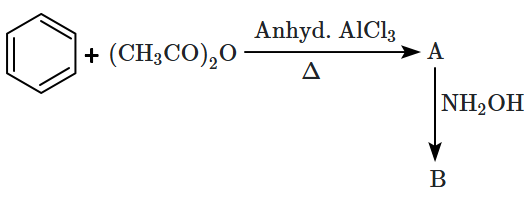A and B in the following reactions are 


1. A=, B=NaOH
2. A=
3. A=
4. A=
| 1. |  |
| 2. |  |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |
What compound results from the catalytic dehydrogenation of a primary alcohol?
1. Aldehyde
2. Ketone
3. Alkene
4. Acid

(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Consider the following reaction:
Product (D) will be :
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |

| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
PCl5 reacts with propanone, to give:
1. gem dichloride
2. vic dichloride
3. propanal
4. propane chloride
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished by:
1. Benedict test
2. Iodoform test
3. Tollen's reagent test
4. Fehling solution test
The product 'D' in the below-mentioned reaction will be:
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
The reactant 'A' in the above reaction is-
1.  2.
2. 
3.  4.
4. 

The best rate for esterification is observed when 'X' is
1. -OH
2. -Cl
3.
4.
The incorrect method for the preparation of Me3COMe in good yield is
1. Me3CCl + MeONa →
2. \(Me_{2}C=CH_{2}\xrightarrow[(ii)NaBH_{4}]{(i) Hg(OAc)_{2}/MeOH}\)
3. Me3CONa + MeCl ⟶
4. \(Me_{2}C=CH_{2}\xrightarrow[MeOH]{H^{+}}\)
1. 
2.
3. 
4.
In the following reactions

1. 
2. 
3. 
4. 
Which of the following is the correct representation for intermediate of nucleophilic addition reaction to the given carbonyl compound (A) :
| a. |  |
| b. |  |
| c. |  |
| d. |  |
Choose the correct option
| 1. | (a, b) | 2. | (b, c) |
| 3. | (c, d) | 4. | (a, d) |
Match the reactions given in Column I with the suitable reagents given in Column II.
| Column I (Reactions) |
Column II (Reagents) |
||
| (i) | Benzophenone → Diphenylmethane | (a) | LiAlH4 |
| (ii) | Benzaldehyde → 1-Phenylethanol | (b) | DIBAL—H |
| (iii) | Cyclohexanone → Cyclohexanol | (c) | Zn(Hg)/Conc. HCl |
| (iv) | Phenyl benzoate → Benzaldehyde | (d) | CH3MgBr |
1. (i) — (a), (ii) — (b), (iii) — (d), (iv) — (c)
2. (i) — (b), (ii) — (c), (iii) — (a), (iv) — (d)
3. (i) — (c), (ii) — (d), (iii) — (a), (iv) — (b)
4. (i) — (d), (ii) — (c), (iii) — (b), (iv) — (a)
Select the correct option based on statements below:
| Assertion (A): | Benzaldehyde undergoes a condensation reaction when heated in the presence of KCN. |
| Reason (R): | Benzaldehyde has no α- H atom. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |
Given the reaction:
\(CH_3Br\ \xrightarrow{KCN}\ A\ \xrightarrow{H_3O^+}\ B\ \xrightarrow{PCl_5}\ C\)
What is the product 'C' in the above mentioned reaction?
1. Acetylchloride
2. Chloro acetic acid
3. α- Chlorocyano ethanoic acid
4. None of the above
HCN not produce a chiral compound with:
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
CH3
(Assume compound X has a chiral centre)
The optical activity associated with product X would be:
| 1. | Laevorotatory | 2. | Dextrorotatory |
| 3. | Mesocompound | 4. | Racemic mixture |
An organic compound (A) contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen, and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollens’ reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite and gives a positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation, it gives ethanoic and propanoic acid. Compound A would be:
1. Pentan-2-one
2. Butanone
3. 3-Methylbutanone
4. Propan-2-ol
Through which of the following reactions number of carbon atoms can be increased in the chain?
a. Grignard reaction
b. Cannizzaro’s reaction
c. Aldol condensation
d. HVZ reaction
Choose the correct option:
1. (a, b)
2. (b, c)
3. (c, d)
4. (a, c)
Select the correct option based on statements below:
| Assertion (A): | The α -hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic. |
| Reason (R): | The anion formed after the loss of the α -hydrogen atom is resonance stabilized. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
The correct order of reactivity of phenyl magnesium bromide (PhMgBr) with the following
compounds will be:
 |
 |
 |
| I | II | III |
1. I > II > III
2. III > II > I
3. II > I > III
4. I > III > II
The below structure is an example of :

| 1. | Cyanohydrin | 2. | Hemiacetal |
| 3. | Acetal | 4. | Cyanoalcohol |
The major product formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with PhMgBr and H3O+ is:
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. | None of these |
The major organic product of the given reaction is:

| 1. |  |
| 2. |  |
| 3. |  |
| 4. | None of the above |
| 1. | HCHO | 2. | CH3CHO |
| 3. | CH3COCH3 | 4. | CH3CH2CHO |
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |

| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |