Botany - Section A
1. In a type of apomixis known as adventive polyembryony, embryo develops directly from the:
| 1. |
synergids or antipodals in an embryo sac |
| 2. |
nucellus or integuments |
| 3. |
zygote |
| 4. |
accessory embryo sac in the ovule |
2.
Select the correct statement:
1. Franklin Stahl coined the term "linkage"
2. Punnett square was developed by a British scientist
3. Spliceosomes take part in translation
4. Transduction was discovered by S. Altman
3. The association of histone H1 with a nucleosome indicates:
1. DNA replication is occurring
2. The DNA is condensed into a chromatin fibre
3. The DNA double helix is exposed
4. Transcription is occurring
4. Mycorrhizal plants have the following benefits, except:
| 1. |
Phosphorus from the soil by means of fungi |
| 2. |
Resistance to root borne pathogens |
| 3. |
Tolerance to salinity, drought, and extremely low temperature |
| 4. |
Overall increase in plant growth and development |
5. Which of the following statements is true?
| 1. |
A British scientist created the conditions proposed by Oparin and Haldane in a closed flask with temperature of 800 degrees Celsius in electric discharge along with gases methane, hydrogen, ammonia and water vapour and observed the formation of amino acid. |
| 2. |
Some similar experimental setups were also prepared by other scientists and the formation of sugar, nitrogenous bases, pigments and fats were recorded. |
| 3. |
The processes of chemical evolution occurring elsewhere in space was concluded by the analysis of content of gaseous cloud. |
| 4. |
The first self-replicating metabolic capsule of life arose 3 billion years back. |
6. Which of the following microbes is used for the commercial production of citric acid?
| 1. |
Aspergillus niger |
2. |
Clostridium butylicum |
| 3. |
Acetobacter aceti |
4. |
Lactobacillus |
7. Frugivorous birds are found in large numbers in tropical forests mainly because of :
1. lack of niche specialisation.
2. higher annual rainfall.
3. availability of fruits throughout the year.
4. temperature conducive for their breeding.
8. The embryo does not have:
| 1. |
Embryonal axis |
2. |
Radicle |
| 3. |
One or two cotyledons |
4. |
Seed coat |
9. Which of the following shows the coordinated movement of cilia?
1. Trypanosoma
2. Entamoeba
3. Paramoecium
4. Plasmodium
10. Which of the following is not a true statement?
| 1. |
In translation, the transfer of genetic information from a polymer of nucleotides to a polymer of amino acids takes place. |
| 2. |
Complementarity exists between nucleotide sequences and amino acid sequences. |
| 3. |
The basis for transcription and replication is complementarity. |
| 4. |
A change in nucleic acid is responsible for a change in amino acid. |
11. Identify the incorrect statement:
| 1. |
Tall plant produces gametes by meiosis and the dwarf plant by mitosis. |
| 2. |
Only one allele is transmitted to a gamete. |
| 3. |
The segregation of alleles is a random process. |
| 4. |
Gametes will always be pure for the trait. |
12. Plants do not contain many parts that can be easily fossilized. Which of the following has proved helpful in preserving pollens as fossils?
1. Pollenkit
2. Cellulosic intine
3. Callose in pollen tetrad
4. Sporopollenin
13. Match the following and choose the correct option:
| Column I |
Column II |
| (a) |
Aleurone layer |
(i) |
without fertilization |
| (b) |
Parthenocarpic fruit |
(ii) |
Nutrition fruit |
| (c) |
Ovule |
(iii) |
Double fertilization |
| (d) |
Endosperm |
(iv) |
Seed |
Options:
|
(a) |
(b) |
(c) |
(d) |
| 1. |
(i) |
(ii) |
(iii) |
(iv) |
| 2. |
(ii) |
(i) |
(iv) |
(iii) |
| 3. |
(iv) |
(ii) |
(i) |
(iii) |
| 4. |
(ii) |
(iv) |
(i) |
(iii) |
14. In RNAi, the genes are silenced using :
1. dsRNA
2. ssDNA
3. ssRNA
4. dsDNA
15. Removal of apical dominance by decapitation is utilised for:
| 1. |
Suppressing the activity of intercalary meristem |
| 2. |
Early senescence |
| 3. |
Hedge making |
| 4. |
Preparing weed-free lawns |
16. Select the option with correct words for the blanks below:
| A. |
Histones are organised to form a unit of eight molecules called _______. |
| B. |
_______ constitute the repeating unit of a structure in nucleus called chromatin. |
| C. |
The chromatin that is more densely packed and stains dark is called ________. |
Options:
|
A |
B |
C |
| 1. |
Nucleosome |
Chromosome |
Euchromatin |
| 2. |
Histone octamer |
Nucleosome |
Heterochromatin |
| 3. |
Histone octamer |
Nucleoid |
Euchromatin |
| 4. |
Nucleosome |
Nucleoid |
Heterochromatin |
17. In the given diagram:
 I:
I: A is filiform apparatus, B is synergid,
II: C is PEN, D are egg cells
III: E is generative nucleus, F is antipodal
| 1. |
Only I is correct |
2. |
Only I and III are correct |
| 3. |
Only II is correct |
4. |
Only II and III are correct |
18. In taxonomy:
| I: |
Nomenclature is critical as it allows a particular organism to be known by the same name all over the world. |
| II: |
Identification is critical as nomenclature or naming is only possible when the organism is described correctly and we know to what organism the name is attached to. |
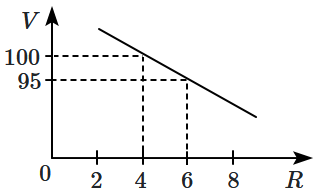
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
19.
| Assertion (A): |
Whole plants can be regenerated from any part of a plant taken out and grown in a test tube, under sterile conditions in special nutrient media |
| Reason (R): |
Every living plant cell is totipotent |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False |
20. The Earth Summit held in Rio de Janeiro in 1992 was called:
| 1. |
for immediate steps to discontinue use of CFCs that were damaging the ozone layer |
| 2. |
to reduce CO2 emissions and global warming |
| 3. |
for conservation of biodiversity and sustainable utilization of its benefits |
| 4. |
to assess threat posed to native species by invasive weed species |
21. Glycolysis is found in the cytoplasm of virtually all types of aerobic/anaerobic cells. In this process, glucose is converted into :
1. PEP
2. acetyl CoA
3. pyruvic acid
4. citric acid
22. The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis is called:
1. Secondary production
2. Primary production
3. Gross primary production
4. Net primary production
23. Which one of the following statements is correct?
| 1. |
The seed in grasses is not endospermic. |
| 2. |
Mango is a parthenocarpic fruit |
| 3. |
A proteinaceous aleurone layer is present in maize grain. |
| 4. |
A sterile pistil is called a staminode. |
24. Select the wrong statement:
| 1. |
Protista have photosynthetic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition |
| 2. |
Some fungi are edible |
| 3. |
Nuclear membrane is present in Monera |
| 4. |
Cell wall is absent in Animalia |
25. Select the wrong statement:
| 1. |
Mycoplasma is a wall-less microorganism |
| 2. |
Bacterial cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan |
| 3. |
Pili and fimbriae are mainly involved in motility of bacterial cells |
| 4. |
Cyanobacteria lack flagellated cells |
26. Which of the following is not true regarding comparison between the gymnosperms
Pinus and
Cycas?
| |
Character |
Pinus |
Cycas |
| 1. |
Root symbiotic association |
Mycorrhiza |
Cynobacteria |
| 2. |
Stem |
Branched |
Unbranched |
| 3. |
Reproductive parts |
Dioecious |
Monoecious |
| 4. |
Scale leaves |
Fall off as branches mature |
Persistent, protective |
27. Consider the following statements (a-d) each with one or two blanks.
| 1. |
All solids that settle during primary treatment of sewage forms (i) and supernatant forms the (ii) . |
| 2. |
Secondary treatment of sewage is also known as (iii) treatment. |
| 3. |
A small part of the activated sludge is pumped back into the aeration tank to serve as the (iv) . |
| 4. |
The sewage water is treated till (v) is reduced. |
Which of the following options correctly fills the above blanks?
|
(i) |
(ii) |
(iii) |
(iv) |
(v) |
| 1. |
Primary sludge |
|
Flocs |
|
DO |
| 2. |
|
Effluent |
Biological |
Inoculum |
BOD |
| 3. |
Primary sludge |
Flocs |
|
Inoculm |
DO |
| 4. |
Effluent |
Primary sludge |
Flocs |
|
BOD |
28. Select the incorrect statement with respect to C3 cycle:
| 1. |
For one CO2 fixation, three ATPs are required |
| 2. |
Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor molecule RuBP is not crucial for the continuation of the cycle |
| 3. |
The first stable product is PGA |
| 4. |
Carboxylation is the most crucial step |
29. The given figure shows a T.S. of:

