In elimination, some compounds follow Hofmann's rule which means:
1. The double bond goes to the most substituted carbon
2. The compound is resistant to elimination
3. No double bond is formed
4. The double bond goes mainly towards the least substituted carbon
The hydrolysis of alkyl halides by aqueous is best termed as:
(1) electrophilic substitution reaction
(2) electrophilic addition reaction
(3) nucleophilic addition reaction
(4) nucleophilic substitution reaction
Optically active substrates via SN1 reaction predominantly result in:
1. Retention in configuration
2. Inversion in configuration
3. Racemic product
4. No product
"The negative part of the addendum adds on the carbon atom joined to the least number of hydrogen atoms."
This statement is called:
1. Markownikoff's rule
2. Peroxide effect
3. Baeyer's strain theory
4. Thiele's theory
Heterolysis of propane gives:
(1) methyl and ethyl free radicals
(2) methylium cation and ethyl anion
(3) methyl anion and ethylium cation
(4) methylium and ethylium cations
The correct statements among the following regarding the \(\text{S}_\text{N}2\) reaction are:
| (i) | The rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of the nucleophile. |
| (ii) | The nucleophile attacks the carbon atom on the side of the molecule opposite to the group being displaced. |
| (iii) | The reaction proceeds with simultaneous bond formation and bond break. |
1. (i), (ii)
2. (i), (iii)
3. (i), (ii), (iii)
4. (ii), (iii)
Carbanions initiate:
1. Addition reactions
2. Substitution reactions
3. Both (1) and (2)
4. None of these
Dehydrogenation of ethanol to give ethanal is:
(1) addition reaction
(2) elimination reaction
(3) elimination reaction
(4) elimination reaction
Ease of abstraction of hydrogen is greater when attached to:
1. 1 Carbon
2. 2 Carbon
3. 3 Carbon
4. neo-carbon
In the following mechanism, the chain termination step is:
| (i) |  |
| (ii) | 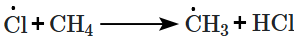 |
| (iii) |  |
| (iv) |  |
1. (i)
2. (ii)
3. (iii)
4. (iv)
Which step is the chain propagation step in the following mechanism?
| (i) |  |
| (ii) |  |
| (iii) |  |
| (iv) |  |
1. (iii)
2. (ii)
3. (i)
4. (iv)
Carbanion can undergo:
1. Rearrangement
2. Combination with cation
3. Addition to a carbonyl group
4. All of the above are correct
The 1 mechanism for substitution reaction by nucleophile is favored by:
1. Low concentration of nucleophile
2. Weak nature of the nucleophile
3. Polar solvent
4. All of the above
1 mechanism for the reaction,
follow:
1. Carbo cation mechanism
2. Carbon ion mechanism
3. Free radical mechanism
4. Either of these
Which of the following is an elimination reaction?
| 1. | CH3CH3 + Cl2 → CH3CH2Cl + HCl |
| 2. | CH3Cl + KOH(aq.) → CH3OH + KCl |
| 3. | CH2=CH2 + Br2 → CH2BrCH2Br |
| 4. | C2H5Br + KOH(aIc.) → C2H4 + KBr + H2O |
The mechanism for, follows with:
(1) 100% inversion
(2) 50% inversion
(3) 40% inversion
(4) 30% inversion
Which of the following is an example of elimination reaction?
1. Chlorination of methane
2. Dehydration of ethanol
3. Nitration of benzene
4. Hydroxylation of ethylene
The formation of cyanohydrin from a ketone is an example of:
1. electrophilic addition
2. nucleophilic addition
3. nucleophilic substitution
4. electrophilic substitution
The compound which reacts with HBr obeying Markownikoff’s rule is:
(1)
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
If is halogen the correct order for reactivity is:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
The electrophile, attacks the benzene ring to generate the intermediate σ-complex. Of the following, which σ-complex is of lowest energy?
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Consider the following bromides;
The correct order of reactivity is :
(1) A>B>C
(2) B>C>A
(3) B>A>C
(4) C>B>A
KI in acetone, undergoes reaction with each of P,Q, R and S. The rates of the reaction vary as :
(1) P>Q>R>S
(2) S>P>R>Q
(3) P>R>Q>S
(4) R>P>S>Q