatids. |
| Statement II: | At metaphase II the bivalent chromosomes align on the equatorial plate and microtubules from the opposite poles of the spindle attach to the kinetochore of homologous chromosomes. |
| 1. | Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect. |
| 2. | Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is incorrect. |
| 3. | Statement I is correct and Statement II is correct. |
| 4. | Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is correct. |
What keeps the lungs inflated even during expiration?
1. The smooth muscles of the lung
2. The diaphragm and the intercostal muscles alone
3. The visceral pleurae and the changing volume of the lungs
4. Surface tension from pleural fluid and negative pressure in the pleural cavity
A person passes a lot of dilute urine and drinks a lot of water but does not have glycosuria. He is most likely suffering from :
1. Type 1 diabetes mellitus
2. Type 2 diabetes mellitus
3. Pituitary diabetes
4. Diabetes insipidus
Select the correct route for the passage of sperms in the male frogs.
(1) Testis → Bidder's canal → Kidney → Vasa efferentia → Urinogenital duct → Cloaca
(2) Testis → Vasa efferentia → Kidney → Seminal Vesicle → Urinogenital duct → Cloaca
(3) Test → Vasa efferentia → Bidder's canal → Ureter → Cloaca
(4) Testis → Vasa efferentia → Kidney → Bidder's canal → Urinogenital duct → Cloaca
Which of the following does not favor the formation of large quantities of dilute urine?
1. Alcohol
2. Caffeine
3. Renin
4. Atrial-natriuretic factor
In human body, which one of the following is anatomically correct ?
1. Floating ribs-2 pairs
2. Collar bones-3 pairs
3. Salivary glands-1 pair
4. Cranial nerves-10 pairs
Which of the following process of urine formation takes place all along the renal tubule and collecting duct?
1. Ultrafiltration and tubular reabsorption
2. Ultrafiltration and tubular secretion
3. Tubular reabsorption and secretion
4. Anti-current mechanism and reabsorption
Which tissue in the tubular parts of nephrons provide the function of secretion and absorption ?
(1) Simple squamous epithelium
(2) Glandular epithelium
(3) Cuboidal epithelium
(4) Ciliated columnar epithelium
A, B, C, D and E in the following diagram are :
(1) Small tubules, seminal vesicle, right phallomere, titillator, left phallomere
(2) Small tubules, seminal vesicle, left phallomere, titillator, right phallomere
(3) Small tubules, phallic gland, right phallomere, pseudopenis, left phallomere
(4) Small tubules, seminal vesicle, ventral phallomere, titillator, left phallomere
What is the main tissue type comprising tendons and ligaments?
1. loose connective
2. fibrous connective
3. cartilage
4. reticular connective
Which of the following layers comes first when one goes from outside to the inside of Bowman's capsule?
1.Endothelium
2.Epithelium of Bowman's Capsule
3.Basement Membrane
4.Macula Densa layer
Which of the following substances are not reabsorbed by passive means of transport in tubules?
1.Water
2.Nitrogenous waste
3.Glutamate
4.Urea
The release of urine does not take place by
(1) Contraction of smooth muscles of the bladder
(2) Simultaneous relaxation of urethral sphincter
(3) Relaxation of smooth muscels of the bladder
(4) Both B and C
The tentacles of Hydra do not help in
1. Capturing prey
2. Locomotion
3. Movement of water out of the body
4. Both A and C
The partial pressure of CO2 is minimum in the
1. atmospheric air
2. Alveoli
3. Deoxygenated blood
4. Oxygenated blood
Sliding filament theory can be best explained as
1. when myofilaments slide pass each other actin filaments shorten while myosin filament do not shorten
2. actin and myosin filaments shorten and slide pass each other
3. actin and myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide pass each other
4. when myofilament slide pass each other myosin filament shorten while actin filaments do not shorten
Normal activities of the human heart are regulated:
1. Intrinsically
2. By the autonomic nervous system
3. By the brain stem
4. By the diencephalon
Lymph has the following
(i) Same mineral distribution as that of plasma
(ii) Intestine also has lymph
(iii) Also known as tissue fluid because it helps in exchange
(iv) Lymph plays role in defence as well
How many statements are correct?
1. 3
2. 2
3. 4
4. 1
The greater the number of blood vessels dilated, the ________.
1. higher the blood pressure
2. lower the blood pressure
3. faster the heartbeat
4. slower the heartbeat
Assertion (A): Hibernation during winter and aestivation during summer is seen in frogs.
Reason (R): Frogs are poikilotherms.
(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation for A.
(2) Both A and R are true both R is not the correct explanation for A.
(3) A is true and R is false.
(4) A is false and R is true.
Identify the incorrect statement regarding anatomy of human kidney:
| 1. | Adrenal gland is located at the inferior pole of each kidney |
| 2. | Columns of Bertini are extensions of cortex into medulla |
| 3. | Right kidney is slightly lower in location than the left kidney |
| 4. | The renal pelvis continues into the ureter |
Which is not correctly matched?
1. Malpighian tubules - Cockroaches, Mosquito
2. Antennal glands - Planaria, Crab
3. Nephridia - Earthworm
4. Protonephridia - Amphioxus
The thickness of the respiratory membrane is approximately
(1) 1 micron
(2) 2 micron
(3) 0.2 mm
(4) 2 mm
Identify the disease characterized by an abnormal, permanent enlargement of air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles, coupled with the destruction of walls, but without obvious fibrosis.
(1) asthma
(2) emphysema
(3) pulmonary fibrosis
(4) pneumothorax
Cilia in the trachea and bronchi:
(1) move air into and out of the lungs
(2) increase the surface area for gas exchange
(3) filter the air that rushes through them
(4) sweep mucus with its trapped particles up and out of the respiratory tract
During muscle contraction the heads of the cross-bridges bind with the ATP:
(1) before contraction begins
(2) just after the contraction begins
(3) midway during the contraction
(4) towards the end of the contraction
The only unpaired bone in the facial skeleton is the:
(1) Palatine
(2) Inferior nasal concha
(3) Lacrimal
(4) Vomer
In a contracted skeletal muscle fiber
1. M line disappears
2. H-zone elongates
3. l-band remains constant
4. A-band disappears
Cardiac muscle fibres are
1. Striated and involuntary
2. Striated and voluntary
3. Non-striated and involuntary
4. Non-striated and voluntary
Match the following columns.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| A. | Proximal convoluted tubule. | 1. | Formation of concentrated urine |
| B. | Distal convoluted tubule | 2. | Filtration of blood |
| C. | Henle’s loop | 3. | Reabsorption of 70-80% of electrolytes |
| D. | Counter current mechanisms | 4. | lonic balance |
| E. | Renal corpuscle | 5. | Maintenance of concentration gradient in medulla. |
Codes
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| 1. | 3 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 2. | 3 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
| 3. | 1 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| 4. | 3 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 2 |
Oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin will shift to right of normal curve if
1. Temperature decreases
2. CO decreases
3. pH decreases
4. BPG is low
| 1. | Pavo | 2. | Ornithorhynchus |
| 3. | Salamandra | 4. | Hippocampus |
| (a) | Locomotion, changes of body postures and heat production are some of the functions of skeletal muscle tissue |
| (b) | Actin filaments are firmly attached to the Z-line |
| (c) | The portion of myofibril between non-consecutive 'Z' lines is called sacromere |
| (d) | Muscles constitute more than 50% of the body weight in an adult human |
| a | b | c | d | |
| 1. | T | T | T | T |
| 2. | T | F | F | T |
| 3. | T | T | F | F |
| 4. | F | T | T | T |
| Assertion (A): | Human heart is myogenic. |
| Reason (R): | Entire human heart is made up of a cardiac muscles. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
| 1. | Is composed of corpuscles but lack plasma |
| 2. | Contains RBCs, WBCs and platelets or thrombocytes and plasma |