| 1. |
Monocot root |
2. |
Dicot root |
| 3. |
Dicot stem |
4. |
Monocot stem |
30. Some stages of development of a dicot embryo are given below:-
| a. |
Proembryo |
| b. |
Globular stage |
| c. |
Heart shape |
| d. |
Mature embryo |
The correct sequence of the given stages is:
| 1. |
a, b, c, d |
| 2. |
c, d, b, a |
| 3. |
a, c, d, b |
| 4. |
b, d, c, a |
31. DNA and RNA differ by:-
1. Nitrogen bases and sugars
2. Nitrogen bases and phosphate groups
3. Number of C-atoms in sugars
4. Sugar and phosphate groups
32. The age pyramid with broad base indicates:
1. high percentage of old individuals
2. low percentage of young individuals
3. a stable population
4. high percentage of young individuals
33. The correct chronology of steps of formation of the given metabolites in TCA cycle is:
| 1. |
Isocitrate – Citrate – Succinyl CoA – α ketoglutarate |
| 2. |
Citrate – Isocitrate – Succinyl CoA – α ketoglutarate |
| 3. |
Citrate – Isocitrate – α ketoglutarate – Succinyl CoA |
| 4. |
Isocitrate – Citrate – α ketoglutarate – Succinyl CoA |
34. In Antirrhinum (Snapdragon), a red flower was crossed with a white flower and in generation, pink flowers were obtained. When pink flowers were selfed, the generation showed white, red and pink flowers. Choose the incorrect statement from the following:
| 1. |
Law of Segregation does not apply in this experiment |
| 2. |
This experiment does not follow the Principle of Dominance |
| 3. |
Pink colour in F1 is due to incomplete dominance |
| 4. |
Ratio of F2 is 1/4(red):2/4(pink):1/4(white) |
35. The sequence that controls the copy number of the linked DNA in the vector is termed :
1. Ori site
2. Palindromic sequence
3. Recognition site
4. Selectable marker
Botany - Section B
36. Find the incorrect statement about cell wall:
| 1. |
determines shape of the cell |
| 2. |
prevent cell from bursting and collapsing |
| 3. |
selective permeable in nature |
| 4. |
provides strong structural support |
37. Identify the correct match:
| 1. |
Coleorhiza |
Dicot family |
| 2. |
Non-albuminous seed |
Thick and swollen cotyledon |
| 3. |
Residual nucellus |
maize |
| 4. |
Residual endosperm |
Pea |
38. Choose correct option with respect to given below inflorescence:
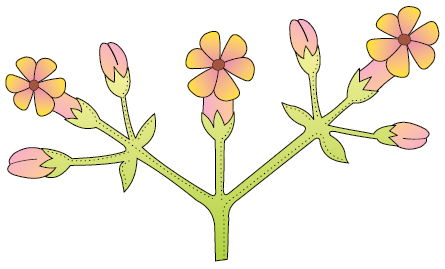
1. Main axis terminates in flower
2. Acropetal arrangement of flowers
3. Unlimited growth of main axis
4. More than one option is correct
39. The diagram shows the inflorescence scheme and the floral diagram of the family:

| 1. |
Liliaceae |
2. |
Gramineae |
| 3. |
Leguminosae |
4. |
Rosaceae |
40. Which plant hormone is used to prepare weed-free lawns?
1. Kinetin
2. 2,4-D
3. Zeatin
4. Dormin
41. In papaya:
| I: |
both male and female flowers are present on the same plant |
| II: |
autogamy is prevented, but not geitonogamy |
| 1. |
Only I is true |
2. |
Only II is true |
| 3. |
Both I and II are true |
4. |
Both I and II are false |
42. The logistic population growth is expressed by the equation:
1.
2.
3.
4.
43. A molecule of GTP is synthesized in Krebs cycle during:
1. the condensation of acetyl group with oxaloacetic acid
2. isomerization of citrate to isocitrate
3. the conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid
4. the regeneration of oxaloacetic acid
44. Which one is true for collenchyma?
| 1. |
forms the hypodermis of dicot stem |
| 2. |
present below the epidermis in layers or patches |
| 3. |
thickened corners due to cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin deposition |
| 4. |
All of the above |
45. Examine the figures A, B, C, and D and identify the one in which all labelings are correct?
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1. |
Laminaria |
Salvinta |
Male thallus of Marchantia |
Cayas |
| 2. |
Polysiphonia |
Equisetum |
Female thallus of Marchantia |
Ginkgo |
| 3. |
Chara |
Selaginella |
Sphagnum |
Ginkgo |
| 4. |
Fucus |
Fern |
Funaria |
Pinus |
46. Select the incorrect statement with respect to light reaction:
| 1. |
The primary acceptor of PS-ll is pheophytin |
| 2. |
The splitting of water is associated with PS-ll |
| 3. |
In PS-l, the reaction centre Chlorophyll-a has an absorption peak at 680 nm |
| 4. |
The LHC are made up of core and antenna molecules |
47. Glycerol would enter the respiratory pathway after being converted to-
| 1. |
PGAL |
2. |
DPGA |
| 3. |
PGA |
4. |
Acetyl CoA |
48. Plant tissue culture may offer certain advantages over traditional methods of propagation, including all the following except:
| 1. |
The production of plants that exhibit large variations from the parent plants. |
| 2. |
Quickly production of mature plants. |
| 3. |
The regeneration of whole plants from plant cells that have been genetically modified. |
| 4. |
Storage of genetic plant material to safeguard native plant species. |
49. Identify the incorrect pair:
1. Lectins - Concanavalin A
2. Drugs - Ricin
3. Alkaloids - Codeine
4. Toxin - Abrin
50. Which stages of cell division do the following figures A and B represent respectively ?
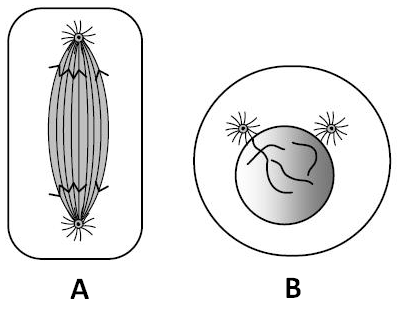
1. Metaphase-Telophase
2. Telophase - Metaphase
3. Late anaphase – Prophase
4. Prophase – Anaphase
Zoology - Section A
51. Which of the following hormone is responsible for cell mediated immunity?
1. Thyroxine
2. adrenaline
3. Thymosins
4. parathyroid
52. Read the following statements carefully:
| A. |
Lipid component of the plasma membrane mainly consists of phosphoglycerides. |
| B. |
Polar molecules can pass through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane, therefore they do not require carrier proteins to facilitate their transport. |
| C. |
The secondary wall is capable of growth and it is formed on the outer side of the cell. |
| D. |
Quasi-fluid nature of lipids enables the lateral movement of proteins within the overall lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane. |
| E. |
Middle lamella glues the different neighboring cells together. |
How many statements are incorrect?
| 1. |
Three |
2. |
Five |
| 3. |
Four |
4. |
Two |
53. Bundles of skeletal muscle fibres called fascicles are enclosed by a connective tissue known as:
| 1. |
Fascia |
2. |
Perimysium |
| 3. |
Endomysium |
4. |
Epimysium |
54. In genetic engineering, the antibiotic resistance gene are used:
1. As selectable markers
2. To select healthy vectors
3. As sequences from where replication starts
4. to keep the cultures free of infection
55. Which one of the following is at high risk of extinction?
| 1. |
Mammals |
2. |
Birds |
| 3. |
Amphibians |
4. |
Echinoderms |
56. Which of the following is true for inspiration?
1. thoracic chamber volume increases
2. Diaphragm contracts
3. pulmonary volume increases
4. All of these
57. Which of the following is not a part of urine formation?
1. Glomerular Filtration
2. Reabsorption
3. Secretion
4. Counter current mechanism
58. Match the items given in Column-I with those in Column-II and select the correct option given below:
|
Column-I |
|
Column-II |
| a. |
Tricuspid valve |
i. |
Between left atrium and left ventricle |
| b. |
Bicuspid valve |
ii. |
Between right ventricle and pulmonary artery |
| c. |
Semilunar valve |
iii. |
Between right atrium and right ventricle |
Options:
|
a |
b |
c |
| 1. |
iii |
i |
ii |
| 2. |
i |
iii |
ii |
| 3. |
i |
ii |
iii |
| 4. |
ii |
i |
iii |
59. Under resting conditions, the axonal membrane is:
| 1. |
impermeable to Na+ ions and relatively more permeable to K+ ions. |
| 2. |
impermeable to Na+ ions and K+ ions. |
| 3. |
freely permeable to Na+ ions and relatively more impermeable to K+ ions. |
| 4. |
freely permeable to Na+ ions and K+ ions. |
60. Which of the following inhibits gastric secretion?
1. Gastrin
2. Secretin
3. Cholecystokinin
4. Gastric inhibitory peptide
61. The structure given below is of:

| 1. |
A purine base |
2. |
Adenosine |
| 3. |
Adenylic acid |
4. |
A pyrimidine base |
62. Match the organism in Column-I with its excretory structure in Column-II:
|
Column-I |
|
Column-II |
| (a) |
Cockroach |
(p) |
Nephridia |
| (b) |
Earthworm |
(q) |
Proboscis gland |
| (c) |
Balanoglossus |
(r) |
Kidney |
| (d) |
Clarias |
(s) |
Malpighian tubules |
|
(a) |
(b) |
(c) |
(d) |
| 1. |
(s) |
(p) |
(q) |
(r) |
| 2. |
(s) |
(p) |
(r) |
(q) |
| 3. |
(q) |
(p) |
(r) |
(s) |
| 4. |
(s) |
(q) |
(r) |
(p) |
63. Pvu I restriction site is present in pBR322 at:
1. rop
2. Tetracycline Resistance gene
3. Ampicillin Resistance gene
4. Ori
64. Relief in allergic reactions can be provided by the use of all of the following except:
| 1. |
Anti-histamines |
2. |
Steroids |
| 3. |
Adrenaline |
4. |
Antibiotics |
65. Which of the following is not true about Homo sapiens?
| 1. |
Arose in 75000- 10000 years ago |
| 2. |
Cave art developed about 18000 years ago |
| 3. |
Agriculture came around 10000 years ago |
| 4. |
Modern man's skull resembles more with adult chimpanzee than baby chimpanzee |
66. A human female with turner's syndrome:
1. has 45 chromosomes with XO
2. has one additional X-chromosome
3. exhibits male characters
4. is able to produce children with normal husband
67. Sertoli cells are found in:
| 1. |
ovaries and secrete progesterone |
| 2. |
adrenal cortex and secrete adrenaline |
| 3. |
seminiferous tubules and provide nutrition to germ cells |
| 4. |
pancreas and secrete cholecystokinin |
68. The Adenosine deaminase deficiency results into:
1. Digestive disorder
2. Addison's disease
3. Dysfunction of Immune system
4. Parkinson's disease
69. Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram:

|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1. |
Z line |
A band |
H zone |
I band |
| 2. |
Z line |
A band |
I band |
H zone |
| 3. |
M line |
A band |
H zone |
I band |
| 4. |
M line |
H zone |
A band |
I band |
70. Given below are four methods (A-D) and their modes of action (a-d) in achieving contraception. Select their correct matching from the four options that follow:
|
Method |
|
Mode of action |
| A. |
The pill |
a. |
Prevents sperms from reaching ovum |
| B. |
Condom |
b. |
Prevents implantation |
| C. |
Vasectomy |
c. |
Prevents ovulation |
| D. |
Copper - T |
d. |
Semen contains no sperms |
Options:
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1. |
c |
a |
d |
b |
| 2. |
d |
a |
b |
c |
| 3. |
c |
d |
a |
b |
| 4. |
b |
c |
a |
d |
71. Skeletal muscles appear striated due to presence of two characteristic proteins in alternating dark and light bands. Which of the following is a correct match of the protein with its light refractive property and colour?
|
Protein |
Colour |
Property |
| 1. |
Myosin |
Light |
Anisotropic |
| 2. |
Actin |
Dark |
Anisotropic |
| 3. |
Myosin |
Dark |
Isotropic |
| 4. |
Actin |
Light |
Isotropic |
72. Exotic species introduced in India are:
1. Lantana camara, Water Hyacinth
2. Water Hyacinth, Prosopis cineraria
3. Nile Perch, Ficus religiosa
4. Ficus religiosa, Lantana camara
73. Which of the following is a correct statement?
| 1. |
Every chemical reaction of metabolism is a catalysed reaction. |
| 2. |
There is no uncatalysed metabolic conversion in the living system. |
| 3. |
The proteins with catalytic power are called as enzymes. |
| 4. |
All of these |
74. Which one of the following pairs of animals comprises ‘jawless fishes’?
1. Guppies and hag fishes
2. Lampreys and eels
3. Mackerels and Rohu
4. Lampreys and hag fishes
75. Which of the following components provides sticky character to the bacterial cell?
1. Cell wall
2. Nuclear membrane
3. plasma membrane
4. Glycocalyx
76. Which one of the following options gives the correct matching of a disease with its causative organism and mode of infection?
|
Disease |
Causative Organisms |
Mode of Infection |
| 1. |
Typhoid |
Salmonella typhi |
With inspired air |
| 2. |
Pneumonia |
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
Droplet infection |
| 3. |
Elephantiasis |
Wuchereria bancrofti |
infected water and food |
| 4. |
Malaria |
Plasmodium vivax |
Bite of male anopheles mosquito |
77. Which one of the following techniques made it possible to genetically engineer living organisms?
1. Recombinant DNA techniques
2. X-ray diffraction
3. Heavier isotope labeling
4. Hybridization
78. The eye of an octopus and the eye of a cat show different patterns of structure, yet they perform similar function. This is an example of:
| 1. |
Homologous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution |
| 2. |
Homologous organs that have evolved due to divergent evolution |
| 3. |
Analogous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution |
| 4. |
Analogous organs that have evolved due to divergent evolution |
79. Which one of the following statements is correct?
| 1. |
Neurons regulate endocrine activity, but not vice versa. |
| 2. |
Endocrine glands regulate neural activity, and nervous system regulates endocrine glands. |
| 3. |
Neither hormones control neural activity nor do the neurons control endocrine activity. |
| 4. |
Endocrine glands regulate neural activity, but not vice versa. |
80. A drop of each of the following is placed separately on four slides. Which of them will not coagulate?
1. Whole blood from pulmonary vein
2. Blood plasma
3. Blood serum
4. Sample from the thoracic duct of lymphatic system
81. Select the answer with correct matching of the structure, its location, and function:
|
Structure |
Location |
Function |
| 1. |
Cerebellum |
Midbrain |
Controls respiration and gastric secretions |
| 2. |
Hypothalamus |
Forebrain |
Controls body temperature, urge for eating and drinking |
| 3. |
Blind spot |
Near the place where optic nerve leaves the eye |
Rods and cones are present but inactive here |
| 4. |
Eustachian tube |
Anterior part of internal ear |
Equalizes air pressure on either side of tympanic membrane |
82. Match the items given in column I with those in column II and select the correct option given below:
| Column I |
Column II |
| (a) |
Glycosuria |
(i) |
Accumulation of uric acid in joints |
| (b) |
Gout |
(ii) |
Mass of crystallised salts within the kidney |
| (c) |
Renal calculi |
(iii) |
Inflammation in glomeruli |
| (d) |
Glomerulonephritis |
(iv) |
Presence of glucose in urine |
Codes:
|
(a) |
(b) |
(c) |
(d) |
| 1. |
(ii) |
(iii) |
(i) |
(iv) |
| 2. |
(i) |
(iii) |
(ii) |
(iv) |
| 3. |
(iii) |
(ii) |
(iv) |
(i) |
| 4. |
(iv) |
(i) |
(ii) |
(iii) |
83. Trachea divides into right and left primary bronchi at the level of:
1. Seventh cervical vertebra
2. Third thoracic vertebra
3. Fifth thoracic vertebra
4. Seventh thoracic vertebra
84. Select the incorrect statement with respect to male reproductive system:
| 1. |
Seminiferous tubules in the testes are a site of sperm formation |
| 2. |
Leydig cells scattered outside the Seminiferous tubules provide nourishment to sperms |
| 3. |
For most mammals, sperm production occurs properly only when the testes are cooler than normal body temperature |
| 4. |
Sperms, while passing through epididymis attain motility |
85. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The alimentary canal in frog is short. |
| Reason (R): |
Frog is a herbivore. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) does not explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False but (R) is True |
Zoology - Section B
86. Which of the following events happen when air is expelled from the lungs?
1. Ribs and sternum return to the original position
2. volume of thorax decreases
3. Diaphragm relaxes and arches upwards
4. All of the above
87. Water retention in plasma is brought about mainly by:
1. Fibrinogens
2. Serum albumins
3. Alpha globulins
4. Gamma globulins
88. During the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle which of the following occur?
| I: |
The primary follicle grows and becomes fully mature Graafian follicle |
| II: |
The endometrium of the uterus regenerates through proliferation |
1. Only I
2. Only II
3. I and II
4. None
89. The protozoans that cause malaria in humans are :
1. Radiolarians
2. Dinoflagellates
3. Chrysophytes
4. Sporozoans
90. Mark the correct character of the following figure:

1. Tetrapedal and having bony plates on the back
2. Tetrapedal and having a collar on the neck
3. Bipedal and have huge fearsome dagger-like teeth
4. Bipedal and have three horns on head
91. The invertebrates have which of the following excretory structures?
1. Simple Tubular forms
2. Complex tubular organs
3. Kidneys
4. Interstitial lamina
92. The ……. receive signals from ……. and transmit it via ……. nerve root
1. Afferent neurons, sensory organs, dorsal
2. Afferent neurons, effector organs, ventral
3. Efferent neurons, sensory organs, ventral
4. Efferent neurons, effector organs, dorsal
93. Which of the following hormone is related to the pigmentation of skin?
1. MSH
2. ACTH
3. LH
4. FSH
94. Mark the feature which is not associated with white muscle fibres:
| 1. |
Lighter in color |
| 2. |
These muscles have a fast rate of contraction but for a short period |
| 3. |
They depend mainly on glycolysis for energy production and soon get fatigued |
| 4. |
Less sarcoplasmic reticulum compared to red muscle fibres |
95. The first type II restriction endonuclease discovered that could cut dsDNA at specific site was:
1. EcoRI
2. SmaI
3. Hind II
4. Hind III
96. What is true about Bt toxin?
| 1. |
The concerned Bacillus has antitoxins. |
| 2. |
The inactive protoxin gets converted into active form in the insect gut |
| 3. |
BT protein exists as active toxin in the Bacillus. |
| 4. |
The activated toxin enters the ovaries of the pest to sterilise it and thus prevent its multiplication |
97. The Leydig cells as found in the human body are the secretory source of:
1. progesterone
2. intestinal mucus
3. glucagon
4. androgens
98. Which of the sets of diseases are completely curable if detected early?
| 1. |
Hepatitis - B, Gonorrhoea, Syphilis |
| 2. |
Genital herpes, Chlamydiasis, Syphilis |
| 3. |
HIV Infections, Chlamydiasis, Gonorrhoea |
| 4. |
Chlamydiosis, Syphilis, Gonorrhoea |
99. The symptoms of common cold lasts for:
1. Generally 1 day
2. Generally 2-3 days
3. Usually, At maximum 14 days
4. Usually 3-7 days
100. The length of E. coli DNA and the length of DNA in a human 2N cell is:
1. 1.36 mm and 2.2 m respectively
2. 1.36 mm and 2.2 mm respectively
3. 1.3 ìm and 2.2 ìm respectively
4. 1.36 cm and 2.2 cm respectively
Chemistry - Section A
101. The compound Y in the above sequence of reactions is:

1. 1-Phenylethene
2. 2-Phenyl-2-propanol
3. Acetophenone
4. Benzaldehyde
102. The d-electron configuration of [Ru(en)3]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2, respectively are:
| 1. |
\(t_{2g}^6 e^0_g\) and \(t_{2g}^4 e^2_g\) |
2. |
\( t_{2 g}^{4} e_{g}^{2}\) and \(t_{2 g}^{4} e_{g}^{2}\) |
| 3. |
\(t_{2 g}^{3} e_{g}^{3} \) and \(t_{2 g}^{4} e_{g}^{2}\) |
4. |
\( t_{2 g}^{4} e_{g}^{2} \) and \( t_{2 g}^{3} e_{g}^{3}\) |
103. Which of the following pairs is expected to have the same bond order?
1. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}, \mathrm{N}_2^{-}\)
2. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}, \mathrm{N}_2^{+}\)
3. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}, \mathrm{N}_2^{-} \)
4. \(\mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{~N}_2 \)
104. Which complex among the following exhibits a paramagnetic nature?
1. [Co(NH3)6]3+
2. [Pt(en)Cl2]
3. [CoBr4]2–
4. Mo(CO)6
(At. No. Mo = 42, Pt = 78)
105. Select the correct option based on the statements below:
| Assertion (A): |
Chlorine is an electron-withdrawing group, yet it exhibits ortho- and para-directing behavior in electrophilic aromatic substitution. |
| Reason (R): |
Inductive effect of chlorine destabilises the intermediate carbocation formed during the electrophilic substitution, however due to the more pronounced resonance effect, the halogen stabilises the carbocation at ortho and para positions. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
(A) is False but (R) is True. |
106. The reaction of NO with at 250 K gives :
| 1. |
N2O5 |
2. |
NO2 |
| 3. |
N2O |
4. |
N2O3 |
107. What is the value of osmotic pressure of a 5 % (W/V) solution of cane sugar at 150 °C?
| 1. |
1.45 atm |
2. |
5.07 atm |
| 3. |
3.46 atm |
4. |
4.01 atm |
108. The major product of the following chemical reaction is :
\( \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CN} \xrightarrow[\text { (3) } \mathrm{Pd} / \mathrm{BaSO}_4, \mathrm{H}_2]{\text { (1) } \mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{O}^{+},\Delta ~~(2) \mathrm{SOCl}_2} ?\)
| 1. |
CH3CH2CH3 |
2. |
CH3CH2CH2OH |
| 3. |
(CH3CH2CO)2O |
4. |
CH3CH2CHO |
109. Which combination among the following, when mixed in equal volumes, will result in the formation of a buffer solution?
| 1. |
0.1 mol dm–3 NH4OH and 0.1 mol dm–3 HCl |
| 2. |
0.05 mol dm–3 NH4OH and 0.1 mol dm–3 HCl |
| 3. |
0.1 mol dm–3 NH4OH and 0.05 mol dm–3 HCl |
| 4. |
0.1 mol dm–3 CH3COONa and 0.1 mol dm–3 NaOH |
110. One mole of sugar is dissolved in three moles of water at 298 K. The relative lowering of vapour pressure is:
| 1. |
0.25 |
2. |
0.15 |
| 3. |
0.50 |
4. |
0.33 |
111. In both DNA and RNA, heterocyclic base and phosphate ester linkages are at:
| 1. |
C5' and C1' respectively of the sugar molecule. |
| 2. |
C1' and C5' respectively of the sugar molecule. |
| 3. |
C2' and C5' respectively of the sugar molecule. |
| 4. |
C5' and C2' respectively of the sugar molecule. |
112. To neutralize 20 mL of 0.1 M aqueous solution of phosphorus acid \((H_3PO_3) \) completely, the volume of 0.1 M aqueous KOH solution required is:
| 1. |
10 mL |
2. |
20 mL |
| 3. |
40 mL |
4. |
60 mL |
113. The increasing order of the first ionization enthalpies of the elements B, P , S and F (lowest first) is:
1. F < S < P < B
2. P < S < B < F
3. B < P < S < F
4. B < S < P < F
114. What is the molality of a urea solution prepared by dissolving 0.0100 g of urea,\(\left[\mathrm{CO}\left(\mathrm{NH}_2\right)_2\right]\) in 0.3000 dm³ of water at STP?
| 1. |
0.555 m |
2. |
5.55 × 10–4 m |
| 3. |
33.3 m |
4. |
3.33 × 10–2 m |
116. With a ground state energy of –13.6 eV for a hydrogen atom, what would be the energy in the second excited state?
1. –6.8 eV
2. –3.4 eV
3. –1.51 eV
4. –4.53 eV
117. H2 gas is absorbed on the metal surface like gold, tungsten, etc. This follows ________ order reaction:
| 1. |
Third |
2. |
Second |
| 3. |
Zero |
4. |
First |
118. SN1 reaction is feasible in:
119. For a chemical reaction,
\(\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g})+3 \mathrm{H}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{CH}_4(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g})\)
At equilibrium, the following factor influence the quantity of product formed:
1. Temperature
2. Pressure
3. Temperature and pressure
4. Temperature, pressure and catalyst
121. For the reaction:
Fe3O4 (s) + Al (s) → Fe (s) + Al2O3 (s)
Which of the following statements about the reaction are correct?
| a. |
Stoichiometric coefficient of Fe is 9. |
| b. |
Aluminium is oxidized. |
| c. |
Ferrous ferric oxide (Fe3O4) is oxidized. |
| d. |
Aluminium is reduced. |
1. a, c
2. a, b
3. b, c
4. c, d
122. The ionization constant of ammonia is 1.77 × 10–5. The pH of a 0.05M of ammonia solution is 11. The ionization constant of the conjugate acid of ammonia is:
1. 2.44 × 10–9
2. 6.14 × 10–12
3. 1.24 × 10–14
4. 5.64 × 10–10
123. The incorrect statement about H2SO4 is:
| 1. |
It is used in the fertilizer industry. |
| 2. |
It is used in the manufacture of pigments, paints, and detergents. |
| 3. |
It is used in the manufacture of storage batteries. |
| 4. |
It is a weak dehydrating agent. |
124. Incorrect match among the following is:
| 1. |
Tetraamminediaquacobalt(III)
chloride |
[Co(H2O)2(NH3)4]Cl3 |
| 2. |
Ammine
bromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II) |
[Pt(NH3)BrCl(NO2)]- |
| 3. |
Dichloridobis (ethane−1,2−diamine)
platinum(IV)nitrate |
[PtCl2(en)2](NO3)2 |
| 4. |
Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II) |
Fe2[Fe(CN)6]3 |
125. Match the oxide given in Column-I with its property given in Column-II:
|
Column-I |
|
Column-II |
| (i) |
|
(a) |
Neutral |
| (ii) |
|
(b) |
Basic |
| (iii) |
|
(c) |
Acidic |
| (iv) |
|
(d) |
Amphoteric |
Which of the following options is correct?
|
(i) |
(ii) |
(iii) |
(iv) |
| 1. |
(b) |
(a) |
(d) |
(c) |
| 2. |
(c) |
(b) |
(a) |
(d) |
| 3. |
(a) |
(d) |
(b) |
(c) |
| 4. |
(b) |
(d) |
(a) |
(c) |
126. The basic structural unit of silicates is:
| 1. |
|
2. |
|
| 3. |
|
4. |
|
127. The general electronic configuration for the 2nd-row transition series is:
| 1. |
[Ne]3d1-10 4s2 |
2. |
[Ar]3d1-10 4s1-2 |
| 3. |
[Kr]4d1-10 5s1-2 |
4. |
[Xe]5d1-10 5s1-2 |
128. The structure of B is:

129. In the graph shown below, which point represents the condition for bond formation?

130. The product(s) formed from the following reaction is/are:

| 1. |
RCOOH only |
2. |
RCH2COOH only |
| 3. |
 |
4. |
RCOOH and RCH2COOH |
131. The structure of the product B formed in the reaction given below is:
\(CH_3 - C \equiv C-H \xrightarrow {(i) NaNH_2/NH_3 (l)} (A) \\ \xrightarrow {CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-Br} (B)\)
1. \(\mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{C}-{CH}_{2}-\mathrm{CH}_{2}-\mathrm{CH}_{3}. \)
2. \(\mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}_{2}\)
3. \(\mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{CH}_{2}-\mathrm{C} \equiv\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_{2}-\mathrm{CH}_{3}\)
4. \(\mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{CH}-\mathrm{CH}_{2}-\mathrm{CH}_{3}\)
132. The correct IUPAC name of the given compound is:
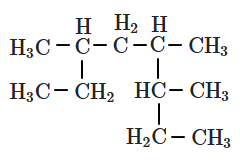
1. 3,5,6-Trimethyloctane
2. 1,2,3,6-Tetramethylheptane
3. 3,4,6-Trimethyloctane
4. None of the above
133. Kohlrausch gives the following relation for strong electrolytes:
\(\wedge=\wedge_{0}-A \sqrt{C}\)
Which of the following equality holds?
\(\text { 1. } \Lambda=\Lambda_{0} \text { as } C \longrightarrow \sqrt{\Lambda}\)
\(\text { 2. } \Lambda=\Lambda_{0} \text { as } C \longrightarrow \infty\)
\(\text { 3. } \Lambda=\Lambda_{0} \text { as } \mathrm{C} \longrightarrow 0\)
\(\text { 4. } \Lambda=\Lambda_{0} \text { as } C \longrightarrow 1\)
134. One mole of an ideal gas at 900 K undergoes two reversible processes, I followed by II, as shown below. If the work done by the gas in the two processes is same, the value of
\(ln {V_3 \over V_2}\) is:

(U: internal energy, S: entropy, p: pressure, V: volume, R: gas constant)
(Given : molar heat capacity at constant volume,
\(C_{v,m}\) of the gas is
\({ 5 \over 2 }R\))
1. 5
2. 10
3. 0.1
4. 0.5
135. The correct options to distinguish nitrate salts of
\(Mn^{2+}\)and
\(Cu^{2+}\) taken separately is:
| a. |
\(Mn^{2+}\) shows the characteristic green color in the flame test |
| b. |
Only \(Cu^{2+}\) shows the formation of a precipitate by passing \(H_2S\) in acidic medium |
| c. |
Only \(Mn^{2+}\) shows the formation of precipitate by passing \(H_2S\) in faintly basic medium |
| d. |
\(Cu^{2+} / Cu\) has higher reduction potential than \(Mn^{2+}/Mn\) (measured under similar conditions) |
1. Both a, and b are correct.
2. Both b, and c are correct.
3. Both c, and a are correct.
4. Both b and d are correct.
Chemistry - Section B
136. Mg is present in:
| 1. |
Chlorophyll |
2. |
Haemoglobin |
| 3. |
Vitamin-B12 |
4. |
Vitamin-B |
137. From the given options, the compound that has a planar structure is:
1. XeF4
2. XeOF2
3. XeO2F2
4. XeO4
138. An organic compound neither reacts with neutral ferric chloride solution nor with Fehling solution. It however, reacts with Grignard reagent and gives a positive iodoform test. The compound is:
139. The molecular geometry of SF6 is octahedral. The geometry of SF4 (including lone pair(s)) of electrons is:
1. Trigonal bipyramidal
2. Square planar
3. Tetrahedral
4. Pyramidal
140. The major product [B] in the following reaction is:

141. 6.023 × 1022 molecules are present in 10 g of substance ‘x’. The molarity of a solution containing 5 g of substance ‘x’ in 2L solution is:
| 1. |
0.00025 |
2. |
2.5 |
| 3. |
0.025 |
4. |
25 |
142. The variation of molar conductivity with the concentration of an electrolyte (X) in an aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.

The electrolyte X is:
| 1. |
CH3COOH |
2. |
KNO3 |
| 3. |
HCl |
4. |
NaCl |
143. For 1 molal aqueous solution of the following compounds, which one will show the highest freezing point ?
1. [Co(H2O)6]Cl3
2. [Co(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O
3. [Co(H2O)4Cl2]Cl.2H2O
4. [Co(H2O)3Cl3].3H2O
144. The solubility product of Pbl2 is 8.0 × 10–9 . The solubility of lead iodide in 0.1 molar solution of lead nitrate is x × 10–6 mol/L. The value of x is:
(Rounded off to the nearest integer)
| 1. |
154 |
2. |
423 |
| 3. |
282 |
4. |
141 |
145. Sucrose hydrolysis in an acidic solution into glucose and fructose follows the first-order rate law with a half-life of 3.33 h at 25°C. After 9 h, the fraction of sucrose remaining is f. The value of \(log(\frac{1}{f})\) is A×10-2 . The value of A is:
(Rounded off to the nearest integer) [Assume : ln 10 = 2.303, ln 2 = 0.693]
1. 78
2. 81
3. 85
4. 75
146. The reaction of cyanamide, NH2CN(s) with oxygen was run in a bomb calorimeter and U was found to be –742.24 kJ mol–1. The magnitude of (KJ) for the given-below reaction is:
NH2CN(s) + \(\frac{3}{2}\)O2(g) → N2(g) + O2(g) + H2O(l)
[Assume ideal gases and \(\mathrm{R}=8.314 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}\)]
| 1. |
741 KJ |
2. |
745 KJ |
| 3. |
720 KJ |
4. |
734 KJ |
147. The number of 𝜎 and 𝜋-bonds in the molecule of tetracyanoethylene is:

1. 9𝜎 and 9𝜋
2. 5𝜎 and 9𝜋
3. 9𝜎 and 7𝜋
4. 5𝜎 and 8𝜋
148. Lattice energy for an ionic compound relies on:
| 1. |
The size and charge of the ion. |
| 2. |
Packing of ions only |
| 3. |
Size of the ions only |
| 4. |
Charge on the ions only |
149. Ph − C ≡ C − CH3 \(\xrightarrow[]{Hg^{2+}/H^{+}}\) A
In the above reaction, the structure of the product (A) is:
150. The increasing order of stability of the following free radicals is:
| 1. |
\(\small{({CH}_3})_2 \dot{{C}}H<{({CH}_3})_3 \dot{{C}}<{({C}_6 {H}_5})_2 \dot{{C}}H <{({C}_6 {H}_5})_3 \dot{{C}}\) |
| 2. |
\(\small({{C}_{6} {H}_{5})}_{3} \dot{{C}}<({{C}_{6} {H}_{5})}_{2} \dot{{C}} {H}<({{CH}_{3})}_{3} \dot{{C}}<({{CH}_{3})}_{2} \dot{{C}}H\) |
| 3. |
\(\small({{C}_{6} {H}_{5})}_{2} \dot{{C}} {H}<({{C}_{6} {H}_{5})}_{3} \dot{{C}}<({{CH}_{3})}_{3} \dot{{C}} <({{CH}_{3})}_{2} \dot{{C}}H \) |
| 4. |
\(\small({{CH}_{3})}_{2} \dot{{C}} {H}<({{CH}_{3})}_{3} \dot{{C}}<({{C}_{6} {H}_{5})}_{3} \dot{{C}} <({{C}_{6} {H}_{5})}_{2} \dot{{CH}}\) |
Physics - Section A
151. The moments of inertia of four bodies, all having the same mass and radius, are reported as follows:
| \(I_1\) |
Moment of inertia of thin circular ring about its diameter |
| \(I_2\) |
Moment of inertia of circular disc about an axis perpendicular to the disc and going through the centre |
| \(I_3\) |
Moment of inertia of solid cylinder about its axis |
| \(I_4\) |
Moment of inertia of solid sphere about its diameter |
Which of the following relationships is correct?
1. \(I_1+I_3<I_2+I_4\)
2. \(I_1+I_2= I_3+\frac{5}{2}I_4\)
3. \(I_1=I_2=I_3>I_4\)
4. \(I_1=I_2=I_3<I_4\)
152. The wave described by
\(y=0.25\sin\left(10\pi x+2\pi t\right)\), where
\(x\) and
\(y\) are in meters and
\(t\) in seconds, is a wave traveling along the:
| 1. |
\(+\)ve X-direction with frequency \(1\) Hz and wavelength \(\lambda=0.2~\text{m}\) |
| 2. |
\(-\)ve X-direction with amplitude \(0.25\) m and wavelength \(\lambda=0.2~\text{m}\) |
| 3. |
\(-\)ve X-direction with frequency \(2\) Hz |
| 4. |
\(+\)ve X-direction with frequency \(\pi\) Hz and wavelength \(\lambda=0.2~\text{m}\) |
153. The Bulk modulus of a perfectly rigid body is equal to:
| 1. |
zero |
| 2. |
unity |
| 3. |
infinity |
| 4. |
may have any finite non-zero value |
154. The flux linked with a coil at any instant \(t\) is given by \(\phi=ct^{2}-20t+3\). If the induced emf at \(t=2~\text{s}\) is zero, then value of \(c\) is:
1. \(2\)
2. \(3\)
3. \(5\)
4. \(10\)
155. A coil of resistance \(10\) ohm and inductance \(5\) henry is connected to a \(100\) volt battery. The energy stored in the coil is:
1. \(250\text{ joule}\)
2. \(250\text{ erg}\)
3. \(125\text{ joule}\)
4. \(125\text{ erg}\)
156. If \({\mathit{\lambda}}_{1}\) and \({\mathit{\lambda}}_{2}\) are the wavelengths of the first members of the Lyman and Paschen series respectively, then \({\mathit{\lambda}}_{1}:{\mathit{\lambda}}_{2}\) is:
1. \(1:3\)
2. \(1:30\)
3. \(7:50\)
4. \(7:108\)
157. A transformer is used to light
\(140\) watts
\(24\) volt lamp from
\(240\) volt AC mains; the current in the main cable is
\(0.7\) amp. The efficiency of the transformer is:
| 1. |
\(63.8\%\) |
2. |
\(84\%\) |
| 3. |
\(83.3\%\) |
4. |
\(48\%\) |
158. A current \(I=I_{0}\sin\left(\omega t-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right) \) flows in an AC circuit. If the potential of \(E=E_{0}\sin\omega t\) has been applied, then the power consumption \(P\) in the circuit will be:
1. \(P=\dfrac{{E}_{0}{I}_{0}}{\sqrt{2}}\)
2. \({P}=\dfrac{EI}{\sqrt{2}}\)
3. \({P}=\dfrac{{E}_{0}{I}_{0}}{2}\)
4. \(P=\text{zero}\)
159. An object placed in front of a concave mirror of a focal length \(15~\text{cm}\) produces a virtual image which is twice the size of the object. The position of the object is:
1. \(\text{-}5.5~\text{cm}\)
2. \(\text{-}6.5~\text{cm}\)
3. \(\text{-}7.5~\text{cm}\)
4. \(8.5~\text{cm}\)
160. If a long hollow copper pipe carries a direct current, the magnetic field associated with the current will be:
| 1. |
only inside the pipe |
| 2. |
only outside the pipe |
| 3. |
both inside and outside the pipe |
| 4. |
neither inside nor outside the pipe |
161. If we shift a body in equilibrium from
\(A\) to
\(C\) in a gravitational field via path
\(AC\) or
\(ABC\), then the work done by the force
\(\vec{F}\) is:
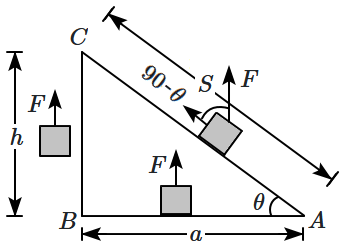
1. same for both the paths
2.
\(W_{AC}>W_{ABC}\)
3.
\(W_{AC}<W_{ABC}\)
4. none of the above
162. Two particles of masses \(m\) and \(2m\) with charges \(2q\) and \(2q\) are placed in a uniform electric field \(E\) and allowed to move for the same time. The ratio of their kinetic energies will be:
1. \(2:1\)
2. \(8:1\)
3. \(4:1\)
4. \(1:4\)
163. When a diamagnetic material is placed in a magnetic field, the field strength within the material is:
| 1. |
increased |
| 2. |
decreased |
| 3. |
unchanged |
| 4. |
fluctuating with time: first increasing and then decreasing |
164. The refractive index of a material of a plano-concave lens is \(\dfrac{5}{3},\) and the radius of curvature is \(0.3\) m. The focal length of the lens in air is:
1. \(-0.45\) m
2. \(-0.6\) m
3. \(-0.75\) m
4. \(-1.0\) m
165. Representing the stopping potential
\(V\) along
\(y\text-\)axis and
\(\left({{1}{/}\mathit{\lambda}}\right)\) along
\(x\text-\)axis for a given photocathode, the curve is a straight line, the slope of which is equal to:
| 1. |
\(\dfrac{e}{hc}\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac{hc}{e}\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{ec}{h}\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{he}{c}\) |
166. An element has binding energy \(8\) eV/nucleon. If it has a total binding energy \(128\) eV, then the number of nucleons are:
1. \(8\)
2. \(14\)
3. \(16\)
4. \(32\)
167. For the given circuit, the potential difference between
\(C\) and
\(D\) is:
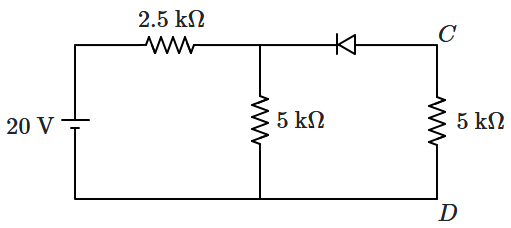
1.
\(0\)
2.
\(5~\text{V}\)
3.
\(10~\text{V}\)
4.
\(15~\text{V}\)
168. In the case of \(\mathrm{p\text-n}\) junction diode at a high value of reverse bias, the current rises sharply. The value of reverse bias is known as:
1. zero voltage
2. Zener voltage
3. inverse voltage
4. critical voltage
169. In an adiabatic process wherein pressure is increased by
\(\frac{2}{3}\%\) if
\(\frac{C_p}{C_v}=\frac{3}{2}\), then the volume decreases by about:
| 1. |
\(\frac{4}{9}\%\) |
2. |
\(\frac{2}{3}\%\) |
| 3. |
\(4\%\) |
4. |
\(\frac{9}{4}\%\) |
170. A particle of mass
\(m\) oscillates in simple harmonic motion between points
\(X_{1}\) and
\(X_{2},\) the equilibrium position being
\(O.\) Its kinetic energy is correctly represented by which of the following graphs?
171. In the interference pattern, the energy is:
| 1. |
created at the position of maxima. |
| 2. |
destroyed at the position of minima. |
| 3. |
conserved but redistributed. |
| 4. |
all of the above. |
172. A plane EM wave of frequency \(30\) MHz travels in free space along the \(X\text-\)direction. The electric field component of the wave at a particular point of space and time is \(E= 6~\text{V/m}\) along \(Y\text-\)direction. Its magnetic field component \(B\) at this point would be:
1. \(2\times{10}^{-8}~\text{T}\) along \(Z\text-\)direction
2. \(6\times{10}^{-6}~\text{T}\) along \(X\text-\)direction
3. \(6\times{10}^{-8}~\text{T}\) along \(Y\text-\)direction
4. \(6\times{10}^{-8}~\text{T}\) along \(Z\text-\)direction
173. Given that
\(T\) stands for time period and
\(l\) stands for the length of simple pendulum. If
\(g\) is the acceleration due to gravity, then which of the following statements about the relation
\(T^{2}~=l/g\) is correct?
| 1. |
It is correct both dimensionally as well as numerically. |
| 2. |
It is neither dimensionally correct nor numerically. |
| 3. |
It is dimensionally correct but not numerically. |
| 4. |
It is numerically correct but not dimensionally. |
174. The friction of the air causes vertical retardation equal to
\(10\%\) of the acceleration due to gravity. The maximum height will be decreased by:
(Take
\(g=10\) ms
-2)
| 1. |
\(8\%\) |
2. |
\(9\%\) |
| 3. |
\(10\%\) |
4. |
\(11\%\) |
175. At what height
\(h\) above the Earth does the value of
\(g\) become
\(\dfrac{g}{2}?\) (where
\(R\) is the radius of the Earth)
| 1. |
\(3R\) |
2. |
\(\sqrt{2}R\) |
| 3. |
\(\left({\sqrt{2}-1}\right){R}\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}R\) |
176. Two rods of equal length and area of the cross-section are kept parallel and lagged between temperatures
\(20^{\circ}\text{C}\) and
\(80^{\circ}\text{C}\). The ratio of the effective thermal conductivity to that of the first rod is:
(the ratio
\(\left(\dfrac{K_1}{K_2}= \dfrac{3}{4}\right) \)
| 1. |
\(7:4\) |
2. |
\(7:6\) |
| 3. |
\(4:7\) |
4. |
\(7:8\) |
177. Let us suppose that the earth (radius \(6400~\text{km}\)) has a net charge equivalent to one electron per square metre of its surface area. The earth's potential (in volt) at the surface will be:
1. \(+0.12\)
2. \(-0.12\)
3. \(+1.2\)
4. \(-1.2\)
178. In the following figure, the reading of the ammeter
\(\mathrm{A}\) is:
(assume the internal resistance of the battery is zero)

