Select the mismatch:
| Column-I | Column-II | |
| 1. | Gas vacuoles | Green bacteria Cells |
| 2. | Large central vacuoles | Animal cells |
| 3. | Protists | Eukaryotes |
| 4. | Methanogens | Prokaryotes |
Select the wrong statement:
| 1. | Bacterial cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan |
| 2. | Pili and fimbriae are mainly involved in the motility of bacterial cells |
| 3. | Cyanobacteria lack flagellated cells |
| 4. | Mycoplasma is a wall-less microorganism |
A cell organelle containing hydrolytic enzyme is:
1. lysosome
2. microsome
3. ribosome
4. mesosome
| 1. | Larger nucleoli are present in dividing cells. |
| 2. | It is a membrane-bound structure. |
| 3. | It takes part in spindle formation. |
| 4. | It is a site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis. |
| 1. | Polysome | 2. | Polyhedral bodies |
| 3. | Plastidome | 4. | Nucleosome |
Which of the following cell organelles is responsible for extracting energy from carbohydrates to form ATP?
1. Ribosome
2. Chloroplast
3. Mitochondrion
4. Lysosome
| 1. | spindle fibres, centrioles and cilia |
| 2. | centrioles, spindle fibres and chromatin |
| 3. | centrosome, nucleosome and centrioles |
| 4. | cilia, flagella and peroxisomes |
| 1. | Chloroplasts | 2. | Lysosomes |
| 3. | Nuclei | 4. | Mitochondria |
Which of the following structure is not found in a prokaryotic cell?
1. Nuclear envelope
2. Ribosome
3. Mesosome
4. Plasma membrane
Match the columns and identify the correct option.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| A. | Thylakoids | (i) | Disc-shaped sacs in Golgi apparatus |
| B. | Cristae | (ii) | Condensed structure of DNA |
| C. | Cisternae | (iii) | Flat membranous sacs in stroma |
| D. | Chromatin | (iv) | Infolding in mitochondria |
1. A → (iv), B → (iii), C → (i), D → (ii)
2. A → (iii), B → (iv), C → (i), D → (ii)
3. A → (iii), B → (i), C → (iv), D → (ii)
4. A → (iii), B → (iv), C → (ii), D → (i)
Identify the correct order of organization of genetic material from largest to smallest.
1. Chromosome, gene, genome, nucleotide
2. Genome, chromosome, nucleotide, gene
3. Genome, chromosome, gene, nucleotide
4. Chromosome, genome, nucleotide, gene
Which of the following is not membrane-bound?
1. Vacuoles
2. Ribosomes
3. Lysosome
4. Mesosomes
The structures that help some bacteria to attach to rocks and/or host tissues are?
1. Rhizoids
2. Fimbriae
3. Mesosomes
4. Holdfast
Cellular organelles with membranes are:
| 1. | Nucleus, ribosome and mitochondria |
| 2. | Chromosomes, ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum |
| 3. | Endoplasmic reticulum, ribosome and nuclei |
| 4. | Lysosomes, Golgi apparatus and mitochondria |
The chromosomes in which the centromere is situated close to one end are:
Select the correct matching among the following pairs.
| 1. | Smooth ER-Oxidation of phospholipids |
| 2. | Smooth ER-Synthesis of lipids |
| 3. | Rough ER-Synthesis of glycogen |
| 4. | Rough ER-Oxidation of fatty acids |
Which one of the following is not an inclusion body found in prokaryotes?
| 1. | Phosphate granule | 2. | Cyanophycean granule |
| 3. | Glycogen granule | 4. | Polysome |
DNA is not present in:
Which of the following structures performs the function of mitochondria in a bacteria?