| 3. | Contains RBCs which are oval, biconvex and nucleated |
| 4. | Is related to more than one option mentioned above |
| Assertion (A): | Role of oxygen in regulation of respiratory rhythm centre is quite insignificant. |
| Reason (R): | Chemosensitive area situated adjacent to respiratory rhythm centre is highly sensitive to CO2 and H+ ion concentration and not to O2. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |
| Statement I: | Morphology refers to the form and structure of animals and plants, studied as a science. |
| Statement II: | Anatomy is concerned with the identification and description of the body structures of living things. |
| I: | closure of semilunar valves occurs. |
| II: | the tricuspid and bicuspid valves are pushed open. |
| (A) | Pulmonary circulation starts by the pumping of deoxygenated blood from right ventricle into lungs and its retun in oxygenated form to right atrium |
| (B) | Systemic circulation starts with pumping of oxygenated blood from left ventricle through aorta to all body systems and return of the blood in deoxygenated form into left atrium through veins |
| Column I | Column II | ||
| a. | Bicephalic ribs | (i) | Lack of relaxation between successive stimuli in sustained muscle contractions |
| b. | Hyaline cartilage | (ii) | 12 in number in an adult man |
| c. | Tetanus | (iii) | Chondroitin salts and lacunae |
| d. | Thoracic vertebrae | (iv) | Rapid spasms in muscle due to low Ca++ in the body fluid |
| (v) | 12 pairs in number in adult human |

| 1. | it is made up of special cardiac muscle. |
| 2. | it is richly innervated by autonomic nerve fibres. |
| 3. | it is located in the posterior wall of the right atrium. |
| 4. | it depolarizes at the fastest rate out of the whole nodal tissue. |
For the energy levels in an atom, which one of the following statements is correct?
1. There are seven principal electron energy levels
2. The second principal energy level can have two 'sub energy levels and contains a maximum of eight electrons
3. The energy level can have a maximum of 32 electrons
4. The 4s sub-energy level is at higher energy than the 3d sub-energy level
The oxidation number of carbon in C3O2 and Mg2C3 are respectively:
1. -4/3, +4/3
2. +4/3, -4/3
3. -2/3, +2/3
4. -2/3, +4/3
The work function of a metal is 4.2 eV. If radiations of 2000 fall on the metal then the kinetic energy of the fastest photoelectron is
1. 1.6 x 10-19J
2. 16 x 1010J
3. 3.2 x 10-19J
4. 6.4 x 10-10J
The mass of CO2 that shall be obtained by heating 10 kg of 80 % pure limestone (CaCO3) is:
1. 4.4 kg
2. 6.6 kg
3. 3.52 kg
4. 8.8 kg
The element having very high electron affinity but zero ionisation enthalpy is:
1. He (due to inert gas configuration)
2. Be (due to fully filled subshell)
3. H (due to presence of allotropes)
4. None of the above
An ideal gas expands at a constant external pressure of 2.0 atmosphere by 20 litre and absorbs 10kJ of heat from surrounding. What is the change in internal energy of the system:-
(1) 4052 J
(2) 5948 J
(3) 14052 J
(4) 9940 J
One mole of methanol when burnt in O2 gives out 723 kJ mol-1 of heat. If one mole of O2 is used, what will be the amount of heat evolved?
1. 482 kJ
2. 241 kJ
3. 723 kJ
4. 924 kJ
The total number of electrons present in 1.6 gm. of methane is [IIT 1976; Roorkee 1985; CPMT 1987, 92]
(1) 6.02 × 1023
(2) 6.02 × 1022
(3) 6.02 × 1021
(4) 4.02 × 1020
10 g of hydrogen and 64 g of oxygen were filled in a steel vessel and exploded. The amount of water produced in this reaction will be:
1. 2 mol
2. 3 mol
3. 4 mol
4. 1 mol
The number of mole of KMnO4 that will be needed to react with one mole of sulphite ion in acidic solution is:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4) 1
Which of the following statements is not true regarding the expansion of one mole of an ideal gas that expands freely and adiabatically into a vacuum until its volume doubles?
1. ΔH = 0
2. ΔS = 0
3. ΔE = 0
4. W = 0
Which of the following represents correct order of electron affinity?