| 1. |
\(\dfrac{20}{3}~\text{A}\) |
| 2. |
\(\dfrac{20}{12}~\text{A}\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{20}{4}~\text{A}\) |
| 4. |
\(\left(\dfrac{20}{3}+\dfrac{20}{12}\right)~\text{A}\) |
179. If the range of a gun which fires a shell with muzzle speed
\(v,\) is
\(R,\) then the angle of elevation of the gun is:
| 1. |
\({\cos}^{{-}{1}}\left({\dfrac{{v}^{2}}{Rg}}\right)\) |
2. |
\({\cos}^{{-}{1}}\left({\dfrac{Rg}{{v}^{2}}}\right)\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{1}{2}{\sin}^{{-}{1}}\left({\dfrac{{v}^{2}}{Rg}}\right)\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{1}{2}{\sin}^{{-}{1}}\left({\dfrac{Rg}{{v}^{2}}}\right)\) |
180. A gas at a temperature of \(250~\text{K}\) is contained in a closed vessel. If a gas is heated through \(1^{\circ}\text{C}\), the percentage increase in its pressure is nearly:
1. \(0.4\%\)
2. \(0.6\%\)
3. \(0.8\%\)
4. \(1.0\%\)
181. The linear density of a wire is
\(1.3\times{10}^{-4}~\text{kg/m}\). A transverse wave represented by the equation,
\(y=0.021\sin\left(x+30t\right)\) is propagating along the wire (
\(x\) and
\(y\) are in
\(\text{m}\) and
\(t\) in sec). The tension of the wire is:
| 1. |
\(0.12~\text{N}\) |
2. |
\(0.48~\text{N}\) |
| 3. |
\(1.2~\text{N}\) |
4. |
\(4.8~\text{N}\) |
182. Two coplanar concentric circular coils, each having
\(10\) turns, have radii
\(20\text{ cm}\) and
\(40~\text{cm},\) respectively. The inner coil carries a current of
\(0.2\text{ A}\) and the outer coil carries a current of
\(0.3~\text{A},\) with the currents flowing in opposite directions. Find the net magnetic field at the common centre, expressed in
\(\text{Wb/m}^2.\)
| 1. |
\(\dfrac{35}{4}\mu_{0}\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac{\mu_0}{80}\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{7}{80}\mu_{0}\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{5}{4}\mu_{0}\) |
183. A massless string passes over a frictionless pulley and carries two masses
\(m_1\) and
\(m_2 (m_1 >m_2)\) at its ends. If
\(g\) is the acceleration due to gravity, then the thrust on the pulley is:

1.
\(\left(\frac{2 m_{1} m_{2}}{m_{1}-m_{2}}\right) g\)
2.
\(\left(\frac{2 m_{1} m_{2}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}\right) g\)
3.
\(\left(\frac{4 m_{1} m_{2}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}\right) g\)
4. zero
184. Three identical thin rods each of length \(l\) and mass \(M\) are joined together to form a letter \(H.\) The moment of inertia of the system about one of the sides of \(H\) is:
1. \(\dfrac{M l^{2}}{3}\)
2. \(\dfrac{M l^{2}}{4}\)
3. \(\dfrac{2 M l^{2}}{3}\)
4. \(\dfrac{4 M l^{2}}{3}\)
185. A body floats in a liquid contained in a beaker. The whole system as shown in the figure is falling under gravity. The upthrust on the body due to liquid is:

| 1. |
zero. |
| 2. |
equal to the weight of liquid displaced. |
| 3. |
equal to the weight of the body in air. |
| 4. |
equal to the weight of the immersed body. |
Physics - Section B
186. Two satellites \(A\) and \(B\) of masses \(200\) kg and \(400\) kg are revolving around the Earth at heights of \(600\) km and \(1600\) km respectively. If \(T_A\) and \(T_B\) are the time periods of \(A\) and \(B\) respectively, then the ratio \(\frac{T_A}{T_B}\) is:
(Given: radius of Earth = \(6400\) km, mass of Earth \(=6\times 10^{24}\) kg)
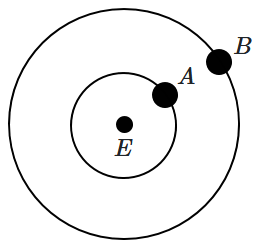
| 1. |
\(\left ( \frac{7}{8} \right )^{3}\) |
2. |
\(\left ( \frac{7}{8} \right )^{3/2}\) |
| 3. |
\(\left ( \frac{7}{8} \right )^{2/3}\) |
4. |
\(\left ( \frac{7}{8} \right )^{1/3}\)
|
187. A body \(A\) is projected vertically upwards. Another body \(B\) of the same mass is projected at an angle of \(60^{\circ}\) with the horizontal. If both the bodies attain the same maximum height, the ratio of the initial kinetic energy of body \(A\) to that of body \(B\) is:
| 1. |
\(\frac{3}{4}\) |
2. |
\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) |
| 3. |
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) |
4. |
\(\frac{1}{2}\) |
188. A wire carrying a current
\(i\) from
\(O\) to
\(A\) is placed inside a uniform magnetic field
\(\overrightarrow{B}=-{B_0}\hat{k}\). The shape of the wire is parabolic and has equation
\(y = 2x-x^2\). The force on the wire will be:
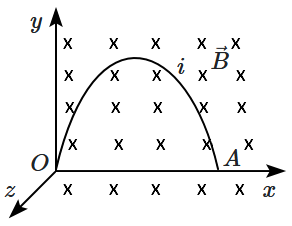
1.
\(F= 2B_0i, ~\text{upwards}\)
2.
\(F= 2B_0i,~\text{downwards}\)
3.
\(F= 4B_0i,~\text{upwards}\)
4.
\(F= 4B_0i,~\text{downwards}\)
189. Consider a system in which the work done by external forces acting equals
\(-10\) Joules and the potential energy decreases by
\(30\) Joules. Which of the following statements is true?
| 1. |
There are definitely no "non-conservative" forces acting in this situation |
| 2. |
At least one of the forces in this situation is "conservative" in nature |
| 3. |
Work done by the "internal" forces would be \(-30\) joules |
| 4. |
Work done by the "internal" forces would be \(-40\) joules |
190. Dispersion of light is caused due to:
| 1. |
intensity of light |
2. |
density of the medium |
| 3. |
wavelength of light |
4. |
amplitude of light |
191. Tanks
\(A\) and
\(B\) open at the top contains two different liquids upto a certain height in them. A hole is made in the wall of each tank at a depth
\(h\) from the surface of the liquid. The area of the hole in
\(A\) is twice that of in
\(B\). If the mass flow rate through each hole is equal, then the ratio of densities of the liquids respectively is:
| 1. |
\(\dfrac{2}{1}\) |
2. |
\(\dfrac{3}{2}\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{2}{3}\) |
4. |
\(\dfrac{1}{2}\) |
192. An
\(\mathrm{n\text-}\)type semiconductor is formed by adding which of the following impurity materials:
| 1. |
aluminum, boron, or selenium |
| 2. |
aluminum, boron, or indium |
| 3. |
phosphorus, antimony, or arsenic |
| 4. |
cobalt, aluminum, or selenium |
193. A gas is heated at constant pressure. The fraction of heat supplied used for external work is:
| 1. |
\(\dfrac{1}{{\gamma}}\) |
2. |
\(\left({{1}{-}\dfrac{1}{{\gamma}}}\right)\) |
| 3. |
\({\gamma}{-}{1}\) |
4. |
\(\left({{1}{-}\dfrac{1}{{{\gamma}}^{2}}}\right)\) |
194. A particle on the trough of a wave at any instant will come to the mean position after a time: (
\(T\) = time period)
| 1. |
\(\frac{T}{2}\) |
2. |
\(\frac{T}{4}\) |
| 3. |
\(T\) |
4. |
\(2T\) |
195. The variation of potential with distance
\(R\) from a fixed point is shown in the figure. The electric field at
\(R=5~\text{m}\) is:
(Given, the potential,
\(V\) in volts and distance,
\(R\) in meters)
| 1. |
\(2.5~\text{Vm}^{-1}\) |
2. |
\(-2.5~\text{Vm}^{-1}\) |
| 3. |
\(\dfrac{2}{5}~\text{Vm}^{-1}\) |
4. |
\(-\dfrac{2}{5}~\text{Vm}^{-1}\) |
196. A photon of wavelength \(6630~\mathring{A}\) is incident on a totally reflecting surface. The momentum delivered by the photon is equal to:
1. \(6.63\times{10}^{-27}~\text{kg-m}{/}{\text{s}}\)
2. \(2\times{10}^{-27}~\text{kg-m}{/}{\text{s}}\)
3. \(10^{-27}~\text{kg-m}{/}{\text{s}}\)
4. none of these
197. With what minimum acceleration can a fireman slide down a rope whose breaking strength is \(\frac{2}{5}^{\text{th}}\) of his weight?
1. \(1~g\)
2. \(0.4~g\)
3. \(0.6~g\)
4. \(0.8~g\)
198. A particle executes simple harmonic motion with a period of \(8~\text{s}\) and amplitude \(4~\text{cm}\). Its maximum speed (in cm/s) is:
1. \(\mathit{\pi}\)
2. \(\dfrac{\mathit{\pi}}{2}\)
3. \(\dfrac{\mathit{\pi}}{3}\)
4. \(\dfrac{\mathit{\pi}}{4}\)
199. Two electric bulbs, one of
\(200~\text{V}-40~\text{W}\) and the other of
\(200~\text{V}-100~\text{W}\) are connected in a domestic circuit. Then:
| 1. |
they have equal currents through them. |
| 2. |
the resistances of both the bulbs are the same. |
| 3. |
the resistance of the bulb of \(40~\text{watts}\) is more. |
| 4. |
the resistance of the bulb of \(100~\text{watts}\) is more. |
200. A closed tube partly filled with water lies in a horizontal plane. The tube rotates about a perpendicular bisector with angular velocity
\(\omega\). If the tube stops rotating, the moment of inertia of the system:
| 1. |
increases. |
| 2. |
decreases. |
| 3. |
remains constant. |
| 4. |
depends on the sense of rotation. |
*If above link doesn't work, please go to test link from where you got the pdf and fill OMR from there
CLICK HERE to get FREE ACCESS for 2 days of ANY NEETprep course
 I: A is filiform apparatus, B is synergid,
I: A is filiform apparatus, B is synergid,