| 1. | Nucleoid | 2. | Ribosomes |
| 3. | Cell wall | 4. | Mesosomes |
The osmotic expansion of a cell kept in water is chiefly regulated by:
1. Mitochondria
2. Vacuoles
3. Plastids
4. Ribosomes
Match the following and select the correct answer:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Centriole | (i) | Infoldings in mitochondria |
| (b) | Chlorophyll | (ii) | Thylakoids |
| (c) | Cristae | (iii) | Nucleic acids |
| (d) | Ribozymes | (iv) | Basal body of cilia or flagella |
1. A-iv, B-ii, C-i, D-iii
2. A-i, B-ii, C-iv, D-iii
3. A-i, B-iii, C-ii, D-iv
4. A-iv, B-iii, C-i, D-ii
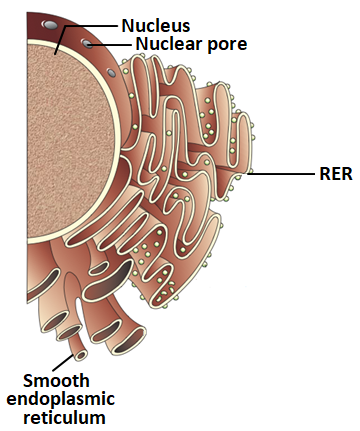
| 1. | Golgi apparatus, protein synthesis |
| 2. | Golgi apparatus, formation of amino acids |
| 3. | Rough endoplasmic reticulum, protein synthesis |
| 4. | Rough endoplasmic reticulum, formation of glycoproteins |
| 1. | in digesting proteins and carbohydrates |
| 2. | as energy transferring organelles |
| 3. | in post-translational modification of proteins and glycosylation of lipids |
| 4. | in trapping the light and transforming it into chemical energy |
A major site for synthesis of lipids is:
1. SER
2. Symplast
3. Nucleoplasm
4. RER
Ribosomal RNA is actively synthesized in:
1. Lysosomes
2. Nucleolus
3. Nucleoplasm
4. Ribosomes
What is true about ribosomes?
| 1. | The prokaryotic ribosomes are 80S, where S stands for sedimentation coefficient |
| 2. | These are composed of ribonucleic acid and proteins |
| 3. | These are found only in eukaryotic cells |
| 4. | These are self-splicing introns of some RNAs |
Select the correct statement from the following regarding cell membrane:
| 1. | Na+ and K+ ions move across cell membranes by passive transport |
| 2. | Proteins make up 60% to 70% of the cell membrane |
| 3. | Lipids are arranged in a bilayer with polar heads towards the inner part |
| 4. | Fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane was proposed by Singer and Nicolson |
Which one of the following structures between two adjacent cells is an effective transport pathway?
1. Plasmodesmata
2. Plastoquinones
3. Endoplasmic reticulum
4. Plasmalemma
1. Golgi apparatus
2. plastid
3. lysosome
4. vacuole
| 1. | mitochondria | 2. | chromoplast |
| 3. | ribosomes | 4. | chloroplast |
Which one of the following has its own DNA?
1. Mitochondria
2. Dictyosome
3. Lysosome
4. Peroxisome
The main arena of various types of activities of a cell is:
| 1. | Plasma membrane | 2. | Mitochondria |
| 3. | Cytoplasm | 4. | Nucleus |
Alage have cell wall made up of:
| 1. | Cellulose, galactans and mannans |
| 2. | Hemicellulose, pectins and proteins |
| 3. | Pectins, cellulose and proteins |
| 4. | Cellulose, hemicellulose and pectins |
Middle lamella is mainly composed of:
1. hemicellulose
2. muramic acid
3. calcium pectate
4. phosphoglycerides
Plasmodesmata are:
| 1. | lignified cemented layers between cells |
| 2. | locomotory structures |
| 3. | membranes connecting the nucleus with plasmalemma |
| 4. | connections between adjacent cells |
The cytoskeleton is made up of:
| 1. | calcium carbonate granules |
| 2. | callose deposits |
| 3. | cellulosic microfibrils |
| 4. | proteinaceous filaments |
| 1. | several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA |
| 2. | many ribosomes attached to a strand of endoplasmic reticulum |
| 3. | a ribosome with several subunits |
| 4. | ribosomes attached in a linear arrangement |
| 1. | is membrane-bound and contains storage proteins and lipids |
| 2. | is membrane-bound and contains water and excretory substances |
| 3. | lacks membrane and contains air |
| 4. | lacks membrane and contains water and excretory substances |
Which one of the following is not a constituent of the cell membrane?
1. Cholesterol
2. Glycolipids
3. Proline
4. Phospholipids
Select the wrong statement from the following:
| 1. | Both chloroplast and mitochondria contain an inner and an outer membrane. |
| 2. | Both chloroplasts and mitochondria have an internal compartment, the thylakoid space bounded by the thylakoid membrane. |
| 3. | Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain DNA. |
| 4. | The chloroplasts are generally much larger than mitochondria. |
The concept of "Omnis cellula-e-cellula" regarding cell division was first proposed by:
1. Aristotle
2. Rudolf Virchow
3. Theodor Schwann
4. Schleiden
Which of the following pair of organelles does not contain DNA?
| 1. | Nuclear envelope and Mitochondria |
| 2. | Mitochondria and Lysosomes |
| 3. | Chloroplast and Vacuoles |
| 4. | Lysosomes and vacuoles |
Which of the following statements is not correct?
| 1. | Lysosomes are formed by the process of packaging in the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| 2. | Lysosomes have numerous hydrolytic enzymes |
| 3. | The hydrolytic enzyme of lysosomes are active under acidic pH |
| 4. | Lysosomes are membrane bound structure. |
Which of the following cell organelles is present in the highest number in secretory cells?
| 1. | Mitochondria | 2. | Golgi complex |
| 3. | Endoplasmic reticulum | 4. | Lysosomes |
Non-membranous nucleoplasmic structures in the nucleus, are the sites for active synthesis of:
| 1. | protein | 2. | mRNA |
| 3. | rRNA | 4. | tRNA |
Which of the following nucleic acids is present in an organism having 70 S ribosomes only?
| 1. | Single-stranded DNA with a protein coat |
| 2. | Double-stranded circular naked DNA |
| 3. | Double-stranded DNA enclosed in nuclear membrane |
| 4. | Double-stranded circular DNA with histone proteins |
Match Column-I with Column-II.
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| (a) | Golgi apparatus | (i) | Synthesis of protein |
| (b) | Lysosomes | (ii) | Trap waste and excretory products |
| (c) | Vacuoles | (iii) | Formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids |
| (d) | Ribosomes | (iv) | Digesting biomolecules |
Choose the right match from the options given below:
| Options: | (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| 1. | (iii) | (iv) | (ii) | (i) |
| 2. | (iv) | (iii) | (i) | (ii) |
| 3. | (iii) | (ii) | (iv) | (i) |
| 4. | (i) | (ii) | (iv) | (iii) |
Which is the important site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids in eukaryotic cells?
| 1. | Peroxisomes | 2. | Golgi bodies |
| 3. | Polysomes | 4. | Endoplasmic reticulum |
Which of the following statements about inclusion bodies is incorrect?
| 1. | These are involved in the ingestion of food particles. |
| 2. | They lie freely in the cytoplasm. |
| 3. | These represent reserve material in cytoplasm. |
| 4. | They are not bound by any membrane. |
Inclusion bodies of blue-green, purple, and green photosynthetic bacteria are:
1. Contractile vacuoles
2. Gas vacuoles
3. Centrioles
4. Microtubules
The biosynthesis of ribosomal RNA occurs in:
1. Ribosomes
2. Golgi apparatus
3. Microbodies
4. Nucleolus
The size of Pleuro Pneumonia Like Organism (PPLO) is:
1. 0.02 m
2. 1-2 m
3. 10-20 m
4. 0.1 m
Match the following columns and select the correct option:
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| (a) | Smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
(i) | Protein synthesis |
| (b) | Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
(ii) | Lipid synthesis |
| (c) | Golgi complex | (iii) | Glycosylation |
| (d) | Centriole | (iv) | Spindle formation |
| Options: | (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| 1. | (ii) | (i) | (iii) | (iv) |
| 2. | (iii) | (i) | (ii) | (iv) |
| 3. | (iv) | (ii) | (i) | (iii) |
| 4. | (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
Which one of the following cellular parts is correctly described?
| 1. | Centrioles - sites for active RNA synthesis |
| 2. | Ribosomes - those on chloroplasts are larger (80s) while those in the cytoplasm are smaller (70s) |
| 3. | Lysosomes - optimally active at a pH of about 8.5 |
| 4. | Thylakoids - flattened membranous sacs forming the grana of chloroplasts |
An elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures present in the cytoplasm which helps in the maintenance of cell shape is called:
1. Endoplasmic Reticulum
2. Plasmalemma
3. Cytoskeleton
4. Thylakoid
Identify the components labelled A, B, C and D in the diagram below from the list (i) to (viii) given along with:
Components :
(i) Cristae of mitochondria
(ii) Inner membrane of mitochondria
(iii) Cytoplasm
(iv) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(v) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
(vi) Mitochondrial matrix
(vii) Cell vacuole
(viii) Nucleus
The correct components are:
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1. | (i) | (iv) | (viii) | (vi) |
| 2. | (vi) | (v) | (iv) | (vii) |
| 3. | (v) | (i) | (iii) | (ii) |
| 4. | (v) | (iv) | (viii) | (iii) |
Which one of the following is not considered as a part of the endomembrane system?
