In a large building, there are \(15\) bulbs of \(40~\text{W}\), \(5\) bulbs of \(100~\text{W}\), \(5\) fans of \(80~\text{W}\) and \(1\) heater of \(1~\text{kW}\). The voltage of the electric mains is \(220~\text{V}\). The minimum capacity of the main fuse of the building will be:
1. \(10~\text{A}\)
2. \(12~\text{A}\)
3. \(14~\text{A}\)
4. \(8~\text{A}\)
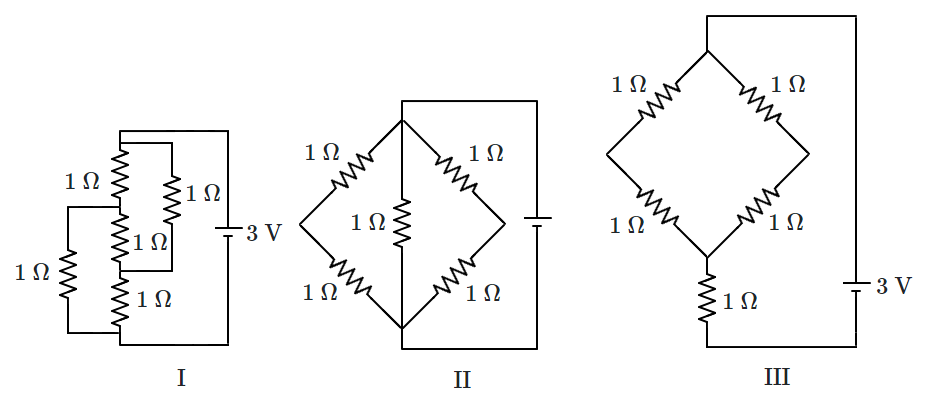
1. \({P}_3>{P}_2>{P}_1 \)
2. \({P}_2>{P}_1>{P}_3 \)
3. \({P}_1>{P}_3>{P}_2\)
4. \({P}_1>{P}_2>{P}_3\)
A cell of internal resistance \(r\) drives current through an external resistance \(R.\) The power delivered by the cell to the external resistance will be maximum when:
1. \(R=1000 r\)
2. \(R=0.001r\)
3. \(R=2r\)
4. \(R=r\)
The resistive network shown below is connected to a D.C. source of \(16~\text{V}\). The power consumed by the network is \(4\) Watt. The value of \(R\) is:
1. \(16~\Omega\)
2. \(1~\Omega\)
3. \(8~\Omega\)
4. \(6~\Omega\)
One kg of water, at \(20^\circ \text{C}\), heated in an electric kettle whose heating element has a mean (temperature averaged) resistance of \(20~\Omega\). The rms voltage in the mains is \(200~\text{V}\). Ignoring heat loss from the kettle, time taken for water to evaporate fully, is close to:
[Specific heat of water = \(4200\) J/(kg ºC), Latent heat of water = \(2260\) kJ/kg]
1. \(10\) minutes
2. \(22\) minutes
3. \(3\) minutes
4. \(16\) minutes
Model a torch battery of length \(l\) to be made up of a thin cylindrical bar of radius '\(a\)' and a concentric thin cylindrical shell of radius '\(b\)' filled in between with an electrolyte of resistivity \(\rho\) (see figure). If the battery is connected to a resistance of value \(R\), the maximum Joule heating in \(R\) will take place for:
1. \( \mathrm{R}=\frac{2 \rho}{\pi l} \ln \left(\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}\right) \)
2. \( \mathrm{R}=\frac{\rho}{\pi l} \ln \left(\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}\right) \)
3. \( \mathrm{R}=\frac{\rho}{2 \pi \mathrm{l}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}\right) \)
4. \( \mathrm{R}=\frac{\rho}{2 \pi \mathrm{l}} \ln \left(\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}\right) \)
A battery of \(3.0~\text{V}\) is connected to a resistor dissipating \(0.5~\text{W}\) of power. If the terminal voltage of the battery is \(2.5~\text{V}\), the power dissipated within the internal resistance is:
1. \(0.10~\text{W}\)
2. \(0.072~\text{W}\)
3. \(0.125~\text{W}\)
4. \(0.50~\text{W}\)
An electrical power line, having a total resistance of \(2~\Omega\), delivers \(1~\text{kW}\) at \(220~\text{V}\). The efficiency of the transmission line is approximately:
1. \(72\%\)
2. \(96\%\)
3. \(91\%\)
4. \(85\%\)
1. \(150~\text{J}\)
2. \(250~\text{J}\)
3. \(350~\text{J}\)
4. \(450~\text{J}\)
1. \(0.033^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
2. \(-0.033^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
3. \(0.011^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
4. \(0.055^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)