(1) Cl>F>S>O
(2) F>O>S>Cl
(3) F>Cl>S>O
(4) Cl>S>O>F
Consider the following conversions:
| (i) | (ii) | ||
| (iii) | (iv) |
That according to given information the incorrect statement is:
| 1. | is more negative than and |
| 2. | is less negative than |
| 3. | , and are negative whereas is positive |
| 4. | and are negative whereas and are positive |
The molecular geometry that is least likely to result from a trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry is:
| 1. | Trigonal planar | 2. | See-saw |
| 3. | Linear | 4. | T-shaped |
Out of the two compounds shown below, the vapour pressure of B at a particular temperature is expected to be:
| (A) |  |
| (B) |  |
1. Higher than that of A
2. Lower than that of A
3. Same as that of A
4. Can be higher or lower depending upon the size of the vessel
The number of antibonding electrons pairs in on the basis of MO theory are:
(1) 4
(2) 3
(3) 2
(4) 5
The bond energies of , C-H, H-H, and C=C are 198, 98, 103, and 145 kcal respectively.
The enthalpy change of the reaction would be:
1. 48 kcal
2. 96 kcal
3. -40 kcal
4. -152 kcal
Which one of the following ions is the most stable in an aqueous solution?
(At. No. Ti = 22, V = 23, Cr = 24, Mn = 25)
1. \(\text{Cr}^{3 +}\)
2. \(\text V^{3 +}\)
3. \(\text{Ti}^{3 +}\)
4. \(\text{Mn}^{3 +}\)
Assuming each reaction is carried out in an open container,
Reaction that shows ΔH=ΔE is :
1.
2.
3.
4.
Cisplatin, an anticancer drug, has the molecular formula . What is the mass (in gram) of one molecule? (Atomic weights : Pt=195, H=1.0, N=14, Cl=35.5)
1.
2.
3.
4.
The energy of an electron moving in nth Bohr's orbit of an element is given by eV/atom (Z=atomic number). The graph of \(E~ vs . Z^ 2\) (keeping "n" constant) will be:
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
The largest de Broglie wavelength among the following (all have equal velocity) is:
1. molecule
2. molecule
3. Electron
4. Proton
Oxidation state of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide is :
1. -1
2. +1
3. 0
4. -2
The oxidation number of phosphorus in \(Ba \left(H_{2} PO_{2}\right)_{2}\) is-
1. -1
2. +1
3. +2
4. +3
Which of the following reactions does not involve disproportionation process?
1.
2.
3.
4.
For the redox reaction,
, the correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced reaction are, respectively:
1. 2, 5, 16
2. 16, 3, 12
3. 15, 16, 12
4. 2, 16, 5
Oxidation states of C in Toluene is/are
1. -3
2. -1
3. 0
4. All of these
Given,
\(\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{O}_3(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{NO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \\
& \Delta \mathrm{H}=-198.9 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol} \\
& \mathrm{O}_3(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 3 / 2 \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=-142.3 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol} \\
& \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g}) ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=+495.0 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol}
\end{aligned}\)
The enthalpy change (∆H) for the following reaction NO(g) + O(g) → NO2(g) is:
1. -304.1 kJ/mol
2. +304.1 kJ/mol
3. -403.1 kJ/mol
4. +403.1 kJ/mol
The enthalpy changes for the following reactions are
The enthalpy change for the transition
will be
1.
2.
3.
4.
Which electronic configuration illustrates the ground state of a carbon atom following Hund's rule?
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
The first ionisation energy of Na, B, N and O atoms follows the order
1. B < Na < O < N
2. Na < B < O < N
3. Na < O < B < N
4. O < Na < N < B
What happens to a gas when it expands at constant temperature and pressure?