| 1. | Lysosome | 2. | Golgi complex |
| 3. | Peroxisome | 4. | Vacuole |
The figure below shows the structure of a mitochondrion with its four parts labelled (A), (B), (C) and (D). Select the part correctly matched with its function.
| 1. | Part (A) : Matrix – a major site for respiratory chain enzymes |
| 2. | Part (D) : Outer membrane – gives rise to the inner membrane by splitting |
| 3. | Part (B) : Inner membrane – forms infoldings called cristae |
| 4. | Part (C) : Cristae – possess single circular DNA molecule and ribosome |
According to the widely accepted "fluid mosaic model", cell membranes are semi-fluid, where lipids and integral proteins can diffuse randomly. In recent years, this model has been modified in several respects. In this regard, which of the following statements is incorrect:
| 1. | Proteins can also undergo flip-flop movements in the lipid bilayer |
| 2. | Many proteins remain completely embedded within the lipid bilayer |
| 3. | Proteins in cell membranes can travel within the lipid bilayer |
| 4. | Proteins can remain confined within certain domains of the membrane |
The main organelle involved in the modification and routing of newly synthesized proteins to their destinations is -
1. Endoplasmic Reticulum
2. Lysosome
3. Mitochondria
4. Chloroplast
Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in:
1. Grana
2. Pyrenoid
3. Stroma
4. Both (1) and (3)
Role of microtubules is:
| 1. | To help in cell division |
| 2. | Cell membrane formation |
| 3. | Respiration |
| 4. | Pinocytosis |
Difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes is in:
| 1. | Circular ss DNA in prokaryotes |
| 2. | Histone with prokaryotic DNA |
| 3. | Operon in eukaryotes |
| 4. | Membrane bound organelles in eukaryotes |
Flagella of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in:
| 1. | Location in cell and mode of functioning |
| 2. | Microtubular organization and type of movement |
| 3. | Microtubular organization and function |
| 4. | Type of movement & placement in the cell |
In chloroplasts, chlorophyll is present in the:
1. Inner membrane
2. Thylakoids
3. Stroma
4. Outer membrane
Double unit membrane is absent in:
1. Ribosomes
2. Nucleus
3. Plastids
4. E.R
In the fluid mosaic model of a plasma membrane:
| 1. | Upper layer is non-polar and hydrophilic |
| 2. | The polar layer is hydrophobic |
| 3. | Phospholipids form a bimolecular layer in the middle part |
| 4. | Proteins form a middle layer |
Ribosomes are produced in:
1. Nucleolus
2. Cytoplasm
3. Mitochondria
4. Golgibody
The mitotic spindle is mainly composed of which protein:
1. Actin
2. Tubulin
3. Actomyosin
4. Myoglobin
Which of the following ribosomes are engaged in protein synthesis in the animal cell:
| 1. | Ribosomes that occur on the nuclear membrane and E.R. |
| 2. | Ribosomes of only cytosol |
| 3. | Ribosomes of only nucleolus and cytosol |
| 4. | Ribosomes of only mitochondria and cytosol |
Extranuclear DNA is found in:
| 1. | Lysosome and chloroplast |
| 2. | Chloroplast and mitochondria |
| 3. | Mitochondria and lysosome |
| 4. | Golgi and E.R. |
Lysosome contains:
| 1. | Oxidative enzymes | 2. | Hydrolytic enzymes |
| 3. | Reductive enzymes | 4. | Anabolic enzymes |
Chromosomes in a bacterial cell can be 1–3 in number and:
| 1. | Are always circular |
| 2. | Are always linear |
| 3. | Can be either circular or linear, but never both within the same cell |
| 4. | Can be circular as well as linear within the same cell |
The difference in gram ⊕ and gram bacteria is due to:
| 1. | Cell wall | 2. | Cell membrane |
| 3. | Ribosome | 4. | Cytoplasm |
Extranuclear chromosomes occur in:
| 1. | Peroxisome and ribosome | 2. | Chloroplast and mitochondria |
| 3. | Mitochondria and ribosome | 4. | Chloroplast and lysosome |
Element necessary for the middle lamella:
1. Ca
2. Zn
3. K
4. Cu
Microtubules are absent in:
1. Mitochondria
2. Flagella
3. Spindle fibers
4. Centriole
When the centromere is situated in the middle of two equal arms of chromosomes, the chromosome is referred as :
1. Sub-metacentric
2. Acrocentric
3. Metacentric
4. Telocentric
Match List-I with List-II
| List-I | List - II | ||
| a. | Cristae | i. | Primary constriction in chromosome |
| b. | Thylakoids | ii. | Disc-shaped sacs in Golgi apparatus |
| c. | Centromere | iii. | Infoldings in mitochondria |
| d. | Cisternae | iv. | Flattened membranous sacs in stroma of plastids |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| 1. | (iii) | (iv) | (i) | (ii) |
| 2. | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (i) |
| 3. | (iv) | (iii) | (ii) | (i) |
| 4. | (i) | (iv) | (iii) | (ii) |
Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
| 1. | The perinuclear space forms a barrier between the materials present inside the nucleus and that of the cytoplasm. |
| 2. | Nuclear pores act as passages for proteins and RNA molecules in both directions between nucleus and cytoplasm. |
| 3. | Mature sieve tube elements possess a conspicuous nucleus and usual cytoplasmic organelles. |
| 4. | Microbodies are present both in plant and animal cells. |
The organelles that are included in the endomembrane system are:
| 1. | Golgi complex, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, and Lysosomes |
| 2. | Golgi complex, Endoplasmic reticulum, Mitochondria, and Lysosomes |
| 3. | The endoplasmic reticulum, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, and Lysosomes |
| 4. | The endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, Lysosomes, and Vacuoles |
Match List-I with List-II.
| List-I | List-II | ||
| (a) | Metacentric chromosome | (i) | Centromere situated close to the end forming one extremely short and one very long arms |
| (b) | Acrocentric chromosome | (ii) | Centromere at the terminal end |
| (c) | Sub-metacentric | (iii) | Centromere in the middle forming two equal arms of chromosomes |
| (d) | Telocentric chromosome | (iv) | Centromere slightly away from the middle forming one shorter arm and one longer arm |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| 1. | (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
| 2. | (iii) | (i) | (iv) | (ii) |
| 3. | (i) | (iii) | (ii) | (iv) |
| 4. | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (i) |
| Statement I: | Mycoplasma can pass through less than 1 micron filter size. |
| Statement II: | Mycoplasma are bacteria with cell walls. |
| 1. | SER are the sites for lipid synthesis |
| 2. | RER has ribosomes attached to ER |
| 3. | SER is devoid of ribosomes |
| 4. | In prokaryotes, only RER is present |
Given below are two statements:
| Statement I: | Membrane-bound organelles of the endomembrane system coordinate cellular functions. |
| Statement II: | Mitochondria and chloroplasts are not considered a part of the endomembrane system. |
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
| 1. | Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect. |
| 2. | Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct. |
| 3. | Both Statement I and Statement II are correct. |
| 4. | Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect. |
Match List-I with List-II
| List-I | List-II | ||
| (a) | Chromoplasts | (i) | Proteins |
| (b) | Amyloplasts | (ii) | Oil and fats |
| (c) | Elaioplasts | (iii) | Starch |
| (d) | Aleuroplasts | (iv) | Carotene |
Choose the correct answer from the option given below
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| 1. | (iv) | (i) | (iii) | (ii) |
| 2. | (iv) | (iii) | (ii) | (i) |
| 3. | (iv) | (ii) | (iii) | (i) |
| 4. | (iv) | (iii) | (i) | (ii) |
| 1. | Substances with hydrophobic moiety |
| 2. | Substances with hydrophilic moiety |
| 3. | All substances, irrespective of hydrophobic and hydrophilic moiety |
| 4. | Substances which are soluble in lipids |
| 1. | Hydrolytic enzymes will function more efficiently |
| 2. | Hydrolytic enzymes will become inactive |
| 3. | Lysosomal enzymes will be released into the cytoplasm |
| 4. | Lysosomal enzymes will be more active |