1. Internal energy decreases
2. Entropy increases and then decreases
3. Internal energy increases
4. Internal energy remains constant
An ion with mass number 37 possesses one unit of negative charge,the ion contains 11.1% more neutrons than the electrons. The symbol of the ion is-
| Assertion (A): | Cdiamond → Cgraphite ∆H and ∆U are the same for this reaction. |
| Reason (R): | Entropy increases during the conversion of diamond to graphite. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |
An electronic configuration that has maximum difference between II and III ionization potential is:
1. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
2. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
3. 1s2 2s2 2p6
4. 1s2 2s2 2p5
The number of significant figures present in the answer of the following calculations [(i), (ii), (iii)] are respectively -
| 1. | 0 . 02856 × 298 . 15 × 0 . 112 / 5785 |
| 2. | 5 × 5.364 |
| 3. | 0.0125 + 0.7864 + 0.0215 |
| 1. | 4, 4, 3 | 2. | 3, 3, 4 |
| 3. | 4, 3, 4 | 4. | 3, 4, 4 |
Consider the following molecules and statements related to them:

| (I) | (B) is more likely to be crystalline than (A) |
| (II) | (B) has a higher boiling point than (A) |
| (III) | (B) dissolves more readily than (A) in water |
Identify the correct option from below :
1. (I) and (II) are false
2. Only (III) are true
3. Only (I) is true
4. (I), (II) and (III) are true
Which of the following graphs correctly represents the potential energy curve for the \(\text{H}_2\) molecule as a function of internuclear distance?
| 1. | 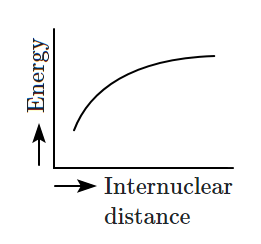 |
2. | 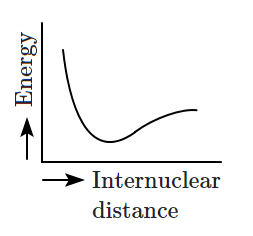 |
| 3. | 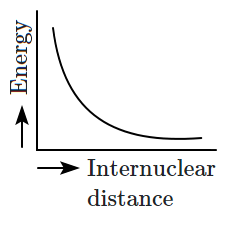 |
4. | 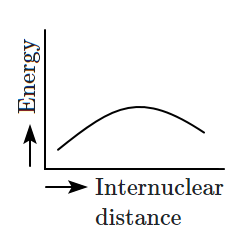 |
Which of the ions among the following is the largest in size?
1. Li+ (aqueous)
2. Cs+ (aqueous)
3. Li+ (g)
4. Cs+ (g)
| Assertion (A): | H2SO4 cannot act as a reducing agent. |
| Reason (R): | Sulphur cannot increase its oxidation number beyond +6. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | (A) is false but (R) is true. |
| Statement I: | \(O^{2-}\) and \(Mg^{2+} \) have equal radii. |
| Statement II: | They are isoelectronic species. |
| 1. | Both Statement I and Statement II are correct. |
| 2. | Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect. |
| 3. | Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect. |
| 4. | Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is correct. |
| Assertion (A): | Beryllium has more first ionization potential than Boron. |
| Reason (R): | Boron has a lower electron affinity than beryllium. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |
| 1. | 0.5 M | 2. | 0.25 M |
| 3. | 0.67 M | 4. | 1.5 M |
One projectile moving with velocity v in space, gets burst into 2 parts of masses in the ratio 1:3. The smaller part becomes stationary. What is the velocity of the other part?
1. 4v
2. v
3.
4.
Which of the following statements is correct?
1. Kinetic energy and momentum both are conserved in all types of collisions
2. Total kinetic energy is not conserved but momentum is conserved in inelastic COI-
lisions
3. Momentum is conserved In elastic collisions but .not in inelastic collisions
4. Total kinetic energy is conserved in inelastic collisions but momentum is not conserved in elastic collisions
A projectile of mass \(m\) is fired with velocity \(v\) from a point \(P\), as shown. Neglecting air resistance, the magnitude of the change in momentum between the points \(P\) and arriving at \(Q\) is:

1. zero
2. \(\frac{mv}{\sqrt{2}}\)
3. \(mv\sqrt{2} \)
4. \(2mv\)
A steel wire can withstand a load up to 2940 N. A load of 150 kg is suspended from a rigid support. The maximum angle through which the wire can be displaced from the mean position, so that the wire does not break when the load passes through the position of equilibrium, is (2008 E)
1. 30
2. 60
3. 80
4. 85
Which of the following is not represented in correct unit
1.
2. Surface tension =
3. Energy
4. Pressure
The density of wood is in the CGS system of units. The corresponding value in MKS units is :
1. 500
2. 5
3. 0.5
4. 5000
Which does not has the same unit as others
1. Watt-sec
2. Kilowatt-hour
3. eV
4. J-sec
Which of the following system of units is not based on units of mass, length and time alone
1. SI
2. MKS
3. FPS
4. CGS
Dimensions of kinetic energy are
1.
2.
3.
4.
Consider the acceleration, velocity and displacement of a tennis ball as it falls to the ground and bounces back. Directions of which of these changes in the process ?
1. Velocity only
2. Displacement and velocity
3. Acceleration, velocity and displacement
4. Displacement and acceleration
Speed of two identical cars are u and 4u at a specific instant. The ratio of the respective distances in which the two cars are stopped from that instant is:
1. 1 : 1
2. 1 : 4
3. 1 : 8
4. 1 : 16
A body is slipping from an inclined plane of height \(h\) and length \(l\). If the angle of inclination is \(\theta\), the time taken by the body to come from the top to the bottom of this inclined plane is:
1. \(\sqrt{\frac{2 h}{g}}\)
2. \(\sqrt{\frac{2 l}{g}}\)
3. \(\frac{1}{\sin \theta} \sqrt{\frac{2 h}{g}}\)
4. \(\sin \theta \sqrt{\frac{2 h}{g}}\)
From the following displacement-time graph , find out the velocity of a moving body.
1. m/s
2. 3 m/s
3. m/s
4. m/s
Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): | A Rocket in flight is not an illustration of a projectile. |
| Reason (R): | The Rocket takes flight due to the combustion of fuel and does not move under the gravitational effect alone. |
Choose the correct option:
| 1. | If both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. |
| 2. | If both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion. |
| 3. | If the assertion is true but the reason is false. |
| 4. | If the assertion and reason both are false. |
If the velocity of a particle is (10 + 2t2) m/s, then the average acceleration of the particle between 2 sec and 5 sec is:
1. 2 m/s2
2. 4 m/s2
3. 12 m/s2
4. 14 m/s2
A particle (A) is dropped from a height and another particle (B) is thrown in the horizontal direction with a speed of 5 m/sec from the same height. The correct statement is:
(1) Both particles will reach at ground simultaneously
(2) Both particles will reach at ground with same speed
(3) Particle (A) will reach at ground first with respect to particle (B)
(4) Particle (B) will reach at ground first with respect to particle (A)
If rope of lift breaks suddenly, the tension exerted by the surface of lift (a = acceleration of lift)
1. mg
2. m(g + a)
3. m(g – a)
4. 0
A body of 2 kg has an initial speed 5ms–1. A force acts on it for some time in the direction of motion. The force time graph is shown in figure. The final speed of the body.
1. 9.25 ms–1
2. 5 ms–1
3. 14.25 ms–1
4. 4.25 ms–1
A body of mass m1 is moving with a velocity V. It collides with another stationary body of mass m2. They get embedded. At the point of collision, the velocity of the system
(1) Increases
(2) Decreases but does not become zero
(3) Remains same
(4) Become zero
The bob of a pendulum of length l is pulled aside from its equilibrium position through an angle and then released. The bob will then pass through its equilibrium position with a speed v, where v equals
1.
2.
3.
4.
Two particles \(A\) and \(B\) are moving in a uniform circular motion in concentric circles of radii \(r_A\) and \(r_B\) with speeds \(v_A\) and \(v_B\) respectively. Their time periods of rotation are the same. The ratio of the angular speed of \(A\) to that of \(B\) will be:
| 1. | \( 1: 1 \) | 2. | \(r_A: r_B \) |
| 3. | \(v_A: v_B \) | 4. | \(r_B: r_A\) |
Two particles \(\mathrm{A}\) and \(\mathrm{B}\), move with constant velocities \(\overrightarrow{{v}_1}\) and \(\overrightarrow{{v}_2}\) respectively. At the initial moment, their position vectors are \(\overrightarrow{{r}_1}\) and \(\overrightarrow{{r}_2}\) respectively. The condition for particles \(\mathrm{A}\) and \(\mathrm{B}\) for their collision will be:
1. \(\vec{r_1} \cdot \vec{v_1}=\vec{r_2} \cdot \vec{v_2}\)
2. \(\dfrac{\vec{r_1}-\vec{r_2}}{\left|\vec{r_1}-\vec{r_2}\right|}=\dfrac{\vec{v_2}-\vec{v_1}}{\left|\vec{v_2}-\vec{v_1}\right|}\)
3. \(\vec{r_1} \times \vec{v_1}=\vec{r_2} \times \vec{v_2}\)
4. \(\vec{r_1}-\vec{r_2}=\vec{v_1}-\vec{v_2}\)
The trajectories of two projectiles are shown in the figure. Let \(T_{1}\)
1. \(T_{2}> T_{1}\)
2. \(T_{1}> T_{2}\)
3. \(u_{1}= u_{2}\)
4. \(u_{1}< u_{2}\)
A stone is thrown with a speed of 20 m/s at an angle of 60 with the ground. Speed of stone when it makes an angle of 30 with the horizontal is
1. 10 m/s
2. 10 m/s
3. m/s
4. None of these
The speed of a particle moving in a circular path decreases with time. The instantaneous power due to the force acting on it will be:
1. Positive
2. Negative
3. Zero
4. Maybe positive or negative
The principle of conservation of energy and conservation of mechanical energy applicable respectively for
(1) Conservative and non-conservative forces
(2) Conservative and conservative force
(3) Non-conservative and conservative forces
(4) All forces and conservative forces
A body is released from the top of an inclined smooth plane of inclination . It reaches the bottom with speed u. If the angle of inclination is doubled keeping the height unchanged, then the speed of the object on reaching on the ground is
(1) u
(2) 2u
(3)
(4)
Which of the following is not a unit of energy?
1. watt-hour
2. joule
3. eV
4. N/m
A particle of mass \(m\) is projected with a velocity at an angle with the horizontal into a uniform gravitational field. The slope of the trajectory varies with horizontal distance \(x\) as:
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
A particle is thrown with velocity u making an angle with the horizontal. It just crosses the top of two poles each of height h after 1 s and 3 s respectively. The time of flight of the particle is:
(1) 4 s
(2) 2 s
(3) 8 s
(4) 6 s
The tension in the string connecting blocks, \(B\) and \(C\), placed on a smooth horizontal surface in the following diagram is:
| 1. | \(25\) N | 2. | \(30\) N |
| 3. | \(32.5\) N | 4. | \(37.5\) N |
A block of mass \(M\) is pulled by a force \(F\), making an angle \(\theta\) with the horizontal on a smooth horizontal surface as shown. If \(a\) is the acceleration of block on the surface, then the contact force between the block and the surface will be:
1. \(Mg+ Ma\cos\theta\)
2. \(Mg- Ma\cos\theta\)
3. \(Mg+ Ma\tan\theta\)
4. \(Mg- Ma\tan\theta\)
A block \(B\) of mass \(3\) kg is kept on block \(A\) of mass \(5\) kg in a lift accelerating upward with an acceleration of \(g.\) The reaction by \(A\) on \(B\) is:

| 1. | \(10g\) | 2. | \(16g\) |
| 3. | \(4g\) | 4. | \(6g\) |
The figure shows the graph of the x-coordinate of a particle moving along the x-axis as a function of time. Average velocity during t=0 to 6 s and instantaneous velocity at t=3 s respectively, will be:
1. 10 m/s, 0
2. 60 m/s, 0
3. 0, 0
4. 0, 10 m/s
If force \(F=500-100t,\) then the function of impulse with time will be:
1. \( 500 t-50 t^2 \)
2. \( 50 t-10 \)
3. \( 50-t^2 \)
4. \( 100 t^2\)
An object of mass \(3\) kg is at rest. Now if a force of \(\overrightarrow{F} = 6 t^{2} \hat{i} + 4 t \hat{j}\) is applied to the object, then the velocity of the object at \(t =3\) second will be:
1. \(18 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j}\)
2. \(18 \hat{i} + 6 \hat{j}\)
3. \(3 \hat{i} + 18 \hat{j}\)
4. \(18 \hat{i} + 4 \hat{j}\)
Each side of a cube is measured to be \(7.203~\text{m}\). What are the total surface area and the volume respectively of the cube to appropriate significant figures?
| 1. | \(373.7~\text{m}^2\) and \(311.3~\text{m}^3\) |
| 2. | \(311.3~\text{m}^2\) and \(373.7~\text{m}^3\) |
| 3. | \(311.2992~\text{m}^2\) and \(373.7147~\text{m}^3\) |
| 4. | \(373.7147~\mathrm{m^2}\) and \(311.2992~\text{m}^3\) |
The position of an object moving along \(x\)-axis is given by \(x=a+bt^2\), where \(a=8.5\) m, \(b=2.5 \text{ ms}^{-2}\) and \(t\) is measured in seconds. Its average velocity between \(t=2.0\) s and \(t=4.0\) s is:
1. \(10~\text{m/s}\)
2. \(15~\text{m/s}\)
3. \(20~\text{m/s}\)
4. \(25~\text{m/s}\)
A batsman hits back a ball straight in the direction of the bowler without changing its initial speed of \(12\) m/s. If the mass of the ball is \(0.15\) kg, then the impulse imparted to the ball is:
(Assume linear motion of the ball.)
1. \(0.15\) N-s
2. \(3.6\) N-s
3. \(36\) N-s
4. \(0.36\) N-s
The radius of a circle is stated as \(2.12\) cm. Its area should be written as:
| 1. | \(14\mathrm{~cm^2}\) | 2. | \(14.1\mathrm{~cm^2}\) |
| 3. | \(14.11\mathrm{~cm^2}\) | 4. | \(14.1124\mathrm{~cm^2}\) |
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined plane of inclination θ with the horizontal. The force exerted by the plane on the block has a magnitude
1. mg
2. mg/cosθ
3. mg cosθ
4. mg tanθ
| List-I | List-II | ||
| (a) | Gravitational constant (\(G\)) | (i) | \([{L}^2 {~T}^{-2}] \) |
| (b) | Gravitational potential energy | (ii) | \([{M}^{-1} {~L}^3 {~T}^{-2}] \) |
| (c) | Gravitational potential | (iii) | \([{LT}^{-2}] \) |
| (d) | Gravitational intensity | (iv) | \([{ML}^2 {~T}^{-2}]\) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| 1. | (iv) | (ii) | (i) | (iii) |
| 2. | (ii) | (i) | (iv) | (iii) |
| 3. | (ii) | (iv) | (i) | (iii) |
| 4. | (ii) | (iv) | (iii) | (i) |
The determination of the value of acceleration due to gravity \((g)\) by simple pendulum method employs the formula,
\(g=4\pi^2\frac{L}{T^2}\)
The expression for the relative error in the value of \(g\) is:
| 1. | \(\frac{\Delta g}{g}=\frac{\Delta L}{L}+2\Big(\frac{\Delta T}{T}\Big)\) |
| 2. | \(\frac{\Delta g}{g}=4\pi^2\Big[\frac{\Delta L}{L}-2\frac{\Delta T}{T}\Big]\) |
| 3. | \(\frac{\Delta g}{g}=4\pi^2\Big[\frac{\Delta L}{L}+2\frac{\Delta T}{T}\Big]\) |
| 4. | \(\frac{\Delta g}{g}=\frac{\Delta L}{L}-2\Big(\frac{\Delta T}{T}\Big)\) |
| 1. | \(\dfrac{\alpha-f}{1+\beta} \) | 2. | \(\dfrac{\alpha+f}{2(\beta-1)} \) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{\alpha+f}{2(1+\beta)} \) | 4. | \(\dfrac{f-\alpha}{2(1+\beta)}\) |
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
| 1. | impulse and surface tension |
| 2. | angular momentum and work |
| 3. | work and torque |
| 4. | Young's modulus and energy |
| Statement I: | We can get displacement from the acceleration-time graph. |
| Statement II: | We can get acceleration from the velocity-time graph. |
| 1. | Both Statement I and Statement II are correct. |
| 2. | Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect. |
| 3. | Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect. |
| 4. | Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is correct. |
| 1. | less than \(50~\text{km/h}\) |
| 2. | greater than \(50~\text{km/h}\) |
| 3. | less than \(100~\text{km/h}\) |
| 4. | greater than \(100~\text{km/h}\) |

| 1. | \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{\sqrt3}{2}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) |